1. What is cloud computing?
The delivery of on-demand computing services over the Internet, such as storage, virtual machines, networks, Internet of Things (IoT), databases, and software, is known as cloud computing.
2. Can you tell me which are the best cloud providers in the Market?
The short answer is that all of them are. Every cloud provider is going to have their own strengths, weaknesses, and areas where they excel, different services may be a better fit for your application depending on what you need out of it. However, AWS Amazon web services have the highest share in the cloud computing market after that Azure is the second largest shareholder of the cloud computing market, and GCP is also growing fast.
3. Why do we need cloud computing? / Benefits of Cloud computing.
- It is omnipresent, which means you can access cloud services from anywhere, even on your mobile device, you only need an internet connection.
- It is cheaper than the traditional computing method or on-prim as it requires operational expenditure, not a capital expenditure. The Cloud computing payment model is pay-as-you-go meaning pay what you use.Note: In some scenarios pay-as-you-go model doesn’t apply say when you are using dedicated hosts there is a host–level charge regardless of how many Azure virtual machines you run on it.
- It is Flexible users can scale services according to their needs, customize applications, and access cloud services from anywhere they have an internet connection.
- Cloud infrastructure can Scale up and down on demand to support rapidly changing business needs.
- It is Fast users can get their applications to market more quickly by developing them in the cloud.
- Due to networked backups, cloud computing is data secure in the sense that hardware failures do not affect data loss.
- It is always up-to-date Cloud computing services are updated regularly to give users access to the most recent technology.
- Using cloud computing is more Productive since you don’t need to maintain infrastructure, allowing your IT staff to pursue business-related tasks.
- Cloud computing is Secure because it manages access and permissions to the resources and services it provides. Access to a certain file could be restricted to a particular group of users, for example.
- The cloud has made Collaboration easier with teams able to easily access, edit, and share real-time data.
4. What are the service models offered by Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing models may vary in terms of their service offerings. Such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), while others offer Platform as a Service (PaaS) or Software as a Service (SaaS).
- At its most basic level, PaaS allows customers to focus on building software applications, which can then be deployed onto a shared hosting platform.
Examples: Windows Azure Compute and App Service, Amazon Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine. - SaaS provides users with easy access to proprietary business apps without having to install or maintain these applications themselves.
Examples: Microsoft Office 365, Google Apps, Gmail. - In IaaS-based solutions, customers are responsible for managing all system resources such as storage and networking infrastructure.
Examples: Windows Azure Virtual Machines, Virtual Networks, Amazon EC2, Google Compute Engine, etc.
5. What are the different deployment models of cloud computing?
When considering cloud deployment models, there are 3 major categories to keep in mind, ownership, scale, and access. When trying to identify what cloud deployment model you are using, you must ask who the cloud is managed by, who has access to it, and how you own it. These three models of cloud computing are :
- Public: Your cloud provider owns the infrastructure, and the servers are multi-subscriber servers.
- Private: It can be your own infrastructure, or your cloud provider can provide you with a service completely.
Example: Hosting your website on a dedicated server or with a cloud provider. - Hybrid: Hybrid Clouds combine both Public Clouds and Private Clouds.
Example: if you could use your own servers for your confidential database on a private cloud, and your public cloud for your company’s public website.
Boost your earning potential with Azure expertise. Explore our certified Azure Courses for a high-paying career
- Explore Azure DevOps Certification
Basics Azure Interview questions and answers
6. What is Microsoft Azure?
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service offered by Microsoft for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications and services through a global network of Microsoft-managed data centers. It provides software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS) through which users can deploy cloud-based applications.
7. What is a Resource Group?
A resource group is a logical container that holds related resources for an Azure solution. It is also a building block of all Azure solutions, containing one or more related services, such as web apps, storage accounts, databases, and much more. A resource group can be used to organize your services in a way that makes sense for your solution.
8. What is a Resource in Azure?
A resource is a virtual machine, web app, SQL database, or any other item that can be created or used through Microsoft’s Azure cloud service.
9. What is a Region in Azure?
Azure is a cloud computing platform, made available across different regions around the world. When you require a service, application, or virtual machine on Azure, you are first asked to specify a region. You select the region of the data center in which your application runs.
10. What is an Azure portal?
An Azure portal is a web-based application that can be used to add, modify, or remove Azure resources and services. It is located at Here.
11. What is an Azure Account?
Azure accounts are unique global entities that allow you to access Azure services and subscriptions. Multiple subscriptions can be created in your Azure account to create separation, for instance, for billing or management purposes.
12. What is an Azure Subscription?
Azure subscriptions can be thought of as a bundle you can buy with an entitlement to use and access resources from Azure. Similar to pre-paid SIM cards that allow you to use your phone while you buy it.
13. How can you get your Azure Subscription?
- Enterprise agreement: allows customers to make a bulk purchase of subscriptions with an upfront financial commitment and use the services throughout the year.
- Cloud resellers: Provide cloud services to medium- to large-sized businesses in a simple, flexible way.
