Create a NAT gateway using the Azure portal
In this quickstart, learn how to create a NAT gateway by using the Azure portal. The NAT Gateway service provides outbound connectivity for virtual machines in Azure.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
Sign in to Azure
Sign in to the Azure portal with your Azure account.
Create a NAT gateway
Before you deploy the NAT gateway resource and the other resources, a resource group is required to contain the resources deployed. In the following steps, you create a resource group, NAT gateway resource, and a public IP address. You can use one or more public IP address resources, public IP prefixes, or both.
For information about public IP prefixes and a NAT gateway, see Manage NAT gateway.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter NAT gateway. Select NAT gateways in the search results.
Select + Create.
In Create network address translation (NAT) gateway, enter or select this information in the Basics tab:
Setting Value Project Details Subscription Select your Azure subscription. Resource Group Select Create new.
Enter test-rg.
Select OK.Instance details NAT gateway name Enter nat-gateway Region Select East US 2 Availability Zone Select No Zone. TCP idle timeout (minutes) Leave the default of 4. For information about availability zones and NAT gateway, see NAT gateway and availability zones.
Select the Outbound IP tab, or select the Next: Outbound IP button at the bottom of the page.
In the Outbound IP tab, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Public IP addresses Select Create a new public IP address.
In Name, enter public-ip-nat.
Select OK.Select the Review + create tab, or select the blue Review + create button at the bottom of the page.
Select Create.
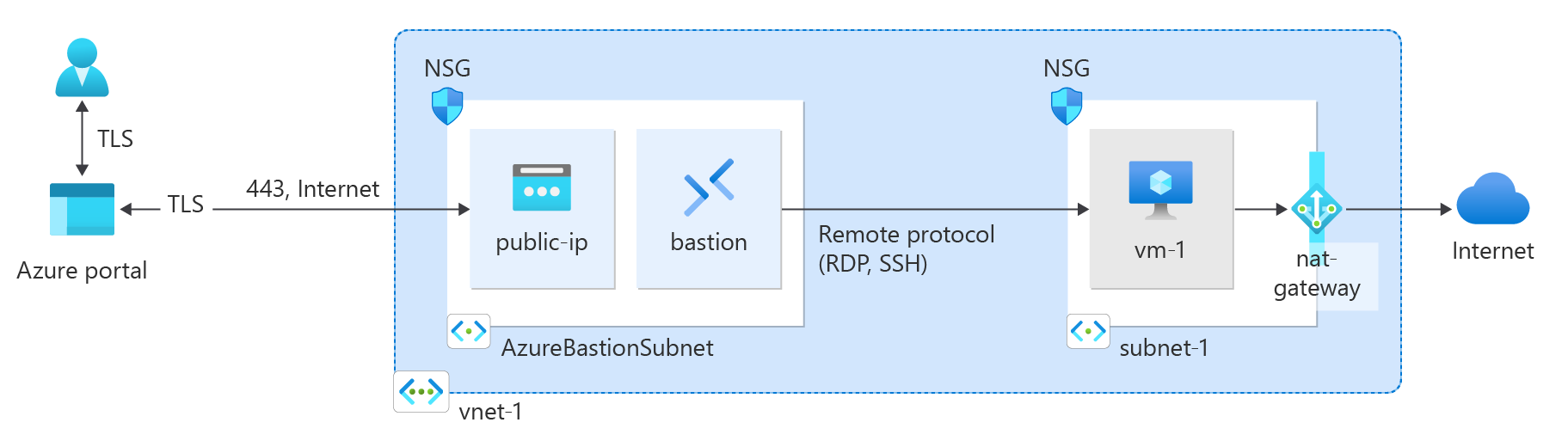
Create a virtual network and bastion host
The following procedure creates a virtual network with a resource subnet, an Azure Bastion subnet, and an Azure Bastion host.
In the portal, search for and select Virtual networks.
On the Virtual networks page, select + Create.
