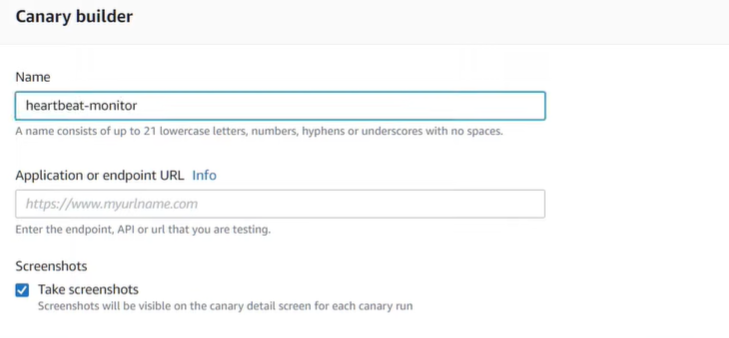
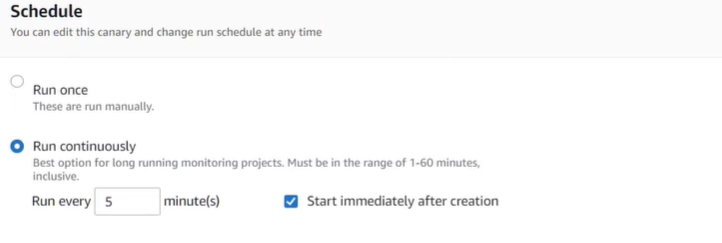
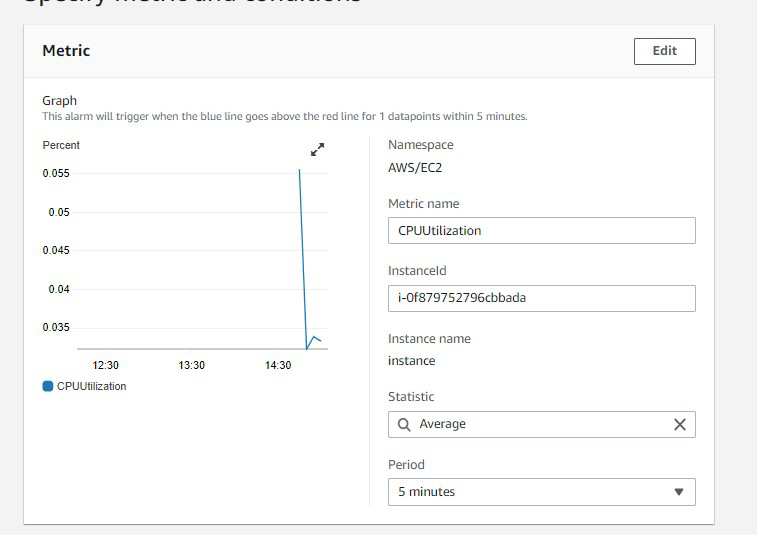
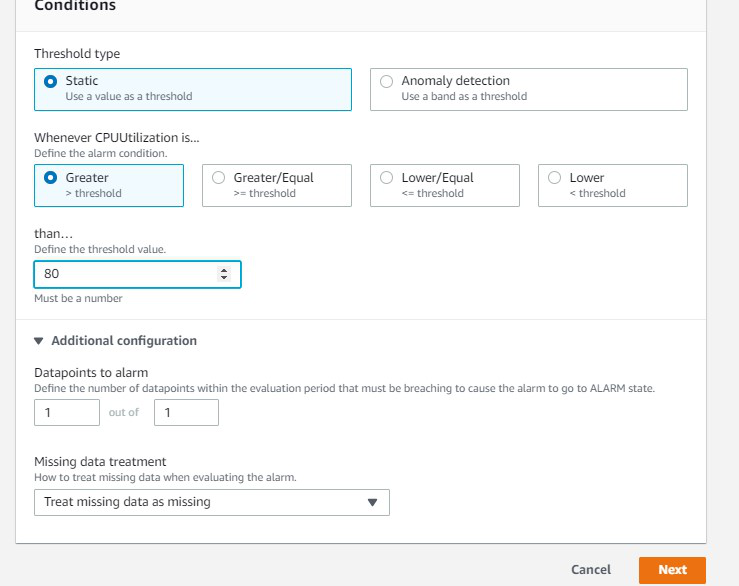
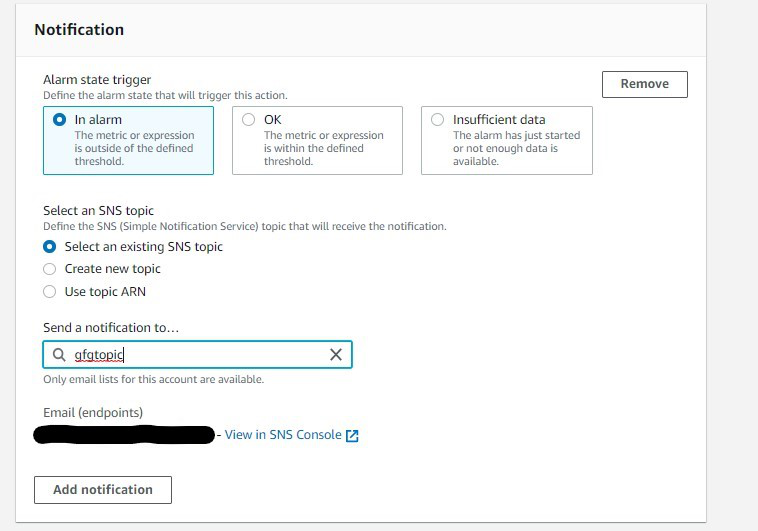
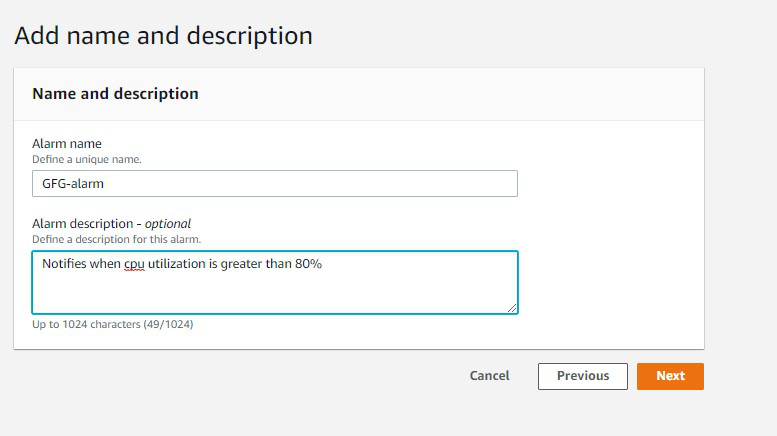
Scalability refers to the capacity of a software solution to manage rising workloads. In simple terms, it is the ability of a system to readily add extra processing resources to handle the increased loads.
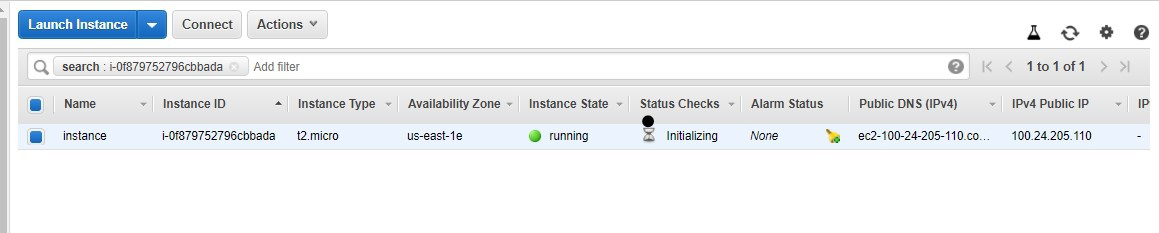
Scaling Amazon EC2 means you start with the resources you require at the time of starting your service and build your architecture to automatically scale in or out, in response to the changing demand. As a result, you only pay for the resources you really utilize. You don’t have to be concerned about running out of computational power to satisfy your consumer’s demand.
Let’s look at an example. Let’s say you try to access a website, and it works flawlessly with no latency. Now, at peak times, the same website doesn’t load or gets timed out often. This is due to the fact that the website started receiving more requests than it could manage.
