Azure Regions | Paired Regions | Availability Zones
This is Part 4 of Azure tutorial. In our previous 2 videos we discussed Azure Datacenters and Geographies. In this video we will discuss
- Azure Regions
- Region Pairs
- Availability Zones
- Update Domains
- Fault Domains,
- Zonal Services
- Zone-redundant services.
What is an Azure Datacenter
An Azure data center is a unique physical building that contains thousands of physical servers with it's own power, cooling and networking infrastructure. These data ceneters are located all over the globe. As of November 2020, there are over 160+ Azure datacenters worldwide. It is these dataceneters that are the building blocks of gloabl Azure infrastructure.

What is an Azure Geography
An Azure geography is an area of the world that contains one or more Azure Regions. For example, India, United States, United Kingdom are a few examples of Azure Geographies.
Why are azure geographies important
For two reasons. First, let's say all of your customers are in India. You don't want to host your application somewhere in the United States. You don't want every request and the associated data travelling around the world. This causes unnecessary latency, delay and hence, poor performance. You want your application and data to be hosted as geographically close to your customer base as possible. Since all our customers are in India, we want to make sure, our application and data is hosted in India. One way Azure ensures this is by using geographies.
Another reason is compliance with regulations. regulated data like financial, health care or credit card data may not be allowed to leave the country. Legally your organisation may be required to store such data in the same country where the operations are being carried out. Again, azure ensures this, by using geographie
So, for example, if you select India as the geography, Azure ensures your data is always stored in India, except for certain global services.
What is an Azure Region
Simply put, an Azure Region is a set of Datacenters that are connected through a dedicated low-latency network. How many datacenters does a region contain. Well, we do not have a fixed number. It varies. There are regions of different sizes. A Region could be made up of just 1 dataceneter or multiple datacenters. The point is, an Azure Region is a group of one or more Azure Datacenters. As of this course recording, Azure has 58 regions worldwide.
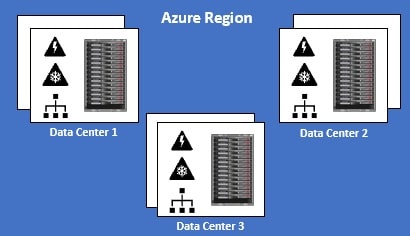
You have the flexibility to deploy your applications and data to any Azure region you want. You can even deploy across multiple regions to deliver cross-region resiliency.
What is cross-region resiliency
Well, in general, resilience is the ability of a software to react to problems in one of its components and still provide the best possible service.
Both your software and the underlying infrastructure must be resilient. If there is a problem, the end user should not know about it. The request must be handled and processed by another region. The end user should get the same level of service.
We can get this resiliency, by deploying our application and data in at least 2 regions. In this example we have our application and data deployed in two regions - Region A and Region B.
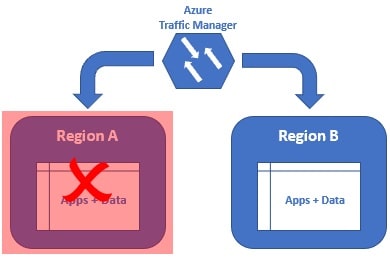
If there is a region level failure, for example, let's say Region A has gone down. The Azure Traffic Manager is smart enough to send all the requests to Region B. The end user gets the same response. He does not even know there is a region level failure. When Region A is back online, the Azure Traffic Manager will distribute the traffic between both the regions again.
Why are Azure Regions important
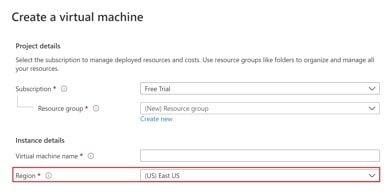
Well, beacuse everytime we create an Azure resource like a Virtual Machine for example, we need to specify the Azure Region where we want this resource to be created.
