Create a chaos experiment that uses a Chaos Mesh fault to kill AKS pods with the Azure portal
Chaos Studio uses Chaos Mesh, a free, open-source chaos engineering platform for Kubernetes, to inject faults into an AKS cluster. Chaos Mesh faults are service-direct faults that require Chaos Mesh to be installed on the AKS cluster. You can use these same steps to set up and run an experiment for any AKS Chaos Mesh fault.
Prerequisites
- An Azure subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
- An AKS cluster with a Linux node pool. If you don't have an AKS cluster, see the AKS quickstart that uses the Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, or the Azure portal.
Limitations
- You can use Chaos Mesh faults with private clusters by configuring VNet Injection in Chaos Studio. Any commands issued to the private cluster, including the steps in this article to set up Chaos Mesh, need to follow the private cluster guidance. Recommended methods include connecting from a VM in the same virtual network or using the AKS command invoke feature.
- AKS Chaos Mesh faults are only supported on Linux node pools.
- Currently, Chaos Mesh faults don't work if the AKS cluster has local accounts disabled.
- If your AKS cluster is configured to only allow authorized IP ranges, you need to allow Chaos Studio's IP ranges. You can find them by querying the
ChaosStudioservice tag with the Service Tag Discovery API or downloadable JSON files.
Set up Chaos Mesh on your AKS cluster
Before you can run Chaos Mesh faults in Chaos Studio, you must install Chaos Mesh on your AKS cluster.
Run the following commands in an Azure Cloud Shell window where you have the active subscription set to be the subscription where your AKS cluster is deployed. Replace
MyManagedClusterandMyResourceGroupwith the name of your cluster and resource group.Azure CLIaz aks get-credentials --admin --name MyManagedCluster --resource-group MyResourceGroupBashhelm repo add chaos-mesh https://charts.chaos-mesh.org helm repo update kubectl create ns chaos-testing helm install chaos-mesh chaos-mesh/chaos-mesh --namespace=chaos-testing --set chaosDaemon.runtime=containerd --set chaosDaemon.socketPath=/run/containerd/containerd.sockVerify that the Chaos Mesh pods are installed by running the following command:
Bashkubectl get po -n chaos-testingYou should see output similar to the following example (a chaos-controller-manager and one or more chaos-daemons):
BashNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE chaos-controller-manager-69fd5c46c8-xlqpc 1/1 Running 0 2d5h chaos-daemon-jb8xh 1/1 Running 0 2d5h chaos-dashboard-98c4c5f97-tx5ds 1/1 Running 0 2d5h
Enable Chaos Studio on your AKS cluster
Chaos Studio can't inject faults against a resource unless that resource is added to Chaos Studio first. You add a resource to Chaos Studio by creating a target and capabilities on the resource. AKS clusters have only one target type (service-direct), but other resources might have up to two target types. One target type is for service-direct faults. Another target type is for agent-based faults. Each type of Chaos Mesh fault is represented as a capability like PodChaos, NetworkChaos, and IOChaos.
Open the Azure portal.
Search for Chaos Studio in the search bar.
Select Targets and go to your AKS cluster.
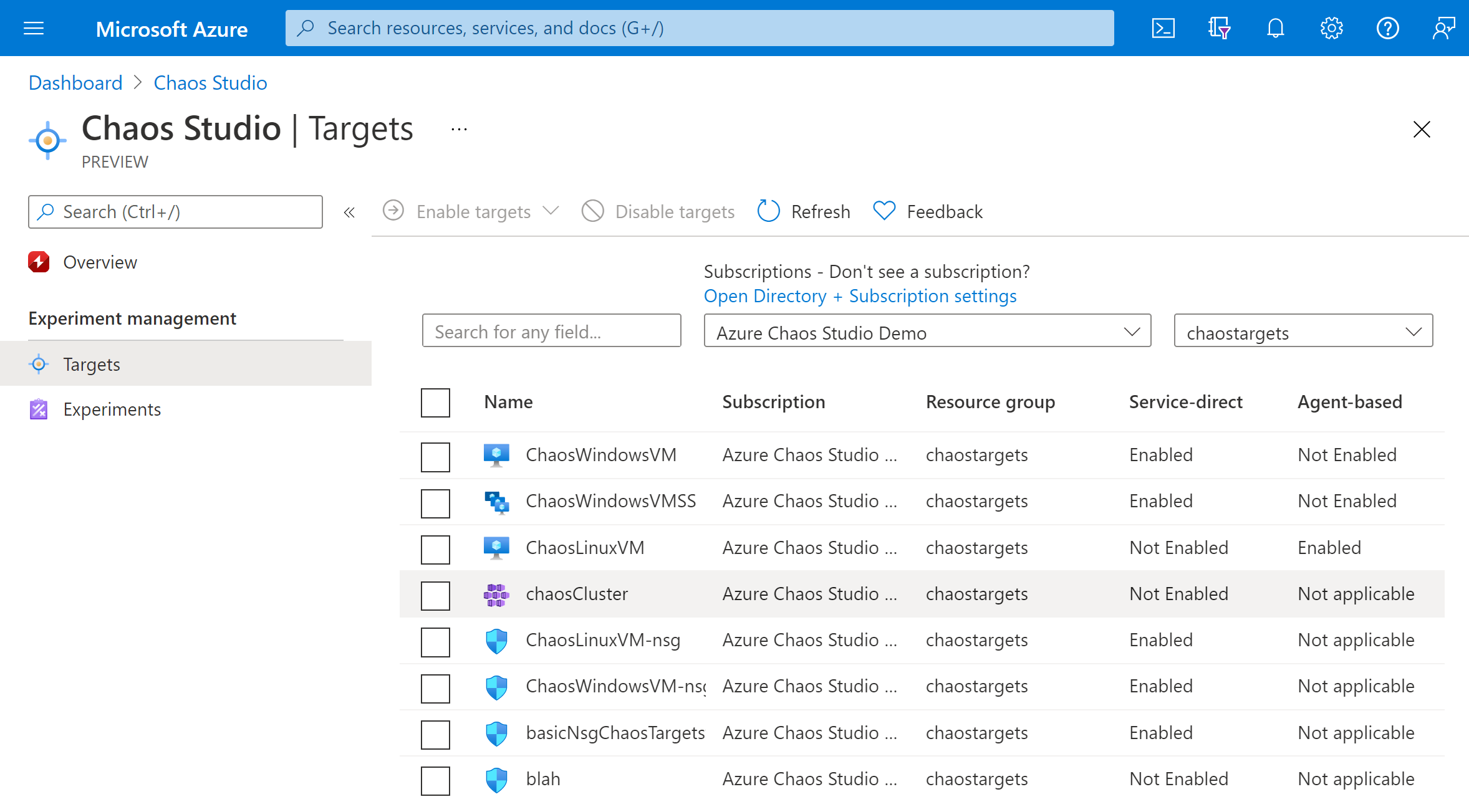
Select the checkbox next to your AKS cluster. Select Enable targets and then select Enable service-direct targets from the dropdown menu.
