AWS Lambda is a responsive cloud service that examines the steps followed within any application and responds to them by compiling the codes that have been defined by the users, also known as functions. The service automatically computes and manages the resources across multiple availability zones and functions through them whenever new actions are called. AWS Lambda supports languages like Java, Python, and Node.js for writing the codes, and the service can also launch its processes in languages that are supported by Amazon Linux (like Bash, Go & Ruby).
Some tips to keep in mind while using AWS Lambda:
- The lambda code must be written in a stateless style.
- No function variable must be declared outside the scope of the handler.
- Users must always have a set of +rx permissions on their files in the uploaded ZIP files to ensure that Lambda can execute the code on the user’s behalf.
- Always try to delete old Lambda functions when not required anymore.
Configuring AWS Lambda
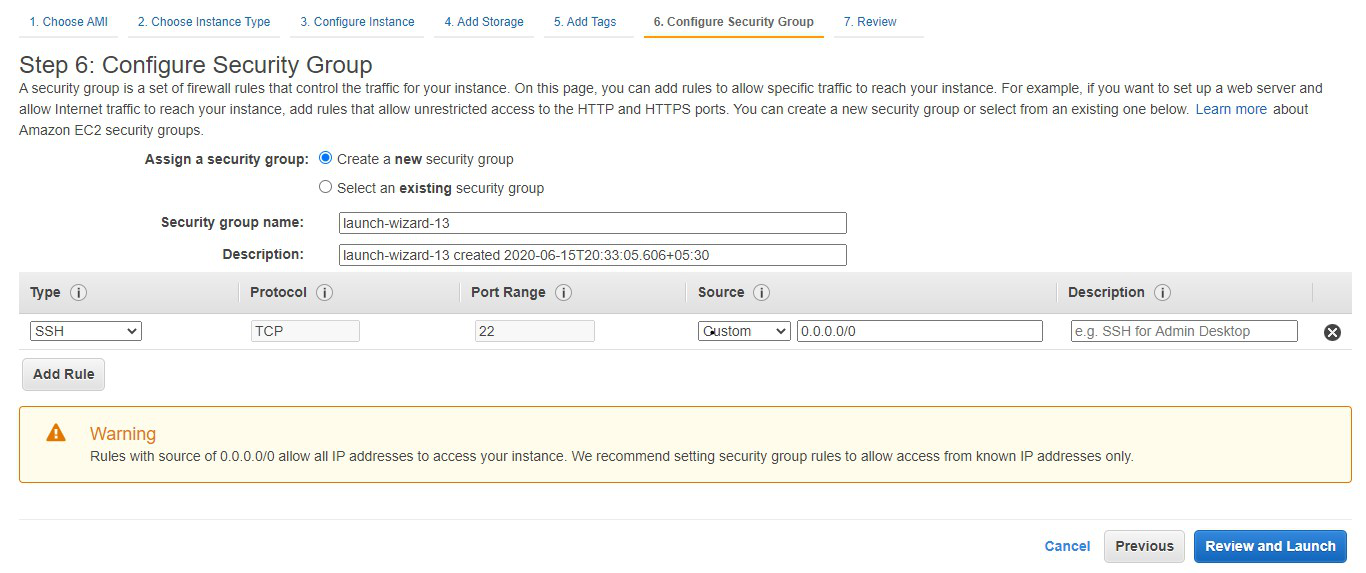
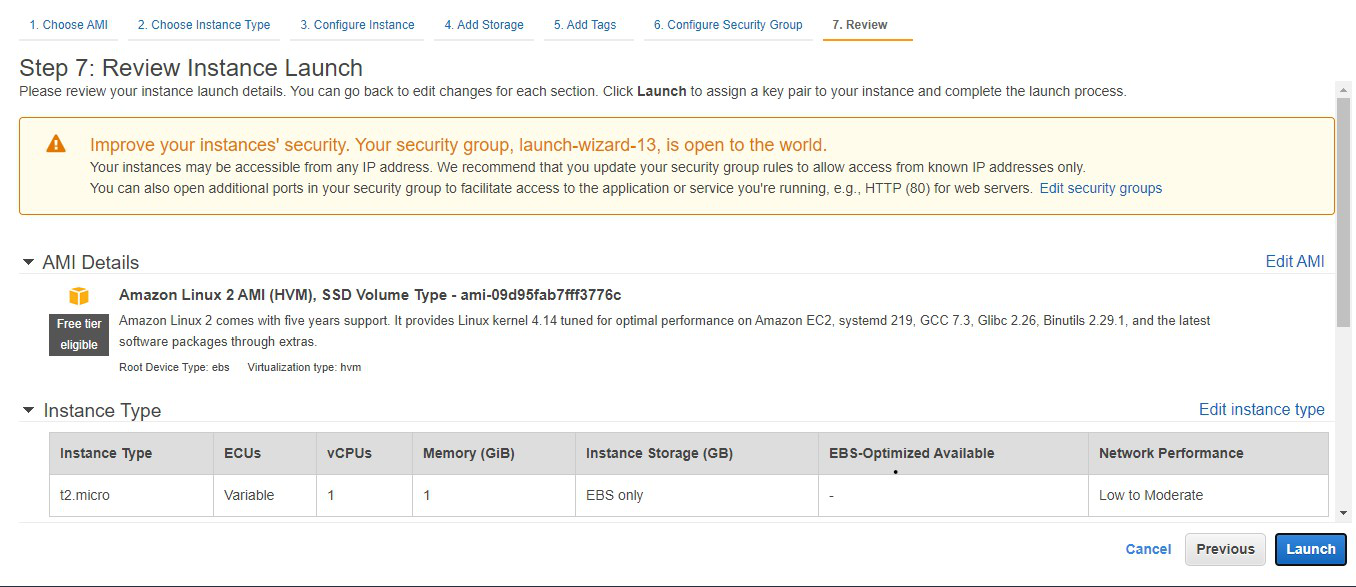
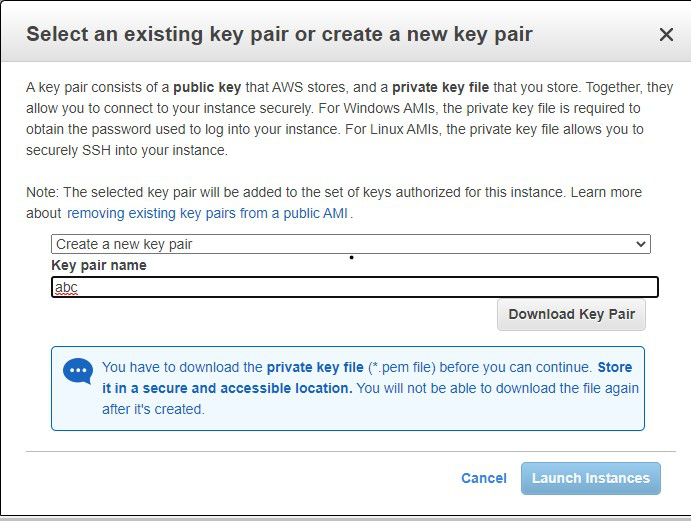
In order to configure AWS Lambda for the first time follow the below steps:
Step 1: Sign In to your AWS Account.
Step 2: Select Lambda from the services section of the homepage.
