1. What is Cloud Computing? Can you talk about and compare any two popular Cloud Service Providers?
For a detailed discussion on this topic, please refer our Cloud Computing blog. Following is the comparison between two of the most popular Cloud Service Providers:
Amazon Web Services Vs Microsoft Azure
| Parameters | AWS | Azure |
| Initiation | 2006 | 2010 |
| Market Share | 4x | x |
| Implementation | Less Options | More Experimentation Possible |
| Features | Widest Range Of Options | Good Range Of Options |
| App Hosting | AWS not as good as Azure | Azure Is Better |
| Development | Varied & Great Features | Varied & Great Features |
| IaaS Offerings | Good Market Hold | Better Offerings than AWS |
2.. Try this AWS scenario based interview question. I have some private servers on my premises, also I have distributed some of my workload on the public cloud, what is this architecture called?
- Virtual Private Network
- Private Cloud
- Virtual Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud
Answer D.
Explanation: This type of architecture would be a hybrid cloud. Why? Because we are using both, the public cloud, and your on premises servers i.e the private cloud. To make this hybrid architecture easy to use, wouldn’t it be better if your private and public cloud were all on the same network(virtually). This is established by including your public cloud servers in a virtual private cloud, and connecting this virtual cloud with your on premise servers using a VPN(Virtual Private Network).
Learn to design, develop, and manage a robust, secure, and highly available cloud-based solution for your organization’s needs with the Google Cloud Platform Course.
3. What is Auto-scaling?
Auto-scaling is a feature that allows you to provision and launch new instances based on demand. It enables you to automatically raise or reduce resource capacity in response to demand.
4. What is geo-targeting in CloudFront?
Geo-targeting is a concept in which businesses may deliver customized information to their audience depending on their geographic location without altering the URL. This allows you to produce personalized content for a specific geographical audience while keeping their demands in mind.
5. Define and explain the three initial orders of all services and the AWS products erected on them.
There are three primary types of cloud services: computing, storage, and networking.
Then there are AWS products built based on the three orders of all services. Computing services such as EC2, Elastic Beanstalk, Lambda, Auto-Scaling, and Lightsail are exemplifications. S3, Glacier, Elastic Block Storage, and the Elastic File System exemplify the storage. VPC, Amazon CloudFront, and Route53 are exemplifications of networking services.
6. What are the steps involved in a CloudFormation Solution?
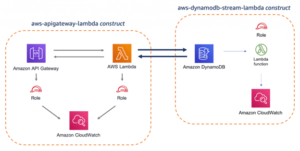
- Create a new CloudFormation template or utilize an existing one in JSON or YAML format.
- Save the code in an S3 bucket, which will act as a repository for it.
- To call the bucket and construct a stack on your template, use AWS CloudFormation.
- CloudFormation scans the file and understands the services that are called, their sequence, and the relationships between the services before provisioning them one by one.
7. What are the main features of Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing has the following key characteristics:
- Massive amounts of computing resources can be provisioned quickly.
- Resources can be accessed from any location with an internet connection due to its location independence.
- Unlike physical devices, cloud storage has no capacity constraints which makes it very efficient for storage.
- Multi-Tenancy allows a large number of users to share resources.
- Data backup and disaster recovery are becoming easier and less expensive with cloud computing.
- Its Scalability enables businesses to scale up and scale down as needed with cloud computing.
8. Explain AWS.
AWS is an abbreviation for Amazon Web Services, which is a collection of remote computing services also known as Cloud Computing. This technology is also known as IaaS, or Infrastructure as a Service.
9. Name some of the non-regional AWS services.
Some of the non-regional AWS services.
- CloudFront
- IAM
- Route 53
- Web Application Firewall
10. What are the different layers that define cloud architecture?
The following are the various layers operated by cloud architecture:
- CLC or Cloud Controller.
- Cluster Controller
- SC or Storage Controller
- NC, or Node Controller
- Walrus
11. What are the tools and techniques that you can use in AWS to identify if you are paying more than you should be, and how to correct it?
You may ensure that you are paying the proper amount for the resources you use by utilizing the following resources:
- Check out the Top Services Table- It is a dashboard in the expense management interface that displays the top five most used services. This will show you how much money you are spending on the resources in question.
- Cost Finder- There are cost explorer programs accessible that will allow you to see and evaluate your consumption expenditures over the previous 13 months. You may also receive a cost prediction for the next three months.
- AWS Budgets- This helps you create a budget for the services. It will also allow you to see if the current plan suits your budget and the specifics of how you utilize the services.
- Cost Allocation Labels- This aids in determining the resource that has cost the most in a given month. It allows you to categorize your resources and cost allocation tags in order to keep track of your AWS charges.
12. What are the various layers of cloud computing? Explain their work.
Cloud computing categories have various layers that include
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is the on-demand provision of services such as servers, storage, networks, and operating systems.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) combines IaaS with an abstracted collection of middleware services, software development, and deployment tools.