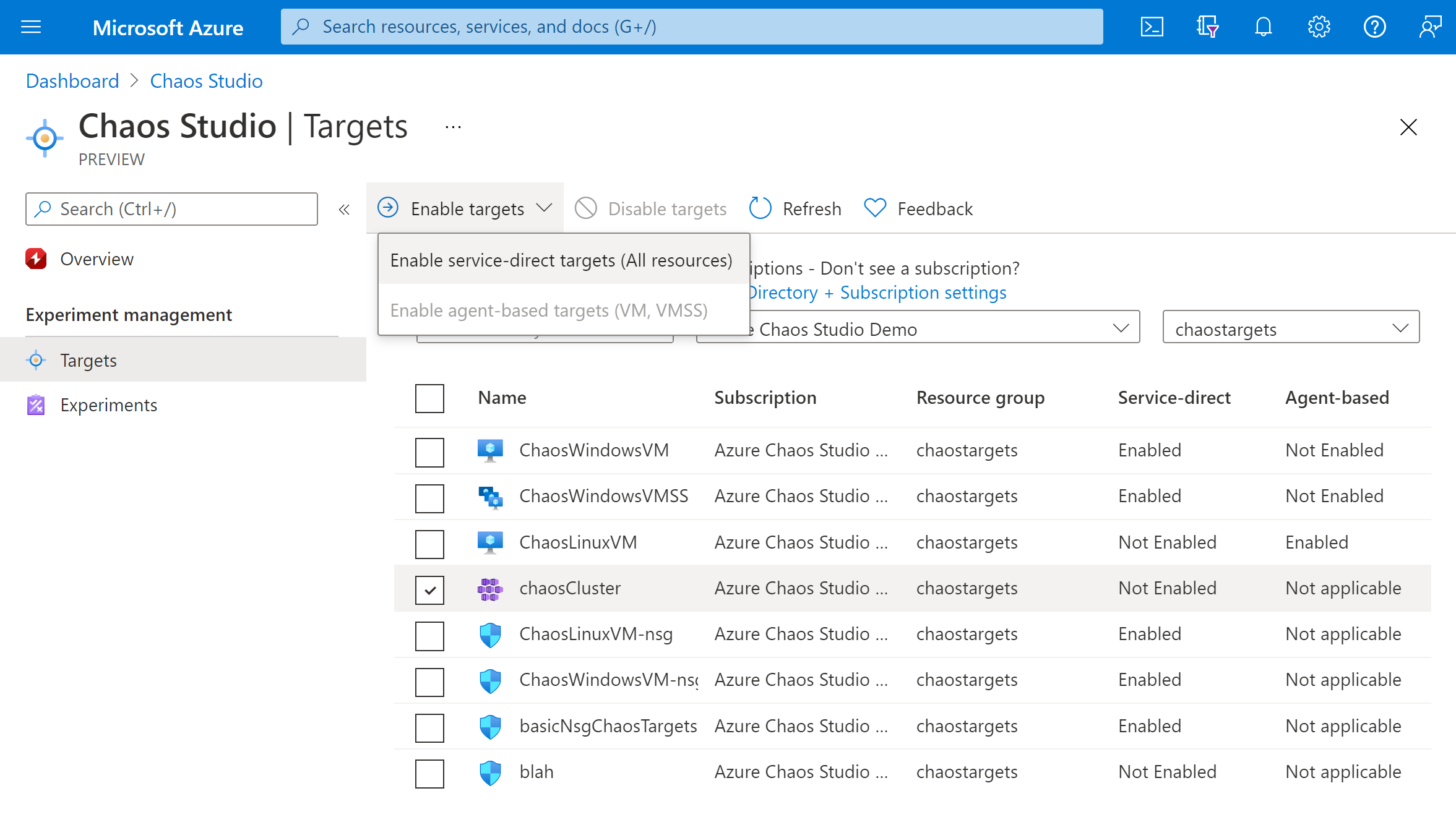
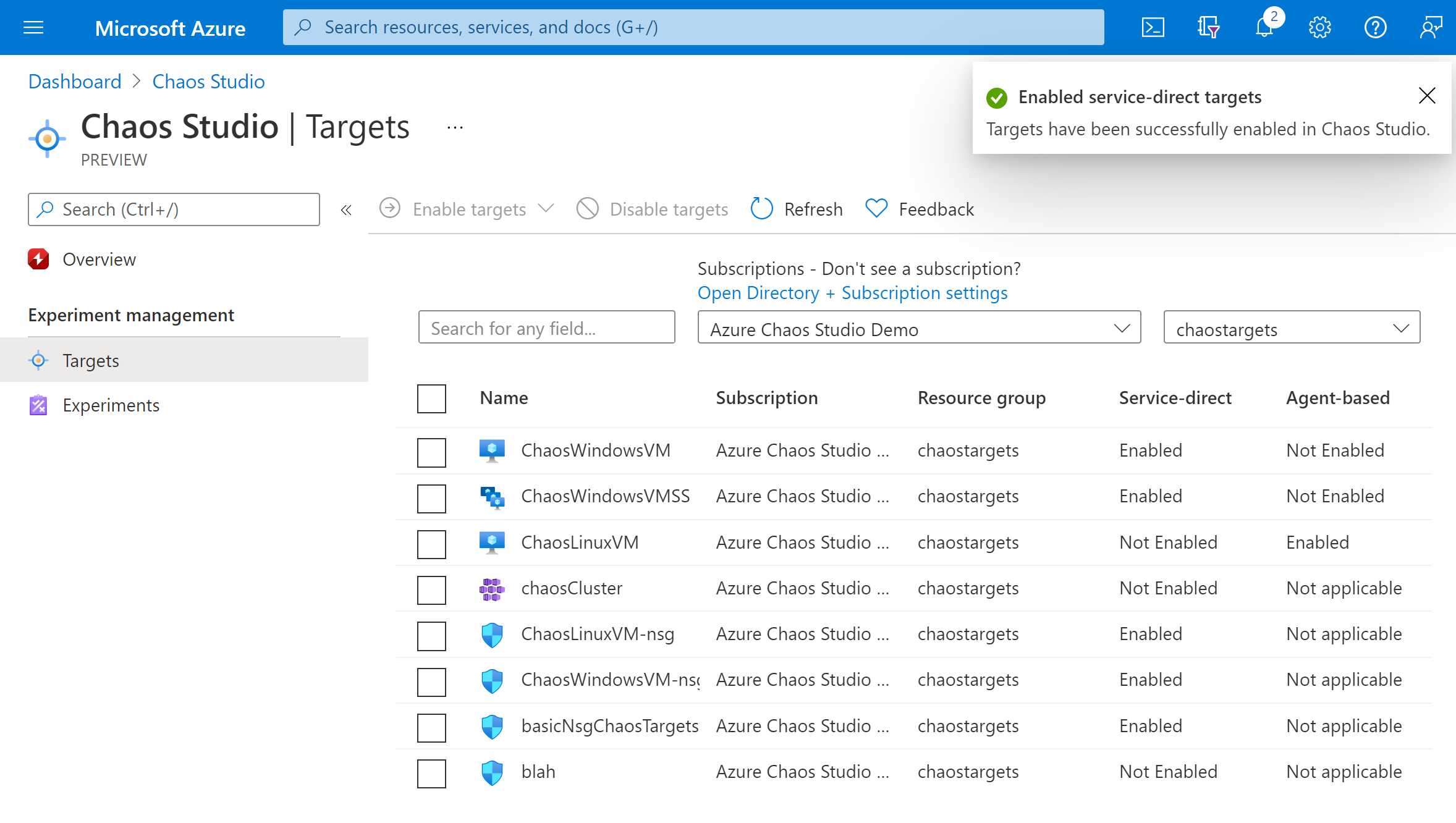
Confirm that the desired resource is listed. Select Review + Enable, then Enable.
A notification appears that indicates that the resources you selected were successfully enabled.
You've now successfully added your AKS cluster to Chaos Studio. In the Targets view, you can also manage the capabilities enabled on this resource. Select the Manage actions link next to a resource to display the capabilities enabled for that resource.
Create an experiment
Now you can create your experiment. A chaos experiment defines the actions you want to take against target resources. The actions are organized and run in