Create an ASP.NET Core app with Azure App Configuration
In this quickstart, you'll use Azure App Configuration to externalize storage and management of your app settings for an ASP.NET Core app. ASP.NET Core builds a single, key-value-based configuration object using settings from one or more configuration providers. App Configuration offers a .NET configuration provider library. Therefore, you can use App Configuration as an extra configuration source for your app. If you have an existing app, to begin using App Configuration, you'll only need a few small changes to your app startup code.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create one for free.
- An App Configuration store. Create a store.
- .NET SDK 6.0 or later
Add key-values
Add the following key-values to the App Configuration store and leave Label and Content Type with their default values. For more information about how to add key-values to a store using the Azure portal or the CLI, go to Create a key-value.
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| TestApp:Settings:BackgroundColor | white |
| TestApp:Settings:FontColor | black |
| TestApp:Settings:FontSize | 24 |
| TestApp:Settings:Message | Data from Azure App Configuration |
Create an ASP.NET Core web app
Use the .NET command-line interface (CLI) to create a new ASP.NET Core web app project. The Azure Cloud Shell provides these tools for you. They're also available across the Windows, macOS, and Linux platforms.
Run the following command to create an ASP.NET Core web app in a new TestAppConfig folder:
dotnet new webapp --output TestAppConfig --framework net6.0
Connect to the App Configuration store
Navigate into the project's directory TestAppConfig, and run the following command to add a Microsoft.Azure.AppConfiguration.AspNetCore NuGet package reference:
.NET CLIdotnet add package Microsoft.Azure.AppConfiguration.AspNetCoreRun the following command. The command uses Secret Manager to store a secret named
ConnectionStrings:AppConfig, which stores the connection string for your App Configuration store. Replace the<your_connection_string>placeholder with your App Configuration store's connection string. You can find the connection string under Access Keys of your App Configuration store in the Azure portal..NET CLIdotnet user-secrets init dotnet user-secrets set ConnectionStrings:AppConfig "<your_connection_string>"Tip
Some shells will truncate the connection string unless it's enclosed in quotes. Ensure that the output of the
dotnet user-secrets listcommand shows the entire connection string. If it doesn't, rerun the command, enclosing the connection string in quotes.Secret Manager stores the secret outside of your project tree, which helps prevent the accidental sharing of secrets within source code. It's used only to test the web app locally. When the app is deployed to Azure like App Service, use the Connection strings, Application settings or environment variables to store the connection string. Alternatively, to avoid connection strings all together, you can connect to App Configuration using managed identities or your other Microsoft Entra identities.
Open Program.cs and add Azure App Configuration as an extra configuration source by calling the
AddAzureAppConfigurationmethod.C#var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Retrieve the connection string string connectionString = builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString("AppConfig"); // Load configuration from Azure App Configuration builder.Configuration.AddAzureAppConfiguration(connectionString); // The rest of existing code in program.cs // ... ...This code will connect to your App Configuration store using a connection string and load all key-values that have no labels. For more information on the App Configuration provider, see the App Configuration provider API reference.
Read from the App Configuration store
In this example, you'll update a web page to display its content using the settings you configured in your App Configuration store.
Add a Settings.cs file at the root of your project directory. It defines a strongly typed
Settingsclass for the configuration you're going to use. Replace the namespace with the name of your project.C#namespace TestAppConfig { public class Settings { public string BackgroundColor { get; set; } public long FontSize { get; set; } public string FontColor { get; set; } public string Message { get; set; } } }Bind the
TestApp:Settingssection in configuration to theSettingsobject.Update Program.cs with the following code and add the
TestAppConfignamespace at the beginning of the file.C#using TestAppConfig; // Existing code in Program.cs // ... ... builder.Services.AddRazorPages(); // Bind configuration "TestApp:Settings" section to the Settings object builder.Services.Configure<Settings>(builder.Configuration.GetSection("TestApp:Settings")); var app = builder.Build(); // The rest of existing code in program.cs // ... ...Open Index.cshtml.cs in the Pages directory, and update the
IndexModelclass with the following code. Add theusing Microsoft.Extensions.Optionsnamespace at the beginning of the file, if it's not already there.C#public class IndexModel : PageModel { private readonly ILogger<IndexModel> _logger; public Settings Settings { get; } public IndexModel(IOptionsSnapshot<Settings> options, ILogger<IndexModel> logger) { Settings = options.Value; _logger = logger; } }Open Index.cshtml in the Pages directory, and update the content with the following code.