- PaaS also enables developers to create web or mobile apps in the cloud quickly.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) is a software application that has been delivered on-demand, in a multi-tenant model
- Function as a Service (FaaS) enables end users to build and execute app functionalities on a serverless architecture.
13. What are the various Cloud versions?
There are several models for deploying cloud services:
- The public cloud is a collection of computer resources such as hardware, software, servers, storage, and so on that are owned and operated by third-party cloud providers for use by businesses or individuals.
- A private cloud is a collection of resources owned and managed by an organization for use by its employees, partners, or customers.
- A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud services.
14. Is there any other alternative tool to log into the cloud environment other than the console?
The following will help you in logging into AWS resources:
- Putty
- AWS CLI for Linux
- AWS CLI for Windows
- AWS CLI for Windows CMD
- AWS SDK
- Eclipse
15. What are the native AWS Security logging capabilities?
Most AWS services provide logging capabilities. AWS CloudTrail, AWS Config, and others, for example, have account level logging. Let’s look at two specific services:
AWS CloudTrail
This is a service that gives a history of AWS API calls for each account. It also allows you to undertake security analysis, resource change tracking, and compliance audits on your AWS environment. The nice aspect about this service is that you can set it to send notifications via AWS SNS when fresh logs are provided.
AWS Setup
This helps you comprehend the configuration changes that occur in your environment. This service offers an AWS inventory that contains configuration history, configuration change notification, and links between AWS resources. It may also be set to send notifications via AWS SNS when fresh logs are received.
16. What is a DDoS attack, and what services can minimize them?
DDoS is a cyber-attack in which the culprit visits a website and creates several sessions, preventing genuine users from accessing the service. The following native tools will help you in preventing DDoS attacks on your AWS services:
- AWS Shield
- AWS WAF
- AAmazon CloudFront
- Amazon Route53
- ELB
- VPC
16. List the pros and cons of serverless computing.
Advantages:
- Cost-effective
- Operations have been simplified.
- Improves Productivity
- Scalable
Disadvantages:
- This can result in response latency
- Due to resource constraints, it is not suitable for high-computing operations.
- Not very safe.
- Debugging can be difficult.
17. What characteristics distinguish cloud architecture from traditional cloud architecture?
The characteristics are as follows:
- In the cloud, hardware requirements are met based on the demand generated by cloud architecture.
- When there is a demand for resources, cloud architecture can scale them up.
- Cloud architecture can manage and handle dynamic workloads without a single point of failure.
Earn Cloud Architect Certification and become certified.
18. What are the featured services of AWS?
AWS’s key components are as follows:
- Elastic compute cloud (EC2): It is a computing resource that is available on demand for hosting applications. In times of uncertain workloads, EC2 comes in handy.
- Route 53: It is a web-based DNS service.
- Simple Storage Device S3: This is a storage device service that is widely used in AWS Identity and Access Management.
- Elastic Block Store: It allows you to store constant volumes of data and is integrated with EC2. It also allows you to persist data.
- Cloud watch: It allows you to monitor the critical areas of AWS and even set a reminder for troubleshooting.
- Simple Email Service: It allows you to send emails using regular SMTP or a restful API call.
Section 2: AWS Interview Questions and Answers for Amazon EC2
For a detailed discussion on this topic, please refer to our EC2 AWS blog.
19. What does the following command do with respect to the Amazon EC2 security groups?
ec2-create-group CreateSecurityGroup
- Groups the user created security groups into a new group for easy access.
- Creates a new security group for use with your account.
- Creates a new group inside the security group.
- Creates a new rule inside the security group.
Answer B.
Explanation: A Security group is just like a firewall, it controls the traffic in and out of your instance. In AWS terms, the inbound and outbound traffic. The command mentioned is pretty straight forward, it says create security group, and does the same. Moving along, once your security group is created, you can add different rules in it. For example, you have an RDS instance, to access it, you have to add the public IP address of the machine from which you want to access the instance in its security group.
20. Here is aws scenario based interview question. You have a video trans-coding application. The videos are processed according to a queue. If the processing of a video is interrupted in one instance, it is resumed in another instance. Currently there is a huge back-log of videos which needs to be processed, for this you need to add more instances, but you need these instances only until your backlog is reduced. Which of these would be an efficient way to do it?
You should be using an On Demand instance for the same. Why? First of all, the workload has to be processed now, meaning it is urgent, secondly you don’t need them once your backlog is cleared, therefore Reserved Instance is out of the picture, and since the work is urgent, you cannot stop the work on your instance just because the spot price spiked, therefore Spot Instances shall also not be used. Hence On-Demand instances shall be the right choice in this case.