sequential steps. The chaos experiment also defines the actions you want to take against branches, which run in parallel.
Select the Experiments tab in Chaos Studio. In this view, you can see and manage all your chaos experiments. Select Create > New experiment.
Fill in the Subscription, Resource Group, and Location where you want to deploy the chaos experiment. Give your experiment a name. Select Next: Experiment designer.
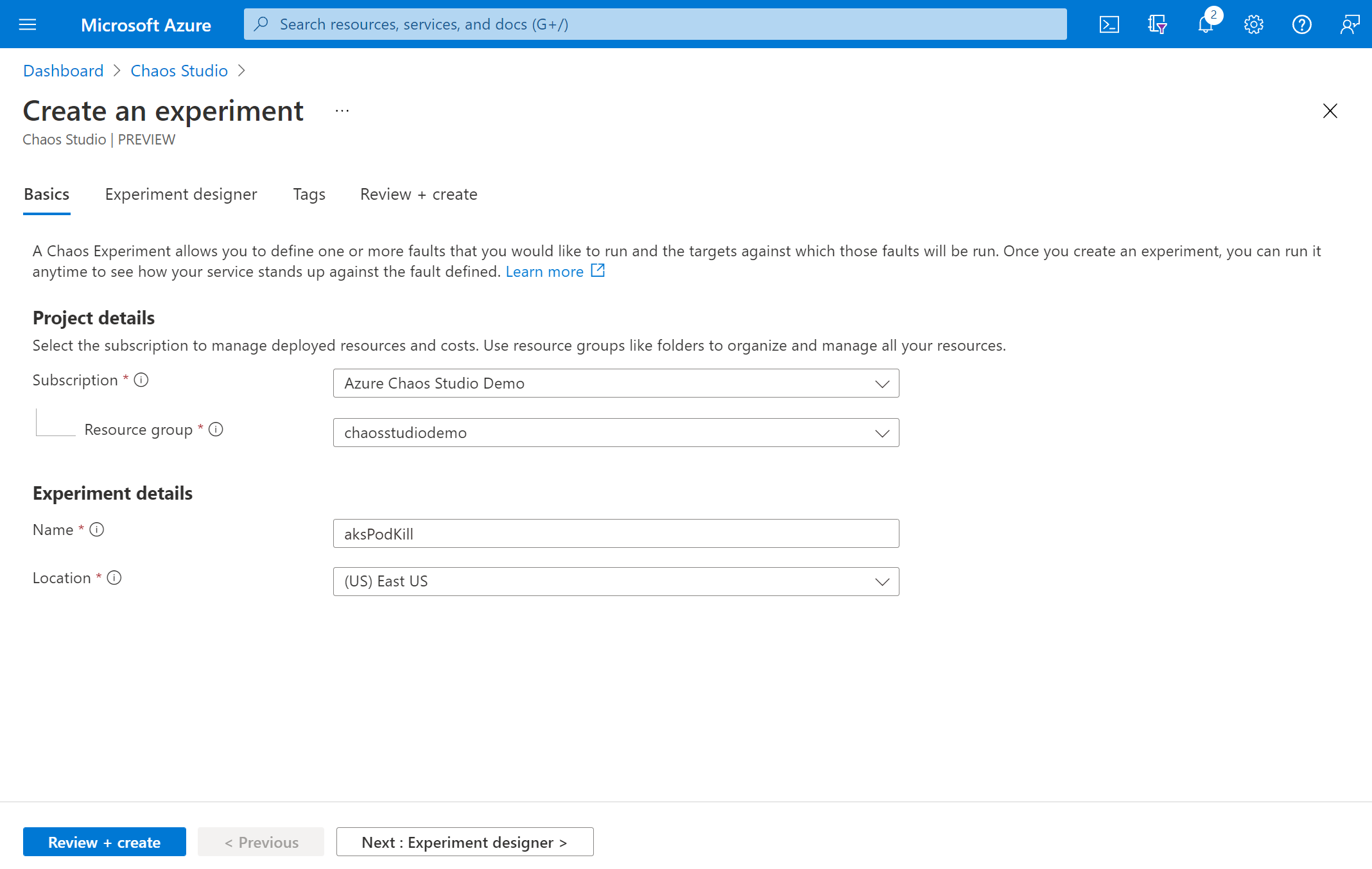
You're now in the Chaos Studio experiment designer. The experiment designer allows you to build your experiment by adding steps, branches, and faults. Give a friendly name to your Step and Branch and select Add action > Add fault.