On the Basics tab of Create virtual network, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select test-rg. Instance details Name Enter vnet-1. Region Select East US 2. 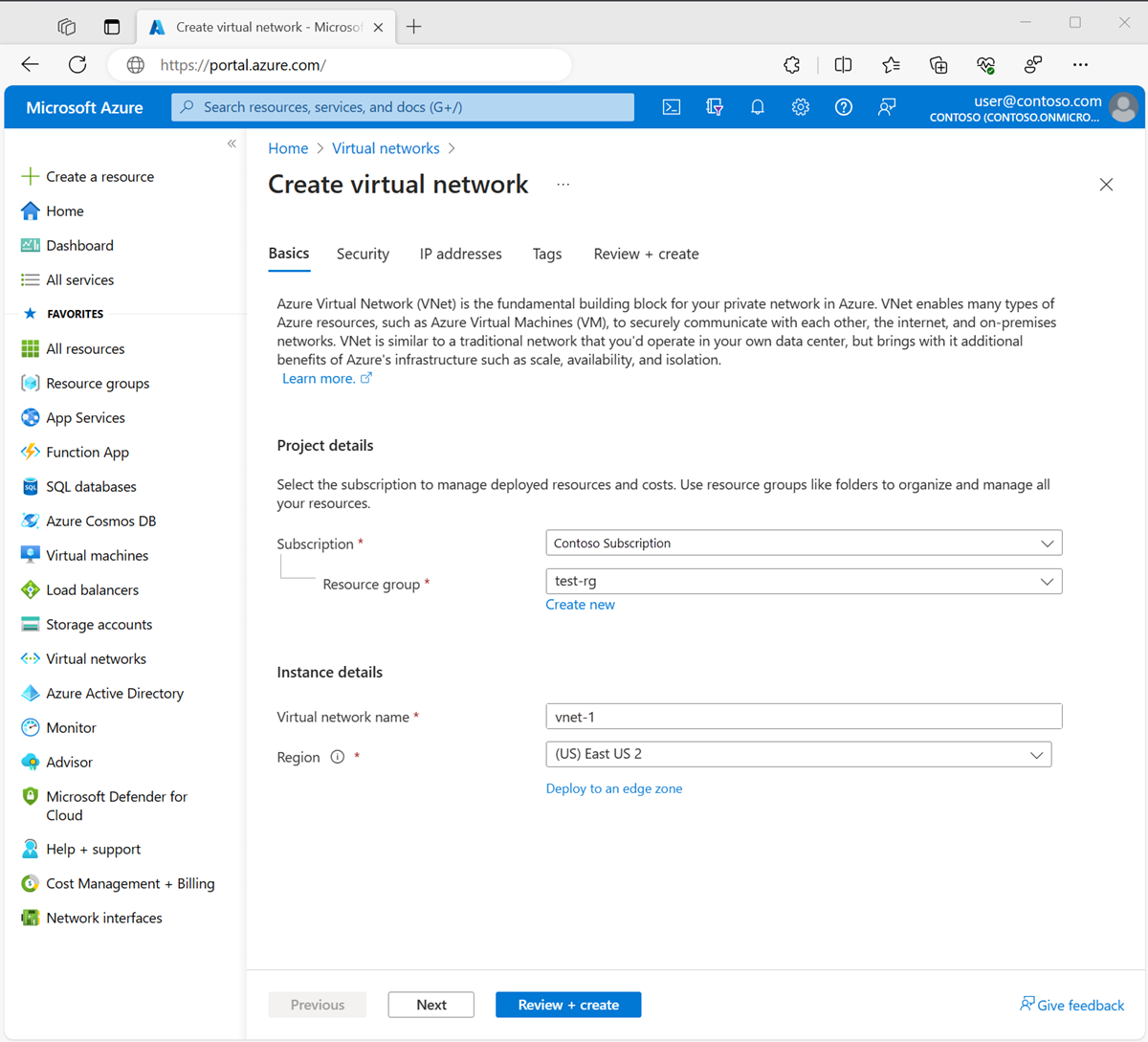
Select Next to proceed to the Security tab.
Select Enable Bastion in the Azure Bastion section of the Security tab.
Azure Bastion uses your browser to connect to VMs in your virtual network over secure shell (SSH) or remote desktop protocol (RDP) by using their private IP addresses. The VMs don't need public IP addresses, client software, or special configuration. For more information about Azure Bastion, see Azure Bastion
Enter or select the following information in Azure Bastion:
Setting Value Azure Bastion host name Enter bastion. Azure Bastion public IP address Select Create a public IP address.
Enter public-ip in Name.