21. You have a distributed application that periodically processes large volumes of data across multiple Amazon EC2 Instances. The application is designed to recover gracefully from Amazon EC2 instance failures. You are required to accomplish this task in the most cost effective way.
Which of the following will meet your requirements?
- Spot Instances
- Reserved instances
- Dedicated instances
- On-Demand instances
Answer: A
Explanation: Since the work we are addressing here is not continuous, a reserved instance shall be idle at times, same goes with On Demand instances. Also it does not make sense to launch an On Demand instance whenever work comes up, since it is expensive. Hence Spot Instances will be the right fit because of their low rates and no long term commitments.
22. How is stopping and terminating an instance different from each other?
Starting, stopping and terminating are the three states in an EC2 instance, let’s discuss them in detail:
- Stopping and Starting an instance: When an instance is stopped, the instance performs a normal shutdown and then transitions to a stopped state. All of its Amazon EBS volumes remain attached, and you can start the instance again at a later time. You are not charged for additional instance hours while the instance is in a stopped state.
- Terminating an instance: When an instance is terminated, the instance performs a normal shutdown, then the attached Amazon EBS volumes are deleted unless the volume’s deleteOnTermination attribute is set to false. The instance itself is also deleted, and you can’t start the instance again at a later time.
23. If I want my instance to run on a single-tenant hardware, which value do I have to set the instance’s tenancy attribute to?
- Dedicated
- Isolated
- One
- Reserved
Answer A.
Explanation: The Instance tenancy attribute should be set to Dedicated Instance. The rest of the values are invalid.
24. When will you incur costs with an Elastic IP address (EIP)?
- When an EIP is allocated.
- When it is allocated and associated with a running instance.
- When it is allocated and associated with a stopped instance.
- Costs are incurred regardless of whether the EIP is associated with a running instance.
Answer C.
Explanation: You are not charged, if only one Elastic IP address is attached with your running instance. But you do get charged in the following conditions:
- When you use more than one Elastic IPs with your instance.
- When your Elastic IP is attached to a stopped instance.
- When your Elastic IP is not attached to any instance.
25. How is a Spot instance different from an On-Demand instance or Reserved Instance?
First of all, let’s understand that Spot Instance, On-Demand instance and Reserved Instances are all models for pricing. Moving along, spot instances provide the ability for customers to purchase compute capacity with no upfront commitment, at hourly rates usually lower than the On-Demand rate in each region. Spot instances are just like bidding, the bidding price is called Spot Price. The Spot Price fluctuates based on supply and demand for instances, but customers will never pay more than the maximum price they have specified. If the Spot Price moves higher than a customer’s maximum price, the customer’s EC2 instance will be shut down automatically. But the reverse is not true, if the Spot prices come down again, your EC2 instance will not be launched automatically, one has to do that manually. In Spot and On demand instance, there is no commitment for the duration from the user side, however in reserved instances one has to stick to the time period that he has chosen.
26. Are the Reserved Instances available for Multi-AZ Deployments?
- Multi-AZ Deployments are only available for Cluster Compute instances types
- Available for all instance types
- Only available for M3 instance types
- D. Not Available for Reserved Instances
Answer B.
Explanation: Reserved Instances is a pricing model, which is available for all instance types in EC2.
27. How to use the processor state control feature available on the c4.8xlarge instance?
The processor state control consists of 2 states:
- The C state – Sleep state varying from c0 to c6. C6 being the deepest sleep state for a processor
- The P state – Performance state p0 being the highest and p15 being the lowest possible frequency.
Now, why the C state and P state. Processors have cores, these cores need thermal headroom to boost their performance. Now since all the cores are on the processor the temperature should be kept at an optimal state so that all the cores can perform at the highest performance.
Now how will these states help in that? If a core is put into sleep state it will reduce the overall temperature of the processor and hence other cores can perform better. Now the same can be synchronized with other cores, so that the processor can boost as many cores it can by timely putting other cores to sleep, and thus get an overall performance boost.
Concluding, the C and P state can be customized in some EC2 instances like the c4.8xlarge instance and thus you can customize the processor according to your workload.
28. What kind of network performance parameters can you expect when you launch instances in cluster placement group?
The network performance depends on the instance type and network performance specification, if launched in a placement group you can expect up to
- 10 Gbps in a single-flow,
- 20 Gbps in multiflow i.e full duplex
- Network traffic outside the placement group will be limited to 5 Gbps(full duplex).
29. To deploy a 4 node cluster of Hadoop in AWS which instance type can be used?
First let’s understand what actually happens in a Hadoop cluster, the Hadoop cluster follows a master slave concept. The master machine processes all the data, slave machines store the data and act as data nodes. Since all the storage happens at the slave, a higher capacity hard disk would be recommended and since master does all the processing, a higher RAM and a much better CPU is required. Therefore, you can select the configuration of your machine depending on your workload. For e.g. – In this case c4.8xlarge will be preferred for master machine whereas for slave machine we can select i2.large instance. If you don’t want to deal with configuring your instance and installing hadoop cluster manually, you can straight away launch an Amazon EMR (Elastic Map Reduce) instance which automatically configures the servers for you. You dump your data to be processed in S3, EMR picks it from there, processes it, and dumps it back into S3.