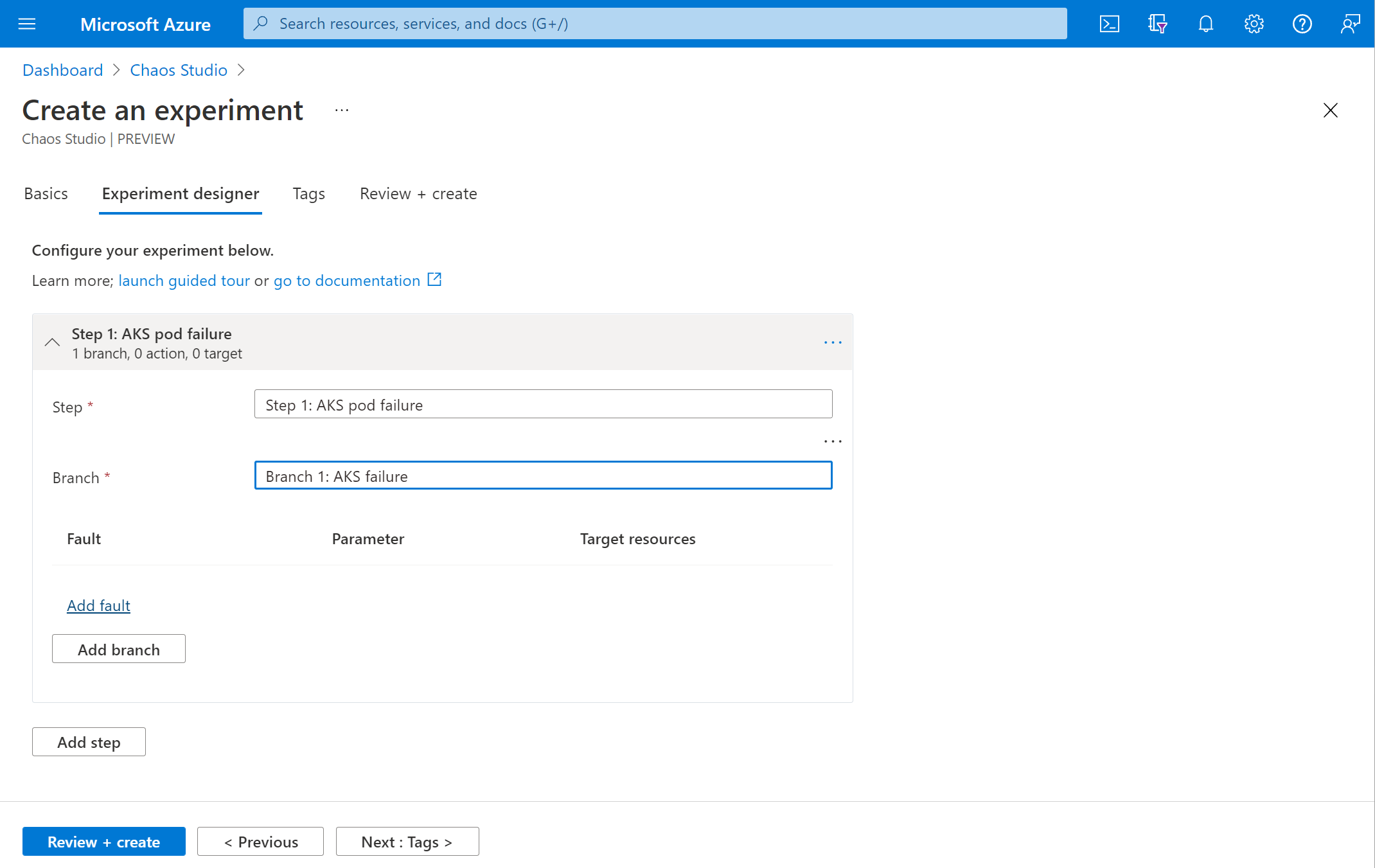
Select AKS Chaos Mesh Pod Chaos from the dropdown list. Fill in Duration with the number of minutes you want the failure to last and jsonSpec with the following information:
To formulate your Chaos Mesh
jsonSpec:See the Chaos Mesh documentation for a fault type, for example, the PodChaos type.
Formulate the YAML configuration for that fault type by using the Chaos Mesh documentation.
YAMLapiVersion: chaos-mesh.org/v1alpha1 kind: PodChaos metadata: name: pod-failure-example namespace: chaos-testing spec: action: pod-failure mode: all duration: '600s' selector: namespaces: - defaultRemove any YAML outside of the
spec(including the spec property name) and remove the indentation of the spec details. Thedurationparameter isn't necessary, but is used if provided. In this case, remove it.YAMLaction: pod-failure mode: all selector: namespaces: - defaultUse a YAML-to-JSON converter like this one to convert the Chaos Mesh YAML to JSON and minimize it.
