Step by Step Azure NAT Gateway – Static Outbound Public IP address #ANG #NAT #WVD #Azure #Security #Cloud #MVPBuzz #AzOps #ITPRO #VirtualNetworks #PowerShell
There a several ways on using an external IP in Azure, What method to use is up to you. Remember there is no good or wrong but only different opinions or insights on how to use it.
Public IP addresses allow Internet resources to communicate inbound to Azure resources. Public IP addresses also enable Azure resources to communicate outbound to Internet and public-facing Azure services with an IP address assigned to the resource. The address is dedicated to the resource, until it is unassigned by you. If a public IP address is not assigned to a resource, the resource can still communicate outbound to the Internet, but Azure dynamically assigns an available IP address that is not dedicated to the resource.
Some of the resources you can associate a public IP address resource with are:
- Virtual machine network interfaces
- Internet-facing load balancers
- VPN gateways
- Application gateways
- Azure Firewall
- NAT Gateway
Matching SKUs must be used for load balancer and public IP resources. You can’t have a mixture of basic SKU resources and standard SKU resources. You can’t attach standalone virtual machines, virtual machines in an availability set resource, or a virtual machine scale set resources to both SKUs simultaneously.
Virtual Network NAT (network address translation) simplifies outbound-only Internet connectivity for virtual networks. When configured on a subnet, all outbound connectivity uses your specified static public IP addresses. Outbound connectivity is possible without load balancer or public IP addresses directly attached to virtual machines. NAT is fully managed and highly resilient.
So this is only for the Outbound connection. why not use the Resource group IP this is also “static” ? using this IP means that al VM’s must be in the same resource group and when the resource group changed the IP is also changing.
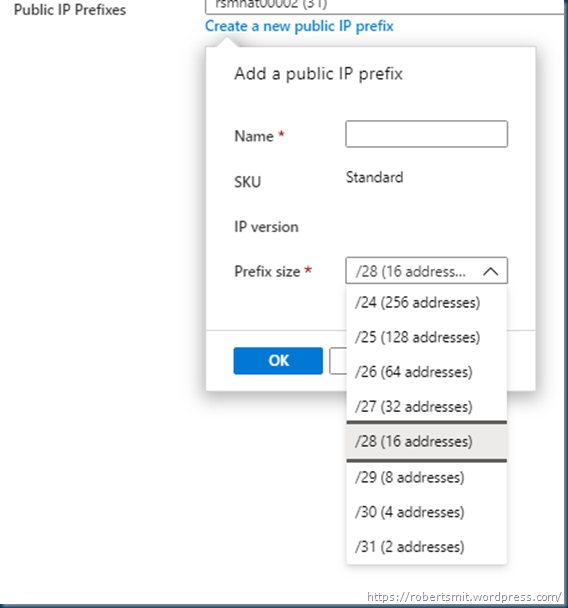
NAT is compatible with standard SKU public IP address resources or public IP prefix resources or a combination of both. You can use a public IP prefix directly or distribute the public IP addresses of the prefix across multiple NAT gateway resources. NAT will groom all traffic to the range of IP addresses of the prefix. Any IP whitelisting of your deployments is now easy.
So How to implement this. a step by step guide. GUI and powershell Looking at my demo setup, There are 2 vm’s both in a different Resource group.
Setting up the NAT gateway is done by 3 tabs to fill in the name and what vnet to use
We add a new NAT gateway.
We create a new resource group and choose NAT gateway name.
The Timeout we leave this on 4 min for now.
We configure an external IP and with a standard SKU. Basic is not supported.
the next step is choose the External outbound IP pool minimal is 2 and max is 256. this is not needed but only if you want to have a pool of External IP’s else it just go the one external ip
you can select max 2 prefixes
Configure which subnets of a virtual network should use this NAT gateway. Subnets with Basic load balancers or virtual machines that are using a Basic public IP are not compatible and cannot be used.
Note: While you do not have to complete this step to create a NAT gateway, the NAT gateway will not be functional until you have added at least one subnet. You can also add and reconfigure which subnets are included after creating the NAT gateway.
in the last step we tag the NAT gateway to a subnet. When checking the VM’s on this subnet for the outbound IP ( remember the VM does not need a public IP on the network card)
Here I have 2 VM’s getting both an IP from the prefix
If there is only a small prefix then both machines will get the same external outbound IP
With this time flow it recycles the External IP, depending on the scope and usage.
So in just a few steps you can use a useful gateway for all your outbound traffic.
Building this in Powershell is also easy. I use a semi automatic script as I want to choose my network. but you can change this to a fixed network if you want.
remember this will need the az.network latest module. in the old modules there is no get-AzNatGateway command. without this the posh is not working.
First we have some parameters
# Set the variables for the NAT Gateway.
$rg = ‘rg-rsm-natgw001’
$Location = ‘Westeurope’
$sku = ‘Standard’
$PublicIpname = ‘pup-rsm-natgw001’
$Publicprefixname = ‘pxp-rsm-natgw001’
$NatGatewayname=’gwn-rsm-natgateway001′
#create Rsource group
New-AzResourceGroup -Name $rg -Location $Location















No comments:
Post a Comment