HTML@page @model IndexModel @{ ViewData["Title"] = "Home page"; } <style> body { background-color: @Model.Settings.BackgroundColor; } h1 { color: @Model.Settings.FontColor; font-size: @(Model.Settings.FontSize)px; } </style> <h1>@Model.Settings.Message</h1>
Build and run the app locally
To build the app using the .NET CLI, navigate to the root directory of your project. Run the following command in the command shell:
.NET CLIdotnet buildAfter the build completes successfully, run the following command to run the web app locally:
.NET CLIdotnet runThe output of the
dotnet runcommand contains two URLs. Open a browser and navigate to either one of these URLs to access your application. For example:https://localhost:5001.If you're working in the Azure Cloud Shell, select the Web Preview button followed by Configure. When prompted to configure the port for preview, enter 5000, and select Open and browse.
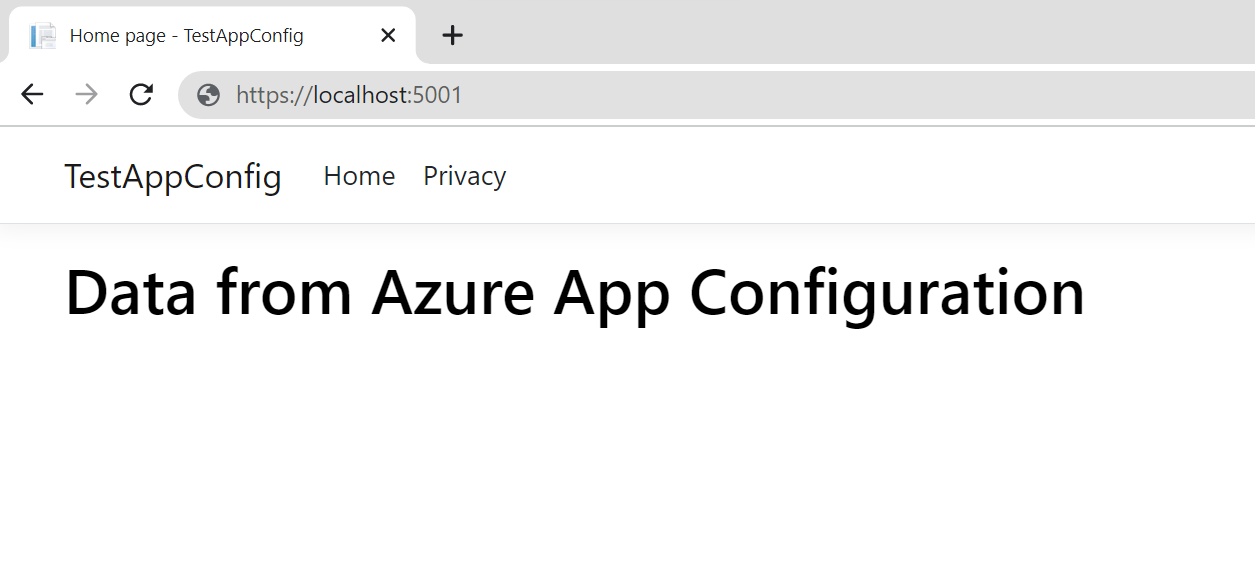
The web page looks like this:

No comments:
Post a Comment