JSON{"action":"pod-failure","mode":"all","selector":{"namespaces":["default"]}}Paste the minimized JSON into the jsonSpec field in the portal.
Select Next: Target resources.
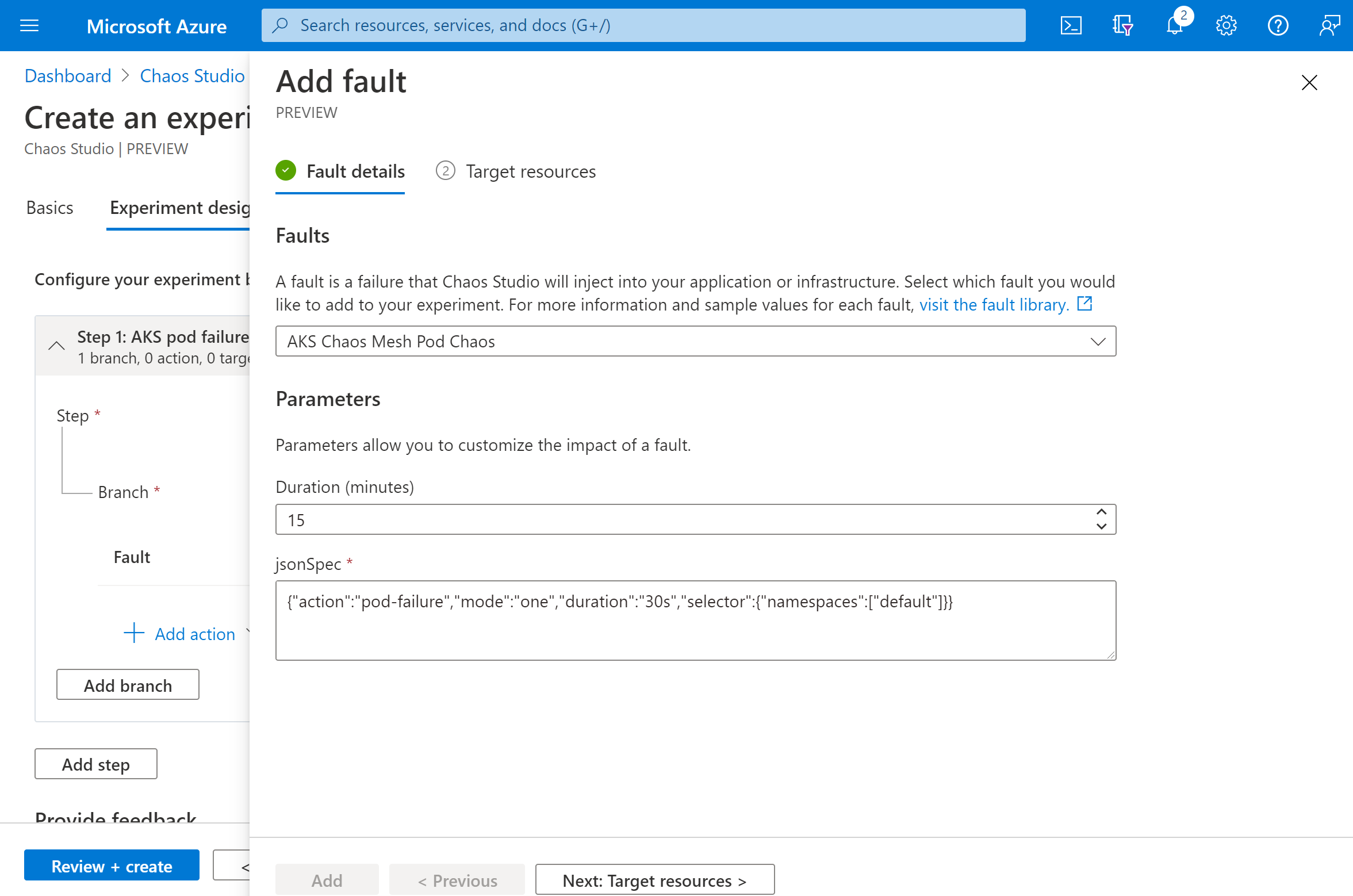
Select your AKS cluster and select Next.
Verify that your experiment looks correct and select Review + create > Create.
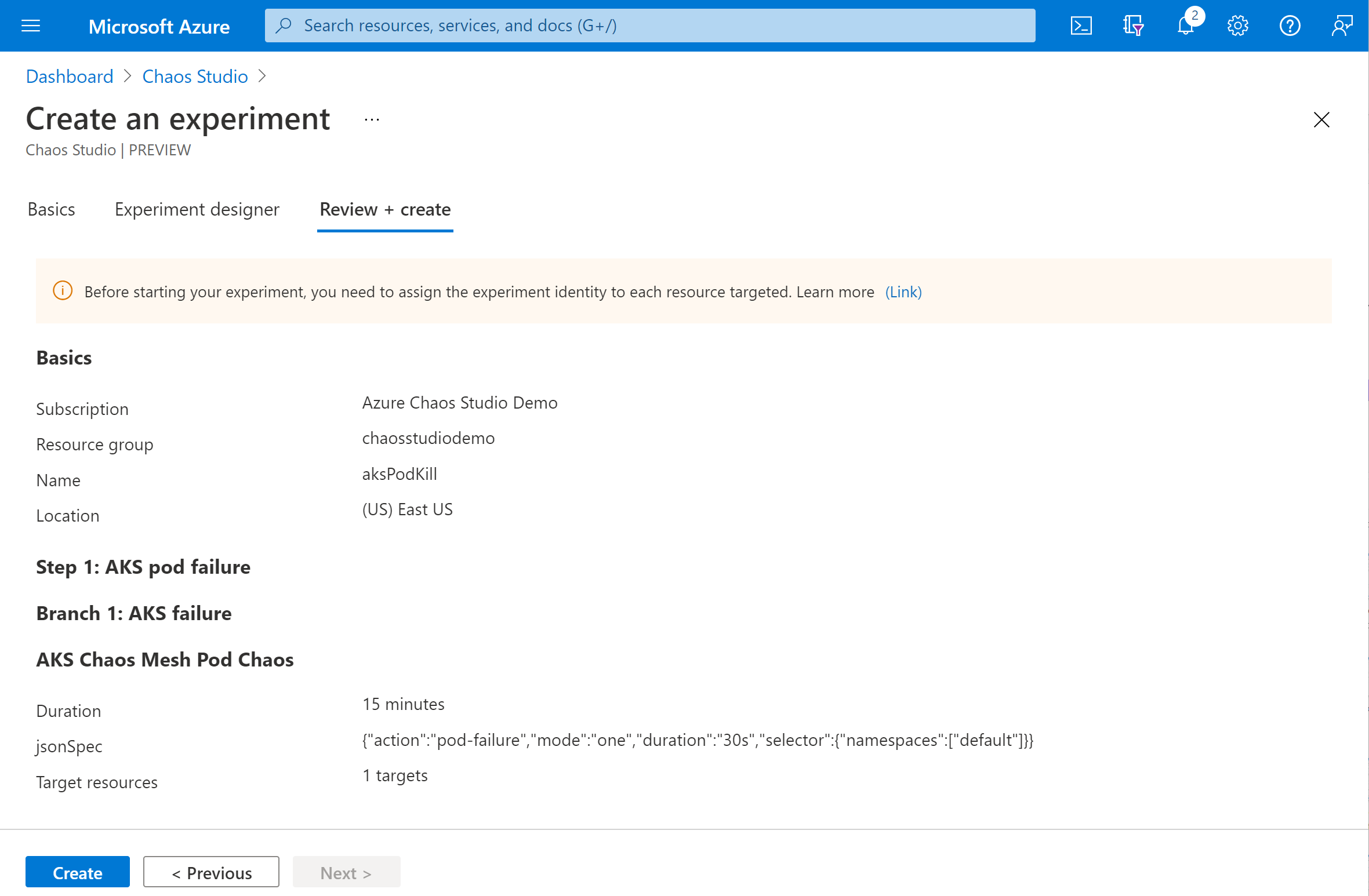
Give the experiment permission to your AKS cluster