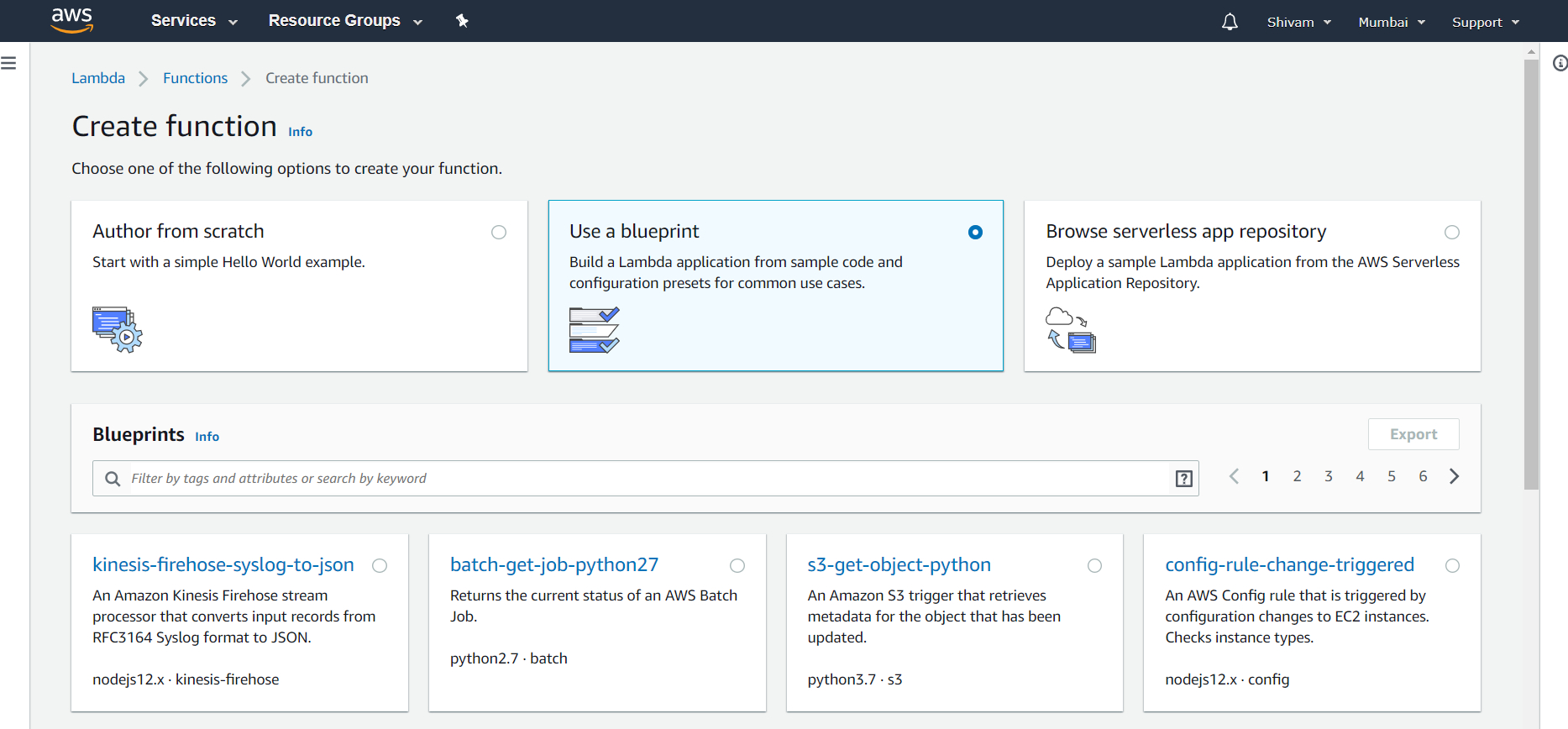
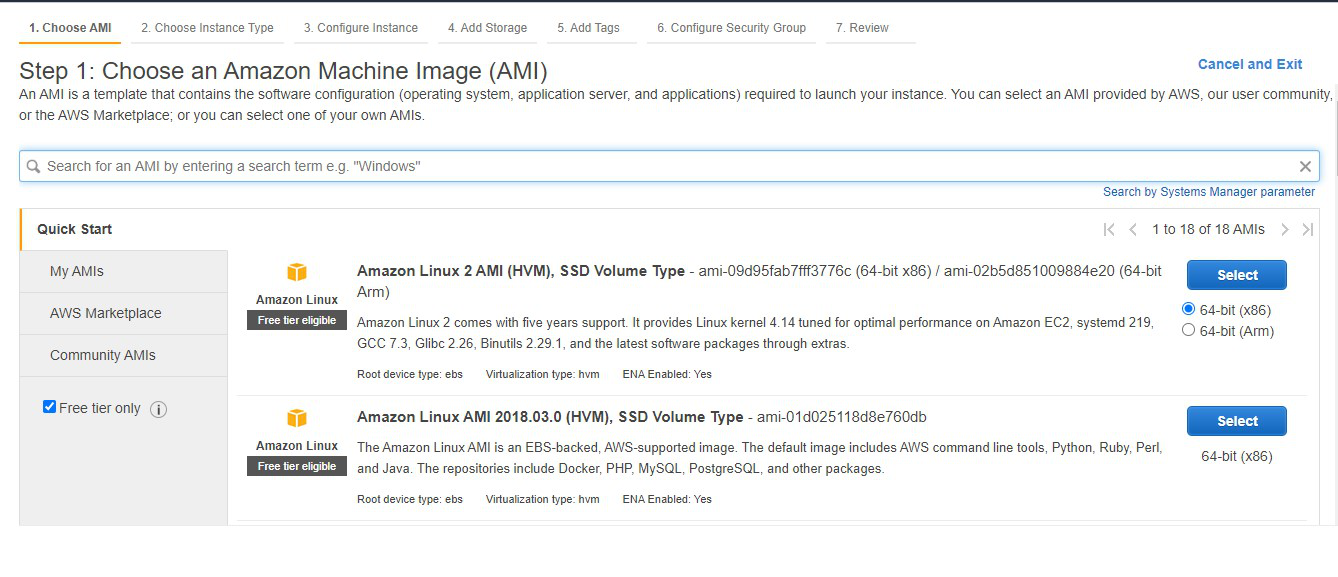
Step 3: Click on create a function and for the basic level choose to select a blueprint. A blueprint is simply a sample code for most commonly used cases that can be used directly.
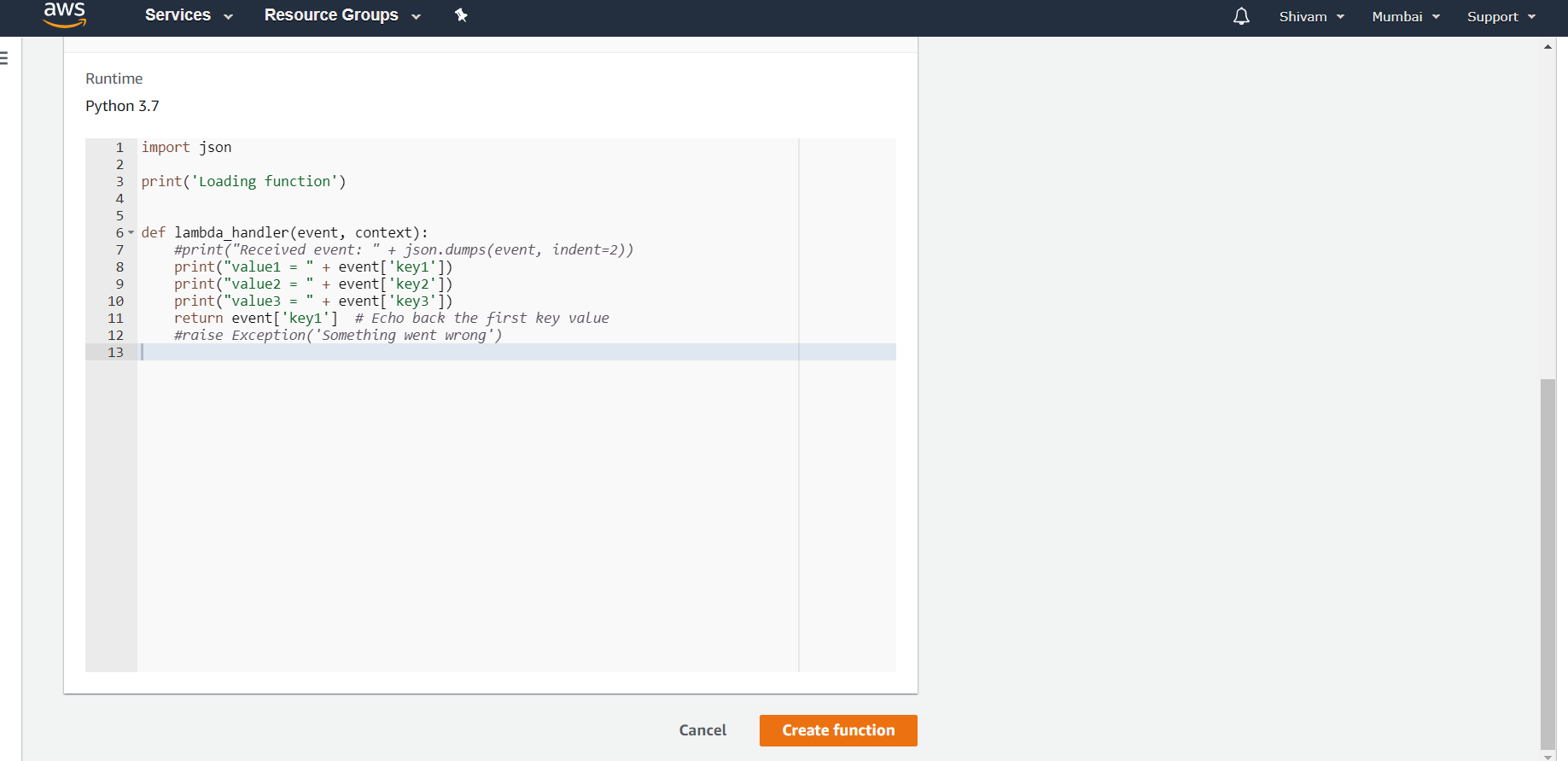
Step 4: For the basic level, just search for a blueprint named hello-world-python. Select it and fill the necessary details which is generally just the name. Hit the create function button and your Lambda function is ready to be used.