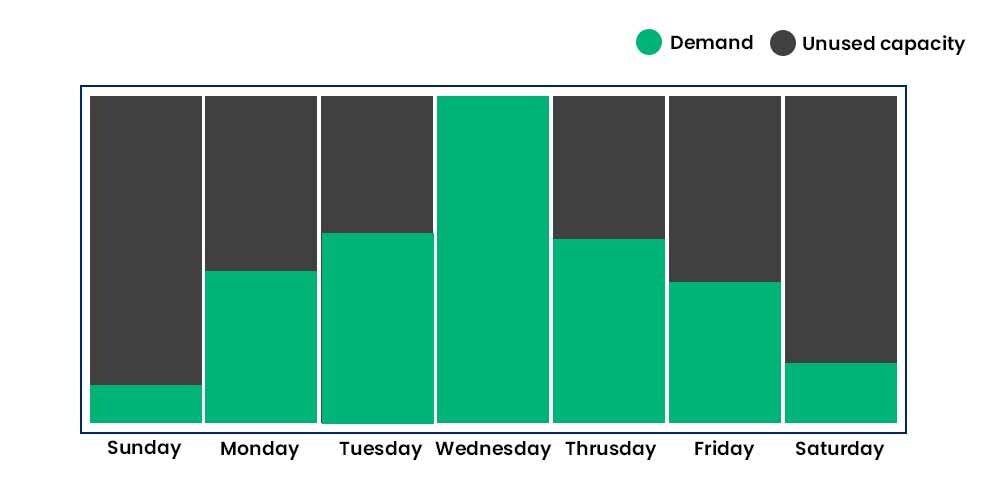
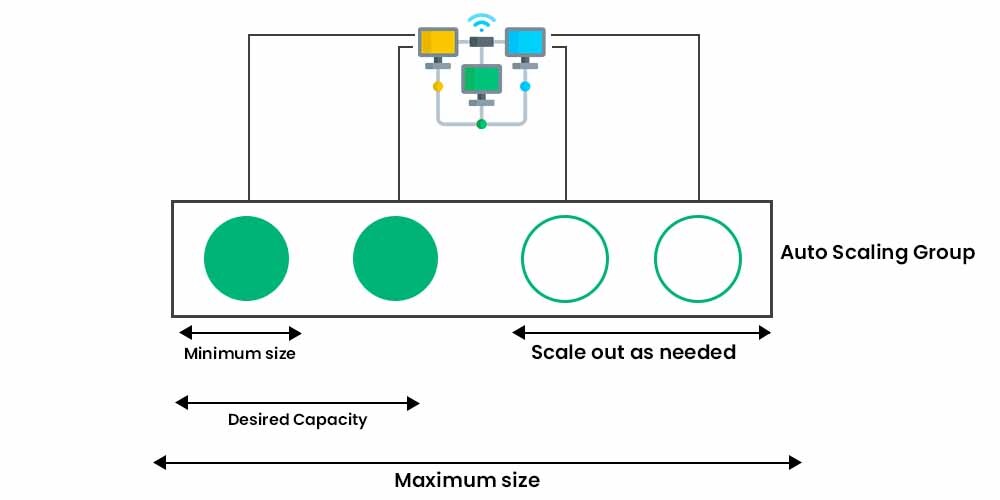
That’s the point where Amazon EC2 Autoscaling comes into the picture. You may use Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling in order to add or delete Amazon EC2 instances with respect to changes in your application demand. You can maintain a higher feeling of application availability by dynamically scaling your instances in and out as needed.
You can use three scaling techniques within Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling i.e. Dynamic Scaling, Predictive Scaling, and Scheduled Scaling. They are explained in detail below:
1. Dynamic Scaling adapts to changing environments and responds with the EC2 instances as per the demand. It helps the user to follow the demand curve for the application, which ultimately helps the maintainer/user to scale the instances ahead of time. Target tracking scaling policies, for example, may be used to choose a loaded statistic for your application, such as CPU use. Alternatively, you might use Application Load Balancer’s new “Request Count Per Target” measure, which is a load balancing option for the Elastic Load Balancing service. After that, Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling will modify the number of EC2 instances as needed to keep you on track.
2. Predictive Scaling helps you to schedule the right number of EC2 instances based on the predicted demand. You can use both dynamic and predictive scaling approaches together for faster scaling of the application. Predictive Scaling forecasts future traffic and allocates the appropriate number of EC2 instances ahead of time. Machine learning algorithms in Predictive Scaling identify changes in daily and weekly patterns and automatically update projections. In this way, the need to manually scale the instances on particular days is relieved.
3. Scheduled Scaling, as the name suggests allows you to scale your application based on the scheduled time you set. For e.g. A coffee shop owner may employ more baristas on weekends because of the increased demand and frees them on weekdays because of reduced demand.
Computing power is a programmed resource in the cloud, so you may take a more flexible approach to scale your applications. When you add Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling to an application, you may create new instances as needed and terminate them when they’re no longer in use. In this way, you only pay for the instances you use, when they’re in use.