When you create a chaos experiment, Chaos Studio creates a system-assigned managed identity that executes faults against your target resources. This identity must be given appropriate permissions to the target resource for the experiment to run successfully.
Go to your AKS cluster and select Access control (IAM).
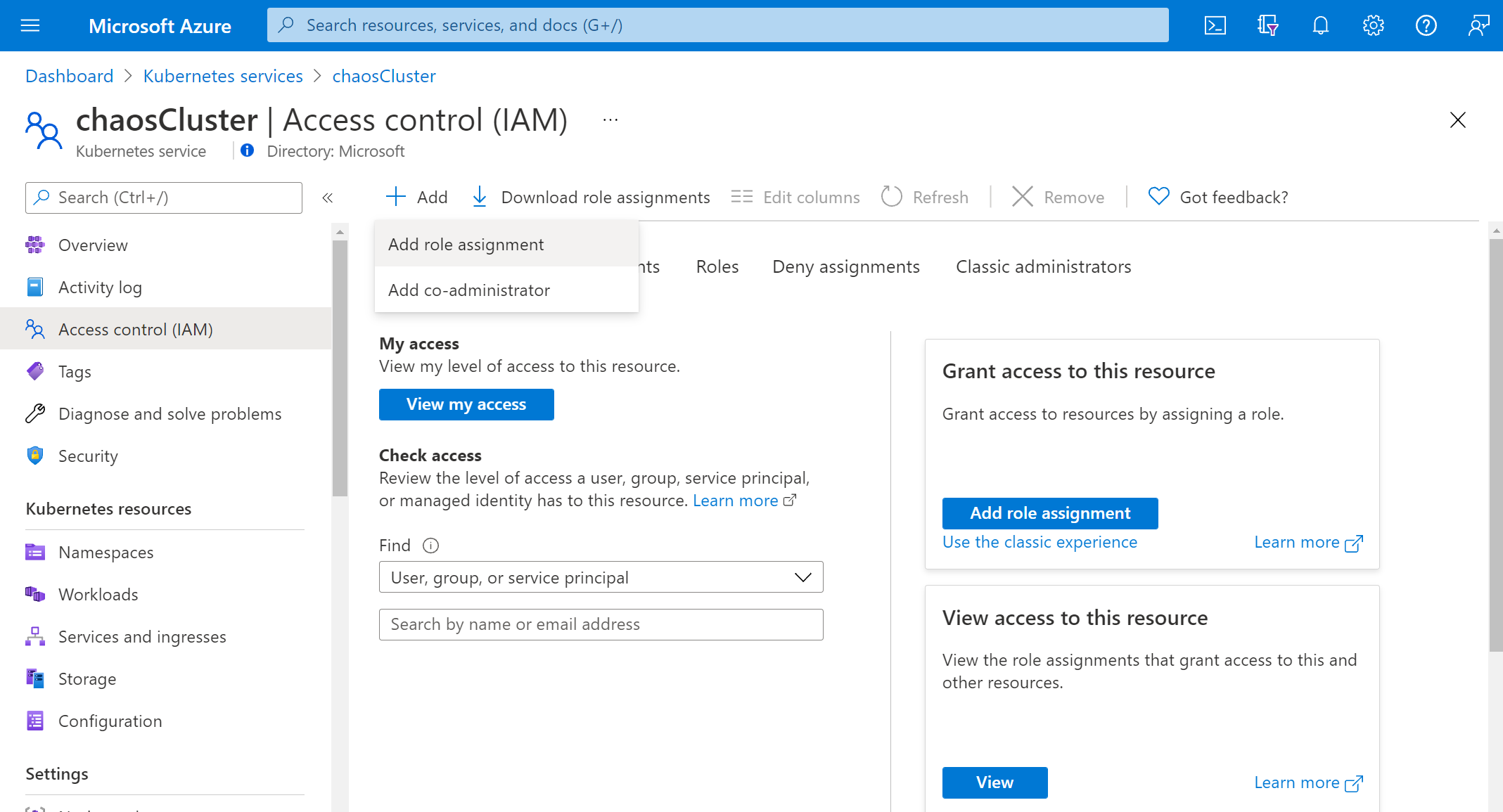
Select Add > Add role assignment.