- Microsoft partners: They can set up your Azure cloud solution for you.
- Individual Free Account: For a limited period of time, Microsoft offers free credits which can be used by companies and/or individuals to try out Microsoft’s services.
14. How many types of Azure Subscriptions are there?
- Free: Creating a free subscription with an email account and a credit card will give you 200$ credit for the first 30 days and one year of free limited access.
- Pay-As-You-Go: Charged based on how much Cloud resource you use.
- Enterprise: an Enterprise agreement is made for large-volume purchases of subscriptions, with discounts for new licenses and Software Assurance for enterprises.
- Student: Activating this subscription does not require a credit card, but verification of your status as a student is required.
15. What are the different ways to log in to an Azure subscription?
You can connect to an Azure subscription using Azure portal, Azure PowerShell, Base machine PowerShell, and Azure CLI.
16. What are the 3 pillars of Azure?
17. What is an Azure virtual machine?
18. How does an Azure Virtual Machine work?
Virtualization is the process of creating a software-based or virtual version of a computer, and, just like your actual computer, the new virtual computer requires the equivalent of processor power, storage, and memory in order to function. This can function as a separate computing environment often run to operate a different operating system or as the users’ sole computing experience, as is often the case for office computers. The virtual machine is separated from the rest of the system so that the software in the VM cannot affect the host computer’s primary operating system.
19. What are VMs used for?
- Cloud-based apps can be built and deployed.
- New operating systems (OS) can be tested.
- Installing a new environment to help developers run development-test scenarios more easily and faster.
- To make a backup of your existing operating system.
20. What categories of Azure VMs can be created?
- General purpose: CPU-to-memory ratio is balanced. It is ideal for testing and development, small to medium databases, and web servers with low traffic.
- Compute optimized: It has a high CPU-to-memory ratio. It is well suited for web servers with medium traffic, network appliances, batch processes, and application servers.
- Memory-optimized: It has a high memory-to-core ratio. The best choice for relational database servers, large caches, and in-memory analytics.
- Storage optimized: I/O and throughput on the disk are high. Great for NoSQL and Big Data databases.
- GPU: A range of virtual machines for video editing and heavy graphics rendering.
- High-performance compute Virtual machines with the fastest and most powerful processors, including high-throughput network interfaces.
21. What are B series / Burstable VMs in Azure?
“Burstable” VMs are ones where you can save up CPU cycles for later use. CPU cycles that are not in use by you are “banked” in a virtual account for you.
22. How many ways you can create an Azure VM?
- We can create an Azure VM using the Azure portal.
- We can create an Azure VM using an ARM template.
- We can also create an Azure VM with PowerShell.
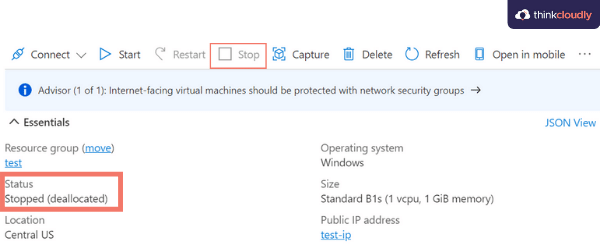
23. What is the Stopped state of Azure VM?
You can issue a command in an Azure VM’s operating system to stop it from running. This will kick you out of the OS and stop all processes, but it will preserve any allocated hardware (including the IP addresses currently assigned). Once the VM is stopped, you’ll see the state listed as Stopped and you will still be charged by the hour for this instance.
24. What is Deallocated state of Azure VM?
Rather than halting the virtual machine from the operating system, it can be terminated from within Azure. When a VM is stopped through Azure, rather than through the OS, it will go into a Stopped (deallocated) state. Any dynamic IPs not reserved will be given up, but this also means you will no longer be paying for VM compute costs. ParkMyCloud is a good way to save money on Azure costs when your VMs are not needed and it sends them into this parked state.
25. What is Azure virtual network (VNet)?
An Azure virtual network (VNet) is a logical network used to create separate secure networks for your Azure resources. Within a VNet, you can deploy one or more subnets, using private IP addresses. You can then assign public IP addresses to specific instances in those subnets. Virtual machines deployed into a subnet without public IP addresses are automatically assigned a private IP address in addition to a dynamically created public IP address that can be assigned to any instance within that subnet.
26. What are the Components of Azure VNet?
Azure networking components are capable of providing companies with an array of features that can help them develop cloud applications that meet their needs.
Below is a list of the components of Azure Networking:
- Subnets
- Routing
- Network Security Groups
27. What is a Subnet?
Users can segment a virtual network into one or more sub-networks by using subnets. These sub-networks can be logically separated, and each subnet consists of a server.
28. What is NSG?
In order to simplify network security for a virtual network, Microsoft is releasing NSGs that allow administrators to filter and route network traffic easily. The network security group will let the administrators set up different rules, one inbound and one outbound, and any Azure virtual network can be added to it.