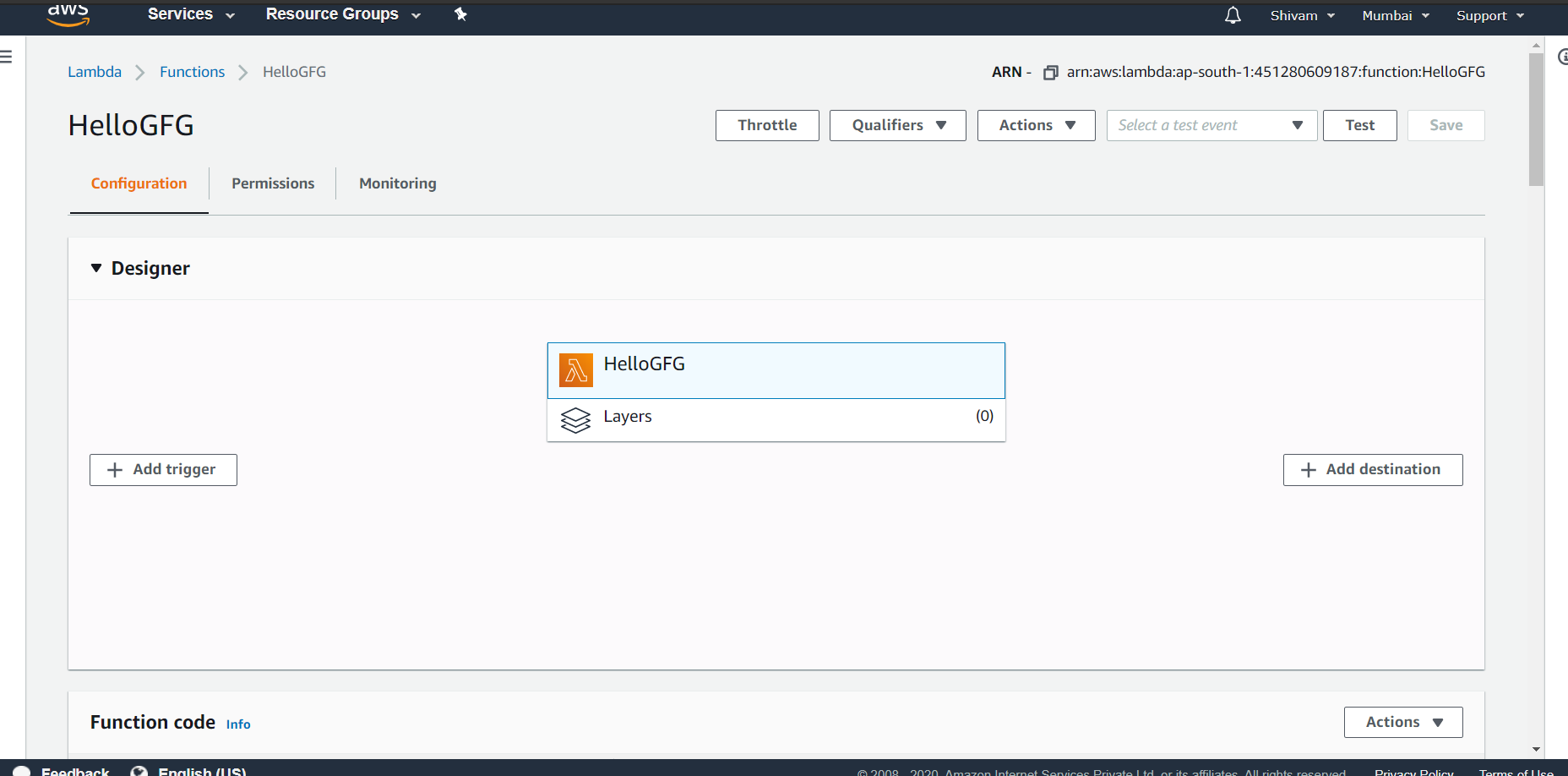
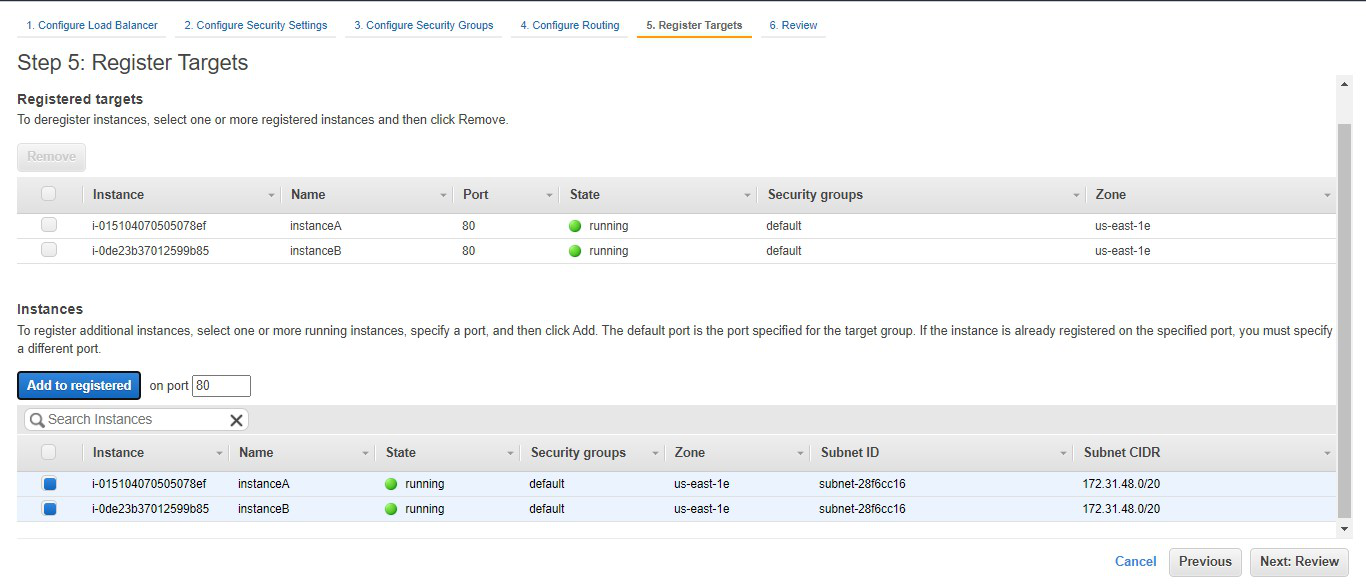
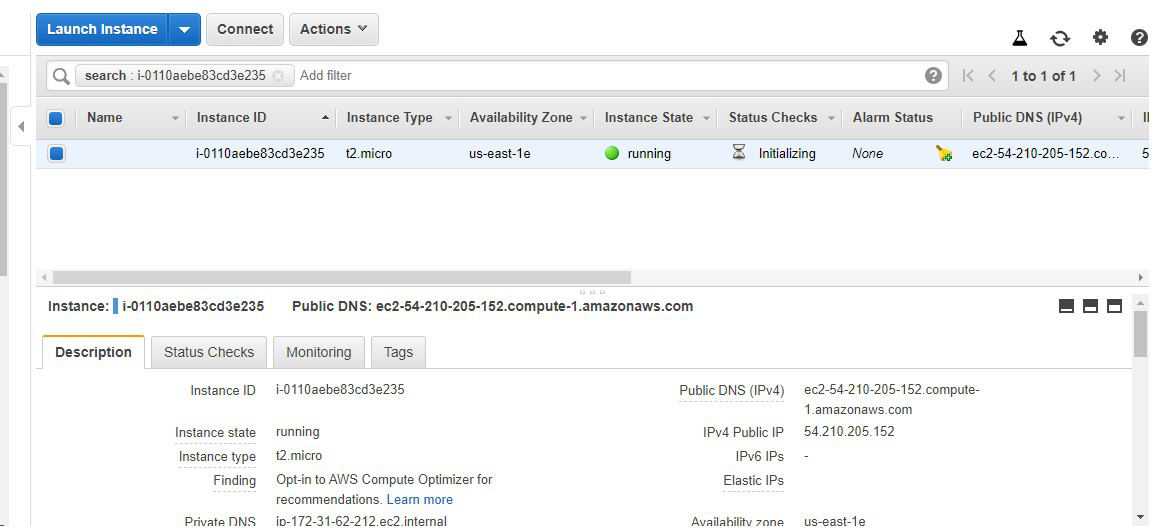
Step 5: The created function’s page looks like this:
Now add a trigger point that will run the function. The trigger can be any other service provided by AWS like Alexa Skills Kit OR DynamoDB or any other partner event sources. For example, add a dynamo DB Table to it. Now the function will work once new entries are made on the table or existing ones are modified or deleted.