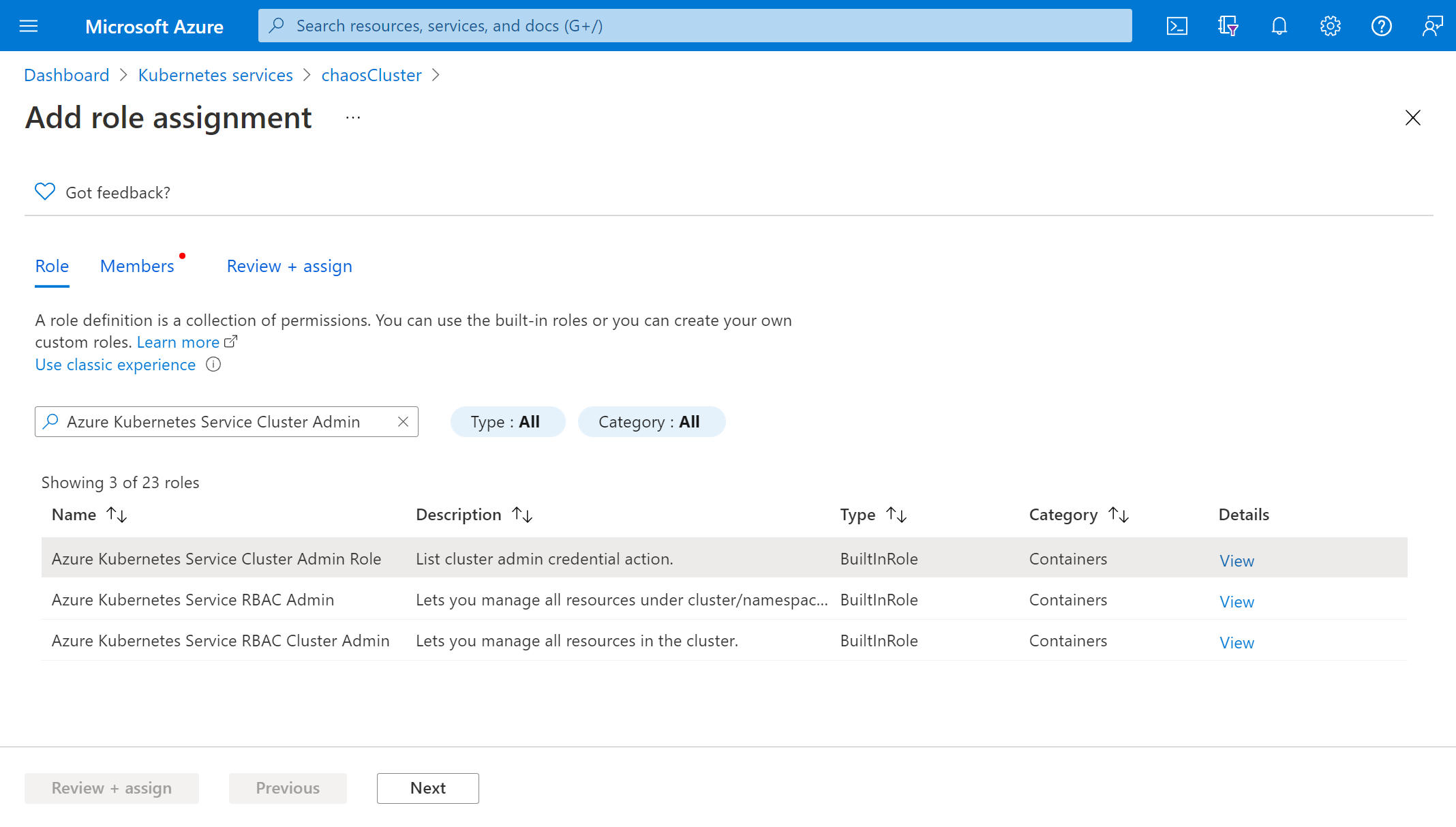
Search for Azure Kubernetes Service Cluster Admin Role and select the role. Select Next.
Choose Select members and search for your experiment name. Select your experiment and choose Select. If there are multiple experiments in the same tenant with the same name, your experiment name is truncated with random characters added.
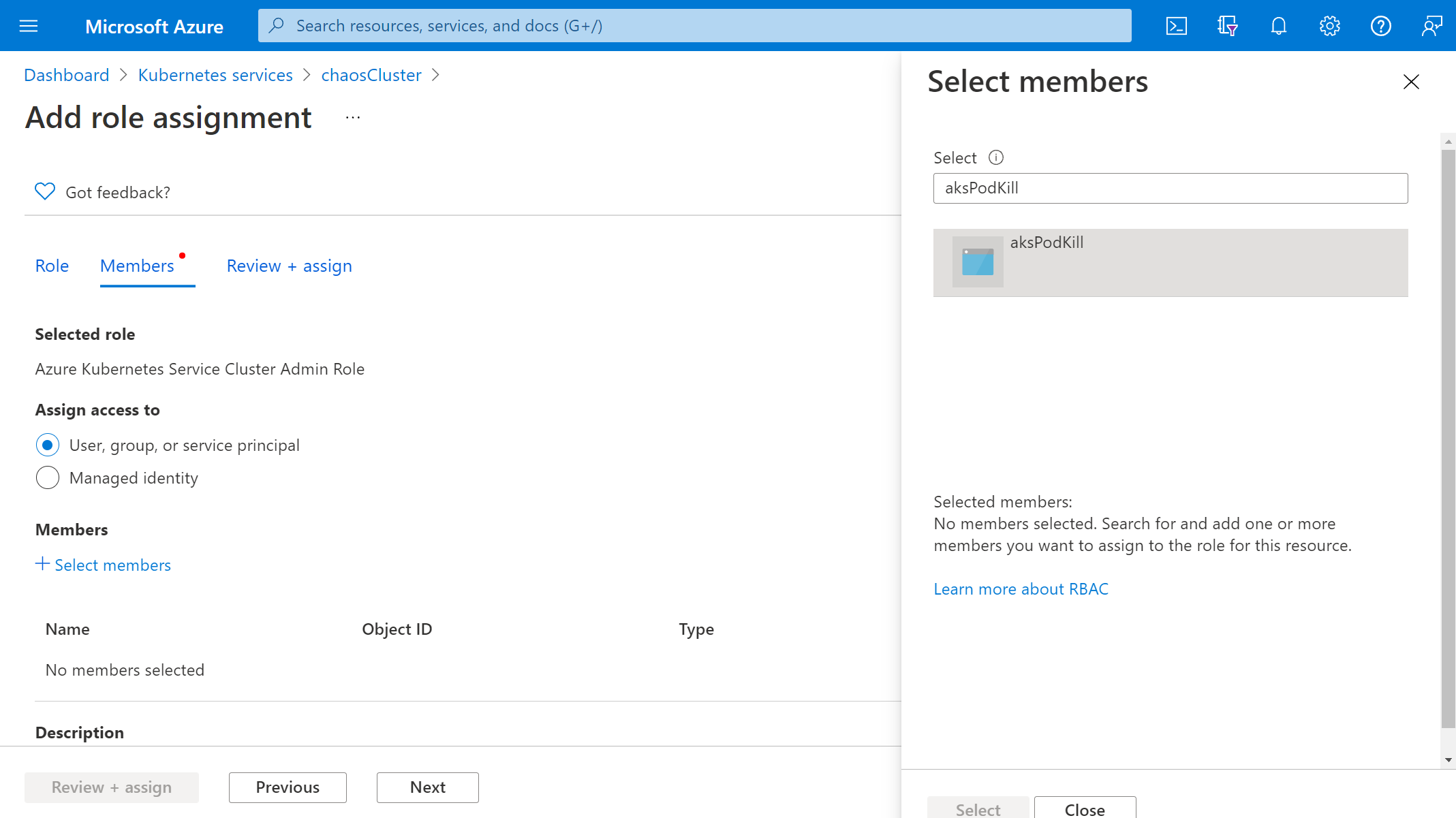
Select Review + assign > Review + assign.
Run your experiment