Select OK.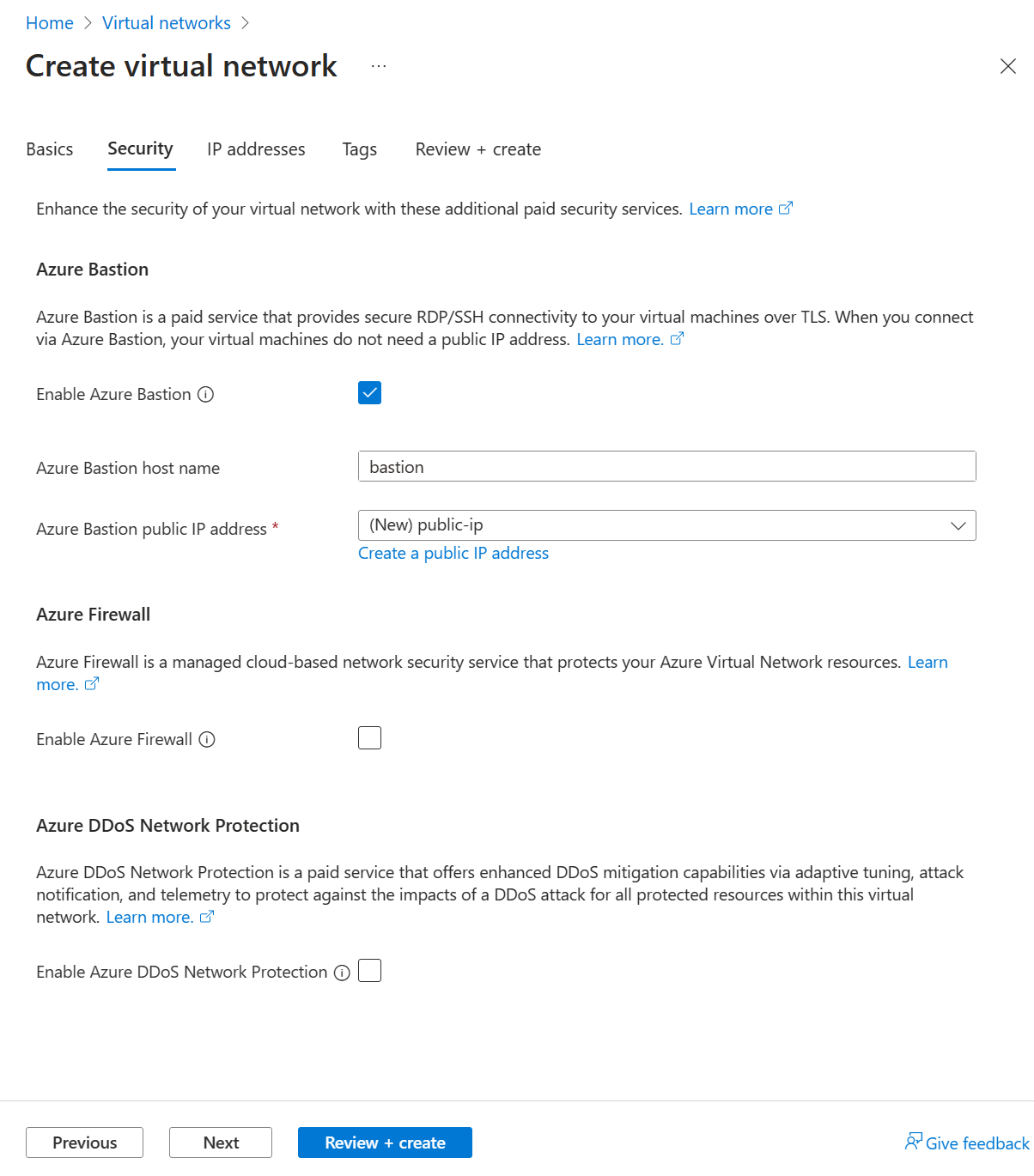
Select Next to proceed to the IP Addresses tab.
In the address space box in Subnets, select the default subnet.