What is an Azure Availability Zone
An Azure Availability Zone is a unique physical location within an Azure region. Each Availability Zone is made up of one or more datacenters with independent power, cooling, and networking. Not all Regions have Availability Zones. Regions that support Availability Zones have a minimum of three separate zones to ensure resiliency.
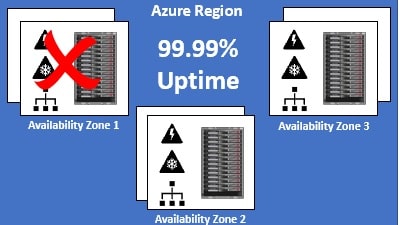
If one of the Availability Zones has gone down for some reason, we still have our applications and data available from the rest of the two Availability Zones. There is a physical separation between each Availability Zone and it is this separation that protects our applications and data from Datacenter failures. With Availability Zones, Azure offers industry best 99.99% VM uptime SLA.
Azure fault domain and update domain
An Availability Zone is a combination of a fault domain and an update domain. For example, if you create three VMs across three zones in an Azure region, your VMs are effectively distributed across three fault domains and three update domains.
For some reason, if there is a power failure or power surge, equipment failure or some other fault in Availability Zone 1, only Availability Zone 1 is affected. As the availability zones are physically separted from each other, faults from one availability zone are not spread to the other availability zones. Since, in this example, we have 3 availability zones, it's like we have 3 separate fault domains. If there is a fault and Availability Zone 1 is down, we still have our VM available from the rest of the two fault domians i.e Availability Zones 2 and 3.

Similarly, if there is an update or a patch to be applied, azure schedules these at different times for different availability zones. So this means, we have just one of the availability zones affected while the update is being applied. The rest of the 2 zones are unaffected.
In our example, since we have 3 availability zones, the updates will be applied at 3 different times. So even, if the VM from Availability Zone 1 is down, due to the update being applied, we have the rest of the 2 VMs still up and running i.e the VMs in Availability Zones 2 and 3.
Azure Zonal services and Zone-redundant services
If you want to make the best use of availability zones and build high-availability systems, you will have to identify your compute, storage, networking, and data resources within an availability zone and replicate them in the other availability zones. Azure services that support Availability Zones are classified into two categories:
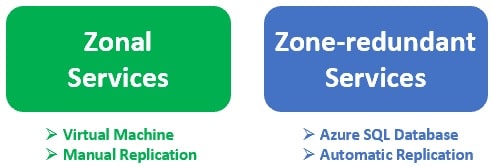
Zonal services - Virtual machine is an example of a zonal service. A zonal service is pinned to a specific availability zone. This means it is only available in the availability zone where it is created. It is not automaically replicated to other availability zones. So, if want to build highly-available systems, identify zonal services, such as a VM for example and replicate them in other availability zones. Other examples of zonal services are managed disks and Standard IP addresses.
Zone-redundant services - Azure SQL Database is an example of zone-redundant service. These zone-redundant services are automatically replicated by the Azure platform across all availability zones. Unlike Zonal services, we don't have to replicate them manually.
What are Azure paired regions
Azure regional pair, paired regions, or region pair, all these terms are used interchangeably and they refer to the same thing, i.e a pair of azure regions. So in simple terms, a regional pair consists of two regions within the same geography.
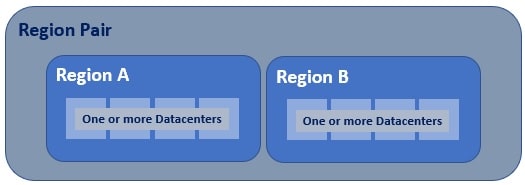
As you can see from the image, at the highest level we have an Azure Geography. As we have already discussed, an Azure geography is an area of the world that contains one or more Azure Regions. For example, India, United States, Europe, Asia Pacific are a few examples of Azure Geographies.