You're now ready to run your experiment. To see the effect, we recommend that you open your AKS cluster overview and go to Insights in a separate browser tab. Live data for the Active Pod Count shows the effect of running your experiment.
In the Experiments view, select your experiment. Select Start > OK.
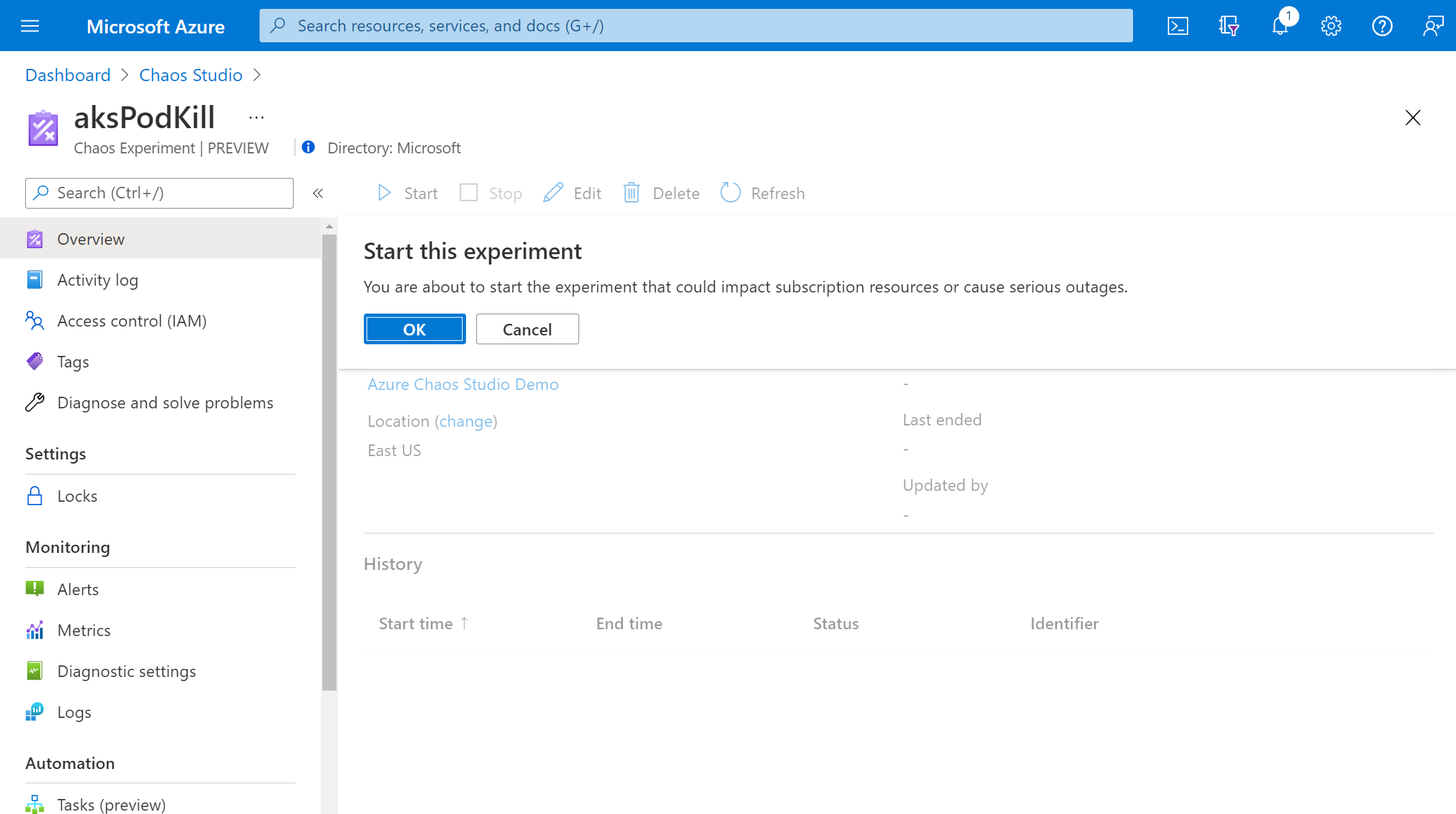
When the Status changes to Running, select Details for the latest run under History to see details for the running experiment.

No comments:
Post a Comment