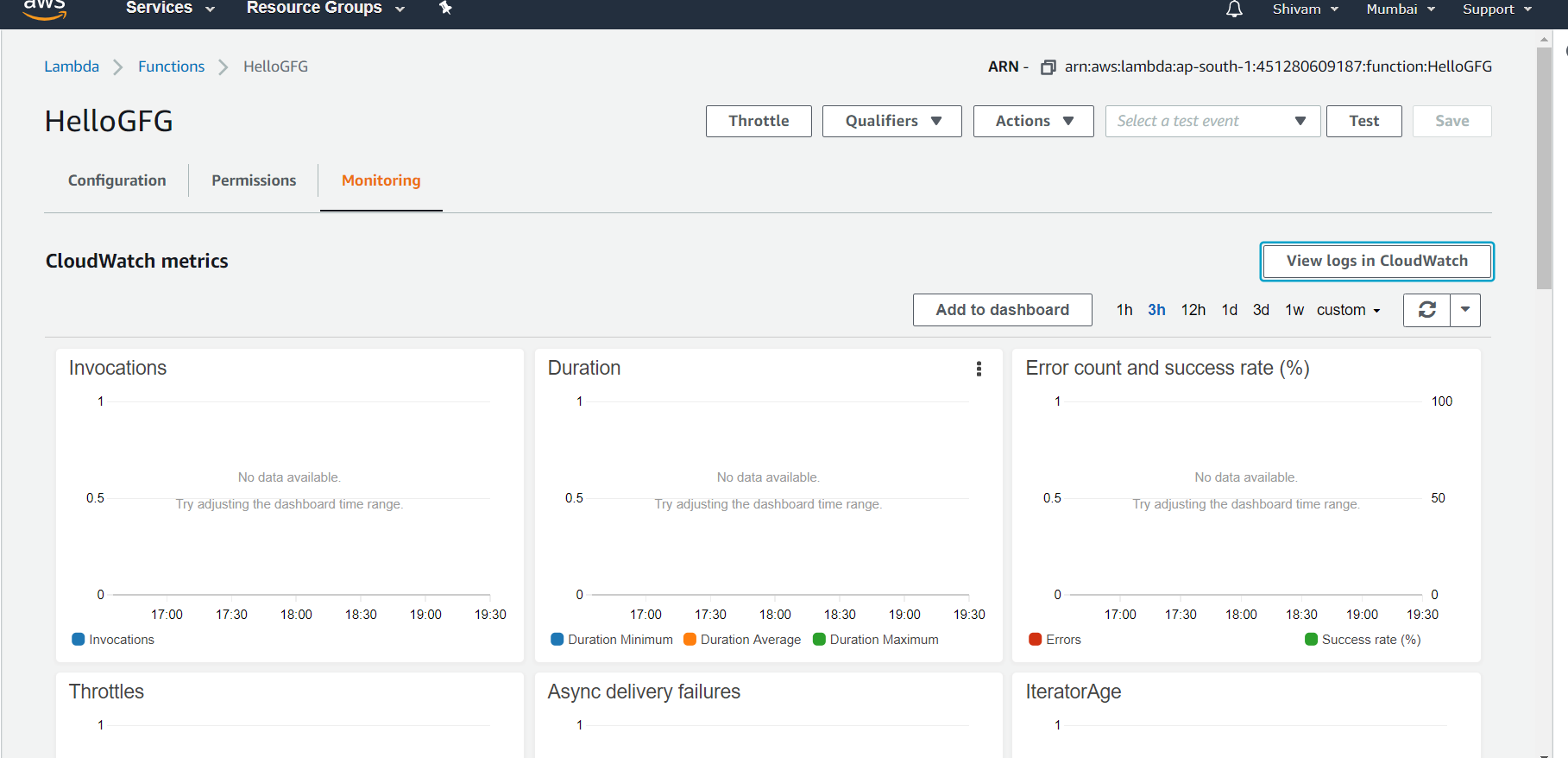
Step 6: To view the logs on the function select the monitoring tab from the lambda page. And then visit view logs in CloudWatch.
Benefits of AWS- Lambda:
- No need to register lambda tasks like Amazon SWF activities.
- Existing Lambda functions can be reused in workflows.
- Lambda functions are called directly by Amazon SWF, there is no need to design a program to implement and execute them.
- Lambda provides the metrics and logs for tracking function executions.
