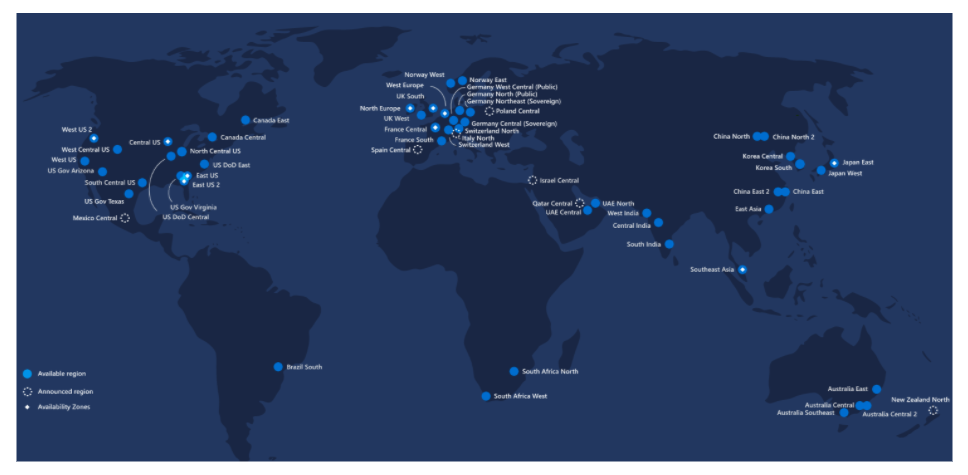
Azure Global Infrastructure
Regions
- Each region has more than one data center, which is a physical location.
- A group of data centers deployed in a latency-defined perimeter and connected through a dedicated regional low latency network.
- Criteria in choosing a Region:
- Location – a region closest to your users minimizes the latency
- Features – some features are not available in all regions
- Price – the price of services vary from region to region
- Each Region is paired within the same geographic area
- If the primary region has an outage, you can failover to the secondary region
- You can use paired regions for replication
- Regions that are unique when it comes to compliance:
- Azure Government Cloud – only US federal, state, local, and tribal governments and their partners have access to this dedicated instance
- China Region – data center is physically located within China and has no connection outside of China, including other Azure regions
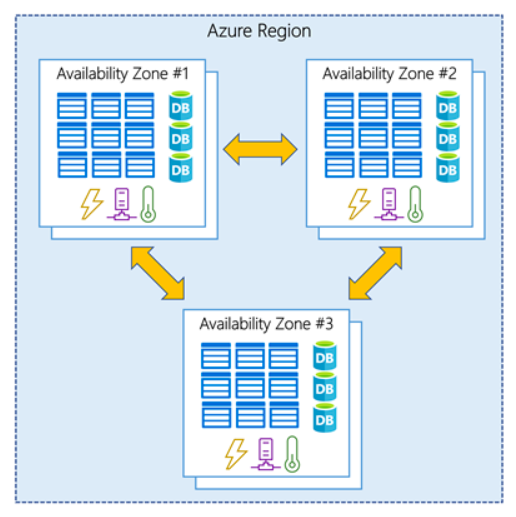
Availability Zones
- Each availability zone is a physical location within a region
- A zone is composed of one or more data centers with independent power, cooling, and networking facilities.
- Azure services that support Availability Zones fall into two categories:
- Zonal services – a resource is pinned to a specific zone
- Zone-redundant services – replicates automatically across zones
- The data moving in and out of Azure data centers, as well as data moving between Azure data centers, is called bandwidth.
- Data transfer to Azure is always free.
- Data transfer between Availability Zones is not free.
- Data transfer within the same Availability Zone is free.
- Data transfer between Azure regions and to other continents is not free.
Resource Groups
- A container that holds related resources
- Each resource can only exist in a single resource group
- You can add or remove resources to any resource group at any time
- Allows you to move a resource from one resource group to another
- Resources from multiple regions can be in one resource group
- You can give users access to a resource group
- Resources can interact with other resources in different resource groups
- A resource group has a location, or region, as it stores metadata about the resources
Azure Resource Manager (ARM)
- A management layer allowing you to create, update and delete resources within your account.
- You can deploy, manage, and monitor resources as a group
- Resource Manager template is mainly used to deploy the resources consistently and repeatedly.
- Define the dependencies between resources so they’re deployed in the correct order.
- Tag resources to logically organize all the resources in your subscription.
- You can check the costs for a group of resources sharing the same tag.
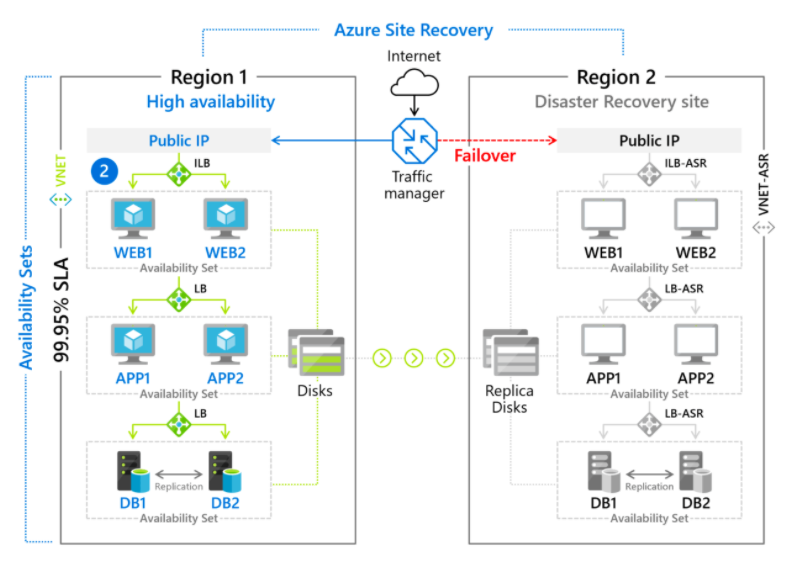
Azure Site Recovery
- Azure’s disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS)
- You can minimize recovery issues by sequencing the order of multi-tier applications that run on several virtual machines.
- Keep applications available from on-premises to Azure or Azure to another Azure region during outages with automatic recovery.




No comments:
Post a Comment