In Edit subnet, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Subnet details Subnet template Leave the default Default. Name Enter subnet-1. Starting address Leave the default of 10.0.0.0. Subnet size Leave the default of /24(256 addresses). Security NAT gateway Select nat-gateway. 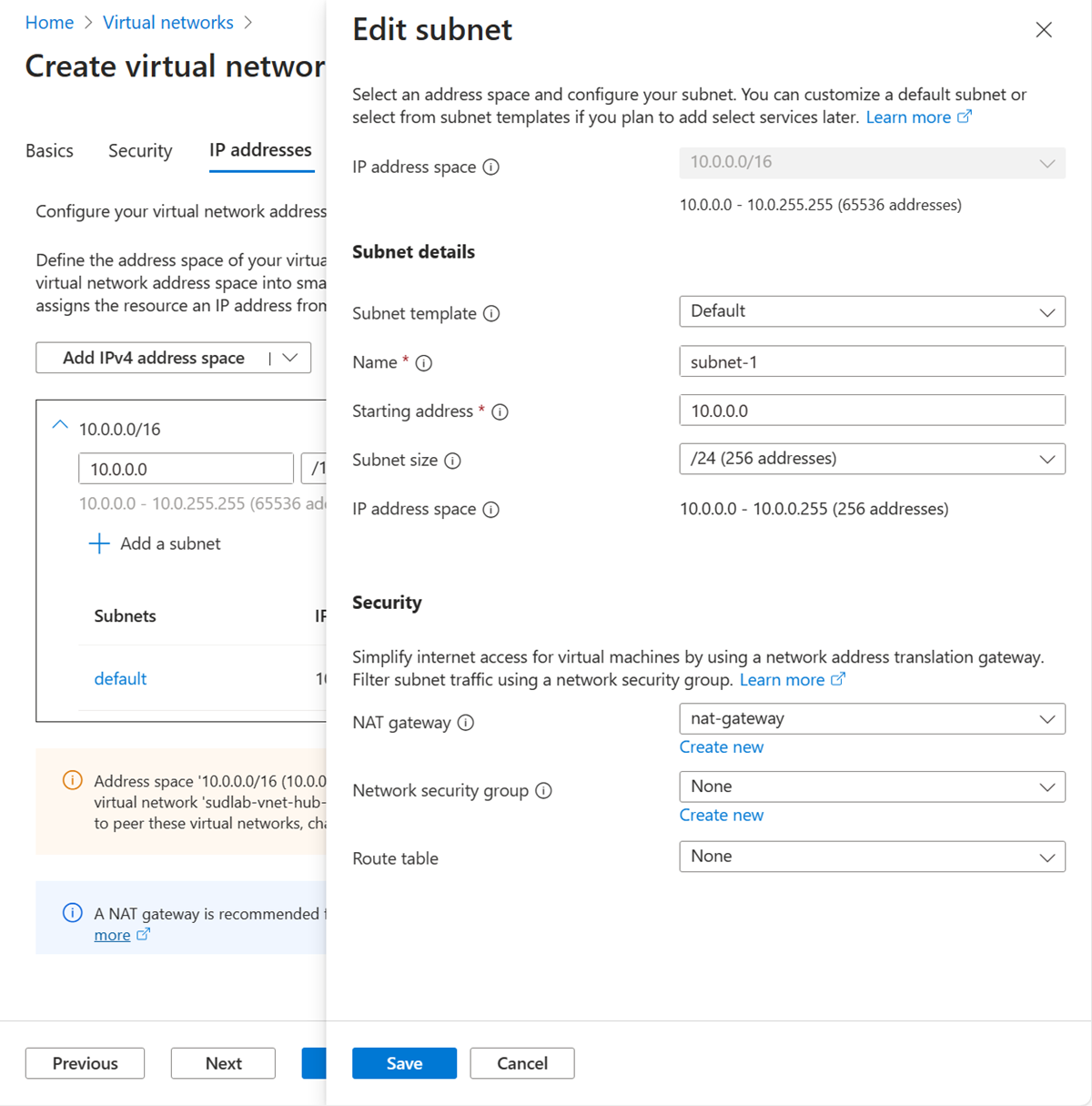
Select Save.
Select Review + create at the bottom of the screen, and when validation passes, select Create.
Create test virtual machine
The following procedure creates a test virtual machine (VM) named vm-1 in the virtual network.
In the portal, search for and select Virtual machines.
In Virtual machines, select + Create, then Azure virtual machine.
On the Basics tab of Create a virtual machine, enter or select the following information:
Setting Value Project details Subscription Select your subscription. Resource group Select test-rg. Instance details Virtual machine name Enter vm-1. Region Select East US 2. Availability options Select No infrastructure redundancy required. Security type Leave the default of Standard. Image Select Ubuntu Server 22.04 LTS - x64 Gen2. VM architecture Leave the default of x64. Size Select a size. Administrator account Authentication type Select Password. Username Enter azureuser. Password Enter a password. Confirm password Reenter the password. Inbound port rules Public inbound ports Select None. Select the Networking tab at the top of the page.
Enter or select the following information in the Networking tab:
Setting Value Network interface Virtual network Select vnet-1. Subnet Select subnet-1 (10.0.0.0/24). Public IP Select None. NIC network security group Select Advanced. Configure network security group Select Create new.
Enter nsg-1 for the name.
Leave the rest at the defaults and select OK.Leave the rest of the settings at the defaults and select Review + create.
Review the settings and select Create.
The default outbound access IP is disabled when one of the following events happens:
- A public IP address is assigned to the VM.
- The VM is placed in the backend pool of a standard load balancer, with or without outbound rules.
- An Azure NAT Gateway resource is assigned to the subnet of the VM.
VMs that you create by using virtual machine scale sets in flexible orchestration mode don't have default outbound access.
For more information about outbound connections in Azure, see Default outbound access in Azure and Use Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) for outbound connections.