Limits in AWS- Lambda: There are three types of Lambda limits:
1. Resources Limit:
Resource | Default Limit |
|---|---|
| Ephemeral disk capacity (“/tmp” space) | 512 MB |
| Number of file descriptors | 1024 |
| Number of processes and threads (combined total) | 1024 |
| Maximum execution duration per request | 300 sec |
| Invoke request body payload size | 6 MB |
| Invoke response body payload size | 6 MB |
2. Service Limits:
ITEM | Default Limit |
|---|---|
| Lambda function deployment package size (.zip/.jar file) | 50 MB |
| Size of code/dependencies that you can zip into a deployment package (uncompressed zip/jar size) | 250 MB |
| Total size of all the deployment packages that can be uploaded per region | 1.5 GB |
| Number of unique event sources of the Scheduled Event source type per account | 50 |
| Number of unique Lambda functions you can connect to each Scheduled Event | 5 |
3. Throttle Limit: The throttle limit is 100 concurrent Lambda function executions per account and is applied to the total concurrent executions across all the functions within the same region. The formula to calculate the number of concurrent executions for the below function:
function = (average duration of the function execution)
X (number of requests or events processed by AWS Lambda)When the throttle limit is reached, it returns a throttling error having an error code 429. After a 15-30 minute user can start working again. The throttle limit can be increased by contacting the AWS support center.