Some Ways to scale Amazon EC2:
- Horizontal Scaling: Horizontal scaling involves adding more instances to your application to handle increased demand. This can be done manually by launching additional instances, or automatically using Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling, which monitors your application’s workload and adds or removes instances based on predefined rules.
- Vertical Scaling: Vertical scaling involves increasing the resources of existing instances, such as CPU, memory, or storage. This can be done manually by resizing instances, or automatically using Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling with launch configurations that specify instance sizes based on the workload.
- Load Balancing: Load balancing involves distributing incoming traffic across multiple instances to improve performance and availability. Amazon Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) is a service that automatically distributes incoming traffic across multiple instances in one or more Availability Zones.
- Multi-Availability Zone Deployment: Multi-Availability Zone (AZ) deployment involves launching instances in multiple AZs to improve availability and fault tolerance. Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling can be used to automatically launch instances in additional AZs to maintain availability in case of an AZ outage.
- Containerization: Containerization involves using containers to package and deploy applications, making them more portable and easier to manage. Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) is a service that makes it easy to run, stop, and manage Docker containers on a cluster of EC2 instances.
Benefits of Auto Scaling EC2:
Scaling as discussed should be implemented in an EC2 instance, in order to achieve more flexibility if the demand for application increases. Let’s discuss what are the detailed benefits of Auto Scaling an EC2.
A method to make the most of AWS Cloud is to incorporate Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling into your application design. The applications benefit the following when you use Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling:
- Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling ensures that your application has enough capacity to handle current traffic demand at all times. This means your application can add or remove new and old instances respectively with respect to the demand of the application. The feature of auto adding and terminating the instances as per demand is termed as Better Availability of the application.
- Suppose an instance, becomes unhealthy by the time and is in use despite this fact. The chances of its crashing increase. Here comes another use case of Auto Scaling EC2. It will recognize which instance is not healthy or in technical terms which instance is slow, low efficient, etc, and automatically terminated the instance and replace it with a brand new instance. Furthermore, a user can employ several availability zones with Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling. If one zone goes down or crashes, EC2 Auto Scaling compensates the same by launching instances in other zones. In this way, the traffic is can be migrated to the other zone in which new instances are added in order to manage traffic till the crashed zone gets healthy again.
- Auto Scaling is highly cost-efficient and must be employed if you’re not sure about the traffic that your application will be receiving. As per the need, Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling can dynamically raise and reduce capacity. The user can save money by this as only according to the demand, new instances will be created and will be charged. As soon as the traffic to the application reduces, some instances get terminated and in this way, you use and pay for the instance that you really need.
Limitations of EC2 Autoscaling:
There are several limitations to consider when using Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling:
- Number of instances: Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling can support a maximum of 500 instances per Auto Scaling group.
- Instance health checks: Auto Scaling uses Amazon EC2 instance health checks to determine the health of an instance. If an instance fails a health check, Auto Scaling will terminate it and launch a new one. However, this process can take some time, which can impact the availability of your application.
- Scaling policies: Auto Scaling allows you to set scaling policies based on CloudWatch metrics, but these policies can be complex to configure and may not always scale your application as expected.
- Application dependencies: If your application has dependencies on other resources or services, such as a database or cache, it may not scale as expected if those resources become overloaded or unavailable.
- Cost: Using Auto Scaling can increase the cost of running your application, as you may be charged for the additional instances that are launched.
Overall, it’s important to carefully consider the limitations of Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling and how they may impact your application when deciding whether to use this service.
How does EC2 Autoscaling work?
Amazon EC2 Autoscaling provides the liberty to automatically scale the instances as per the demand. Even if some problems are detected, the model replaces the unhealthy instances with ones that are fully functional. To automate fleet management for EC2 instances, Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling will perform three major functions:
- Balancing the capacities across different Availability zones: If your application has three availability zones, Amazon EC2 Autoscaling can help you balance the number of instances across the three zones. As a result, each zone receives no more or fewer instances than the others, resulting in a balanced distribution of traffic and burden.
- Replacing and Repairing unhealthy instances: If the instances fail to pass the health check, Autoscaling replaces them with healthy instances. As a result, the problem of instances crashing is reduced, and you won’t have to manually verify their health or replace them if they’re determined to be unhealthy.
- Monitoring the health of instances: While the instances are running, Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling ensures that they are healthy and that traffic is evenly allocated among them. It does health checks on the instances on a regular basis to see if they’re experiencing any issues.