Test NAT gateway
In this section, you test the NAT gateway. You first discover the public IP of the NAT gateway. You then connect to the test virtual machine and verify the outbound connection through the NAT gateway.
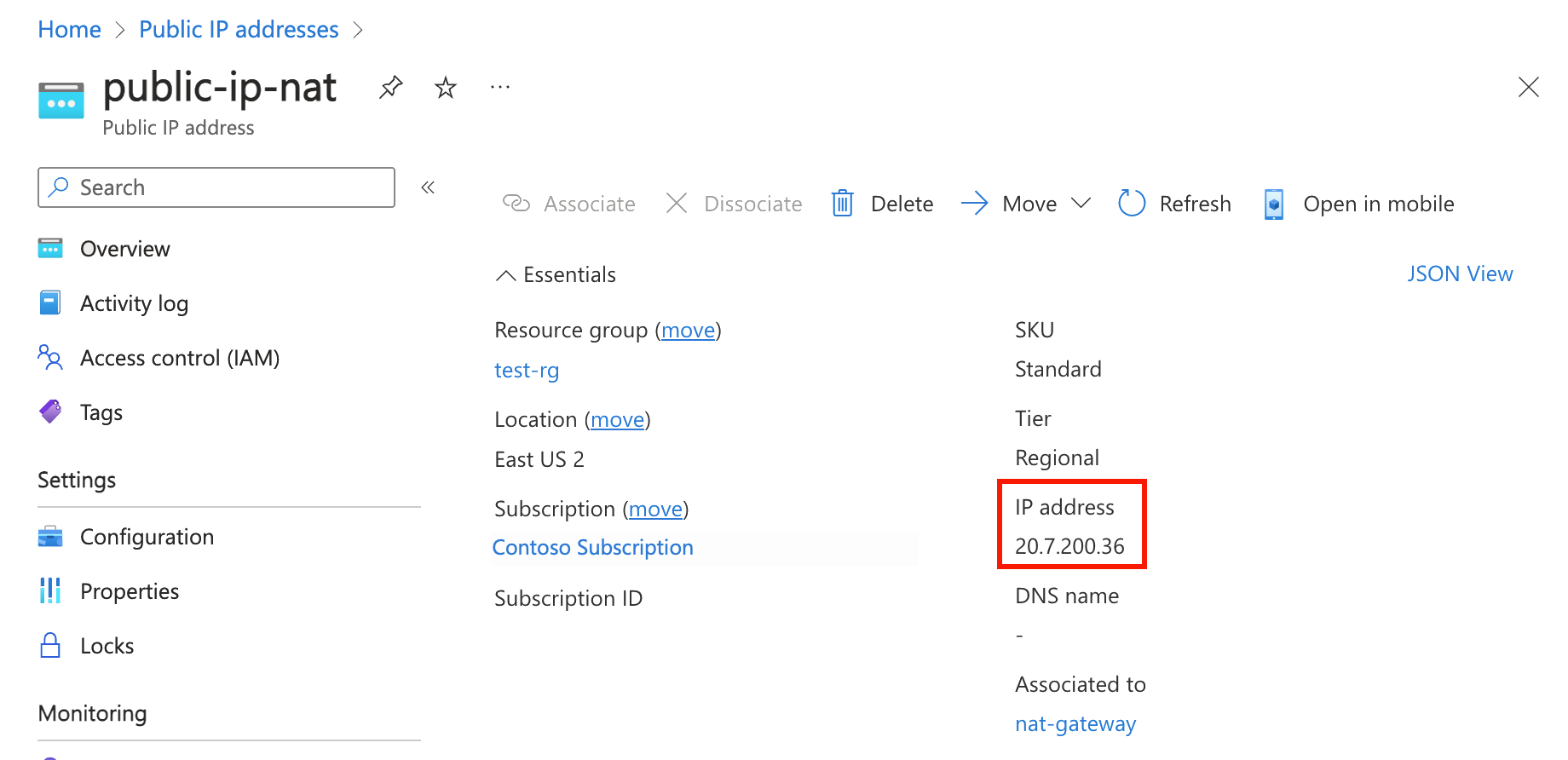
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Public IP. Select Public IP addresses in the search results.
Select public-ip-nat.
Make note of the public IP address:
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Virtual machine. Select Virtual machines in the search results.
Select vm-1.
On the Overview page, select Connect, then select the Bastion tab.
Select Use Bastion.
Enter the username and password entered during VM creation. Select Connect.
In the bash prompt, enter the following command:
Bashcurl ifconfig.meVerify the IP address returned by the command matches the public IP address of the NAT gateway.
Outputazureuser@vm-1:~$ curl ifconfig.me20.7.200.36

No comments:
Post a Comment