29. What is Azure Vnet peering?
Peering is a way to connect two virtual networks together over an IPsec VPN. Virtual Networks (VNets) in Azure are logically isolated from each other, and cross-premises connectivity can be achieved by setting up VPN connections. However, peering enables you to extend your on-premises network directly into Azure through your existing IPsec infrastructure.
30. What is the Azure resource manager template?
31. How can you do Automation in Azure?
32. What are Azure functions?
Functions in Azure are serverless compute services that let you execute event-triggered code without manually managing or provisioning infrastructure.
33. What are logic apps?
The Azure Logic Apps service integrates apps, data, systems, and services, automatically carrying out scheduled, automatic, and orchestrated tasks. Azure Logic Apps streamlines orders from one location to another, integrating on-premises and cloud-based systems.
34. What is Blog Storage?
Azure Blob storage is a type of cloud storage where unstructured data is stored as objects. Documents, media files, and application installers, among others, can be stored in binary or textual format.
35. What is Azure Queue Storage?
Storage in Azure Queue provides the capacity to store millions of incoming messages, and each message can have a maximum size of 64 KB.
36. What is Azure File Storage?
37. What is Azure Table storage?
38. What are Azure storage tiers?
To store data in blob storage, Azure offers three storage tiers:
- Hot – Better for storing data that is frequently accessed.
- Cool – Data is stored for at least 30 days and is optimized for rarely accessed data
- Archive – Ideal for archiving data that is rarely accessed and should be stored for at least 180 days with a flexible latency requirement (in the order of hours).
Different tiers of storage offer cost-effective options for storing data at different stages of its lifecycle.
39. What is the difference between managed disk and an unmanaged disk?
Managed Disks:
Disks that are managed by Microsoft Azure don’t require a storage account to be created. Since Azure manages the storage account, you do not have complete control over the disks created.
Unmanaged Disks:
An unmanaged disk is something that requires you to create a storage account before creating a new one. You have full control over all the data that is stored on your storage account since it is created and owned by you. Additionally, you yourself will have to take care of encryption, data recovery plans, etc.
40. What is Azure CDN?
Using the Azure Content Delivery Network will reduce load times, bandwidth, and responsiveness. Whether you are a developer, webmaster, game developer, mobile app creator, media broadcaster, firmware engineer, or building IoT systems, Azure Content Delivery Network is the ideal resource.
41. What is Azure SQL Database?
Microsoft Azure SQL Database is a reliable and secure relational database that offers higher performance and requires less time and less cost for management.
42. What is Azure Firewall?
Network firewalls are fundamental to securing a company’s data. Similar to local area network (LAN) firewalls, cloud-based firewalls in Microsoft Azure inspect the traffic based on access control rules defined by administrators. Unlike traditional firewalls, which often serve as both network perimeter security devices and virtual private network (VPN) termination points, Microsoft Azure Firewall provides role-based access control for ports and services based on your subscription level.
43. What is Azure Data Lake?
Microsoft Azure Data Lake is a public cloud-based service that houses many Microsoft Azure products and services. Azure Data Lake is designed to accommodate big data analytics. Dropbox offers unlimited storage for structured, semi-structured, or unstructured data. It can be used to store any type of data in any amount.
44. What do you mean by Azure Data Factory?
Data Factory in Azure is a data integration system that lets users transfer data between on-premises and cloud systems and establish scheduled data flows.
45. What is Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)?
More easily deploy and manage containerized applications with a fully managed Kubernetes service. Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) provides serverless Kubernetes, an integrated continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) experience, and enterprise-grade security and governance.
46. What are Azure Containers?
Containers can run batch jobs with a consistent environment and dependencies in order to free up the machines to efficiently handle the ingestion of data, processing, and storage. Dynamic compute options, such as Azure Container Instances (ACI), offer easy scaling for such data processing projects.
47. What is Docket in Azure?
Docker is a modern software containerization platform for creating, managing, and deploying applications. Containers provide an isolated, virtualized runtime environment for applications where it’s easy to create, deploy, and run multiple applications side-by-side on a single physical server or VM. Each container shares a single OS kernel with other containers.
48. What do you know about Azure DevOps?
DevOps is a development practice that focuses on communication, collaboration, integration, and automation between software developers and information technology (IT) professionals. The goal of DevOps is to produce high-quality products quickly while maintaining high-quality systems. Automation helps to reduce errors in these complex environments by ensuring that code and infrastructure meet quality standards before release. DevOps usually involves many IT professionals, developers, and project managers across an organization.
49. What is Azure IoT?
The Azure Internet of Things (IoT) is a collection of Azure cloud services that connect, monitor and control billions of IoT assets. In simpler terms, an IoT solution is made up of one or more IoT devices and one or more back-end services running in the cloud.
50. What are Azure IoT Edge modules?
IoT Edge modules are essentially containerized packages that contain Azure services, third-party services, or even custom code that will run on an IoT Edge device and will essentially function locally on the device. The IoT Edge runtime can be found on each IoT Edge-enabled device and manages the modules installed on each device.

No comments:
Post a Comment