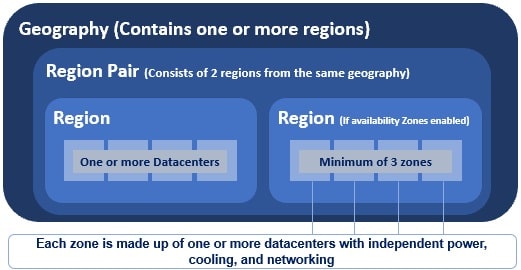
An azure region is made up of one or more datacenters. If availability zones are enabled, an azure region contains a minimum of three availability zones. An Availability Zone is made up of one or more datacenters. So the point is, an Azure region contains one or more datacenters or 3 or more availability zones if enabled.
Most regions in a geography are paired to ensure business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR). The following are a few examples of azure paired regions. For the complete list of Azure paired regions, please check out the Microsoft official docs.
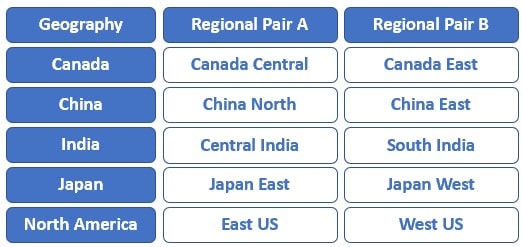
A regional pair consists of two regions within the same geography. However, there is one exception to this. Brazil South region is paired with South Central US region, which obviously, is outside of Brazil's geography.

Regions are paired by Microsoft
Can I select the regions that I want in a region pair. No, you can't. Regions in a Region Pair are determined by Microsoft. We do not have any control over it. However, you are not limited to using just the regions in one given region pair. You can of course create your own business continuity and disaster recovery solutions by deploying in any number of regions. Obviously, if they are deployed across regional pairs we will have better business continuity and disaster recovery.
Benefits of paired regions
Physical separation between datacenters : When possible, there is at least 300 miles of separation between datacenters in a regional pair, although this isn't practical or possible in all geographies. Physical datacenter separation reduces the likelihood of natural disasters, civil unrest, power outages, or physical network outages affecting both the regions at the sametime. So for whatever reason, if one of the regions is down, we still have the other region available.
Region recovery in the event of an outage : If for whatever reason, several regions world-wide are down, azure prioritizes recovery of one region out of every pair. So if you want your apps and data to be highly available, deploy them in paired regions. With this setup, if both the regions are down, azure prioritizes to recover at least one region from the pair, so we have our apps and data available again soon. If applications are deployed across regions that are not paired, recovery might be delayed, in the worst case the chosen regions may be the last two to be recovered.
Automatic Platform-provided replication : Some services such as Geo-Redundant Storage provides automatic replication to the paired region. This is a great benefit. In an event, where one of the regions go down, you still have the data available from the other region in the region pair.
Data residency, compliance and legal requirements : With the exception of Brazil South, regions with in a region pair are from the same geography. This helps us meet data residency, compliance and legal requirements.
Sequential system updates : From time to time, patches and software updates need to be applied. Regions in a region pair are never updated simultaneously at the same time. They are always applied sequentially. This reduces the downtime to a great extent. If the planned update contains any bugs or logical errors, only one region is affected. Our apps and data will still be available from the other region in the region pair.
On the map below you can see the currently available Azure Regions and Availability Zones.
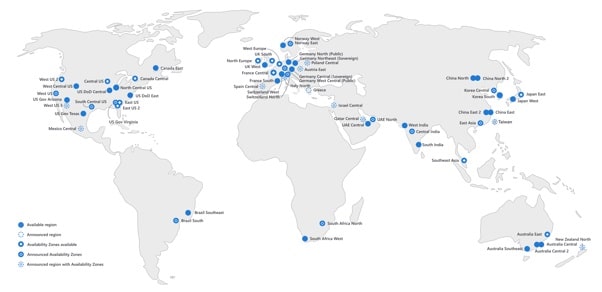
Please don't worry if some of the terms and services are a bit confusing at the moment. We will be revisiting most of these several times as we progress through the course. We will also see them practically in action. So I assure you, you will get quite comfortable with them as we progress through the course.

No comments:
Post a Comment