30. Where do you think an AMI fits, when you are designing an architecture for a solution?
AMIs(Amazon Machine Images) are like templates of virtual machines and an instance is derived from an AMI. AWS offers pre-baked AMIs which you can choose while you are launching an instance, some AMIs are not free, therefore can be bought from the AWS Marketplace. You can also choose to create your own custom AMI which would help you save space on AWS. For example if you don’t need a set of software on your installation, you can customize your AMI to do that. This makes it cost efficient, since you are removing the unwanted things.
31. How do you choose an Availability Zone?
Let’s understand this through an example, consider there’s a company which has user base in India as well as in the US.
Let us see how we will choose the region for this use case :
 So, with reference to the above figure the regions to choose between are, Mumbai and North Virginia. Now let us first compare the pricing, you have hourly prices, which can be converted to your per month figure. Here North Virginia emerges as a winner. But, pricing cannot be the only parameter to consider. Performance should also be kept in mind hence, let’s look at latency as well. Latency basically is the time that a server takes to respond to your requests i.e the response time. North Virginia wins again!
So, with reference to the above figure the regions to choose between are, Mumbai and North Virginia. Now let us first compare the pricing, you have hourly prices, which can be converted to your per month figure. Here North Virginia emerges as a winner. But, pricing cannot be the only parameter to consider. Performance should also be kept in mind hence, let’s look at latency as well. Latency basically is the time that a server takes to respond to your requests i.e the response time. North Virginia wins again!
So concluding, North Virginia should be chosen for this use case.
32. Is one Elastic IP address enough for every instance that I have running?
Depends! Every instance comes with its own private and public address. The private address is associated exclusively with the instance and is returned to Amazon EC2 only when it is stopped or terminated. Similarly, the public address is associated exclusively with the instance until it is stopped or terminated. However, this can be replaced by the Elastic IP address, which stays with the instance as long as the user doesn’t manually detach it. But what if you are hosting multiple websites on your EC2 server, in that case you may require more than one Elastic IP address.
33. What are the best practices for Security in Amazon EC2?
There are several best practices to secure Amazon EC2. A few of them are given below:
- Use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access to your AWS resources.
- Restrict access by only allowing trusted hosts or networks to access ports on your instance.
- Review the rules in your security groups regularly, and ensure that you apply the principle of least
- Privilege – only open up permissions that you require.
- Disable password-based logins for instances launched from your AMI. Passwords can be found or cracked, and are a security risk.
34. How can you upgrade or downgrade a system with little to no downtime?
The following steps can be used to update or downgrade a system with near-zero downtime:
First, you will have to Launch the EC2 console, then secondly, select the AMI Operating System. The next step is creating an instance using the new instance type; you need to install the updates and go to set up apps. Then check to determine if the instances are operational or not, and if everything is well, you will deploy the new instance and replace all the old ones. Now once everything is ready for installation, you can upgrade or downgrade the system with very little to no downtime
35. What’s the Amazon EC2 root device volume?
The image used to boot an EC2 instance is saved on the root device slice, which happens when an Amazon AMI launches a new EC2 case. This root device volume is supported by EBS or an instance store. In general, the lifetime of an EC2 instance does not affect the root device data stored on Amazon EBS.
36. Mention and explain the many types of Amazon EC2 instances.
The various instances available on Amazon EC2 General-purpose Instances:
- They are used to compute a wide range of tasks and aid in allocating processor, memory, and networking resources.
- Instances optimized for computing: These are suitable for compute-intensive workloads. They can handle batch processing workloads, high-performance web servers, machine learning inference, and a wide range of other tasks.
- Memory-optimized: They process and provide tasks that manage massive datasets in memory.
- Computing speed: It accelerates the execution of floating-point number calculations, data pattern matching, and graphics processing.
- Optimized Storage: They conduct operations on local storage that need sequential read and write access to big data sets.
37. What exactly do you mean by ‘changing’ in Amazon EC2?
Amazon EC2 now provides the option for customers to move from the current ‘instance count-based constraints’ to the new ‘vCPU Based restrictions.’ As a result, when launching a demand-driven mix of instance types, usage is assessed in terms of the number of vCPUs.
38. Your application is running on an EC2 instance. When your instance’s CPU consumption reaches 80%, you must lower the load on it. What method do you employ to finish the task?
Setting up an autoscaling group to deploy new instances when an EC2 instance’s CPU consumption exceeds 80% and distributing traffic among instances via the deployment of an application load balancer and the designation of EC2 instances as target instances can do this.
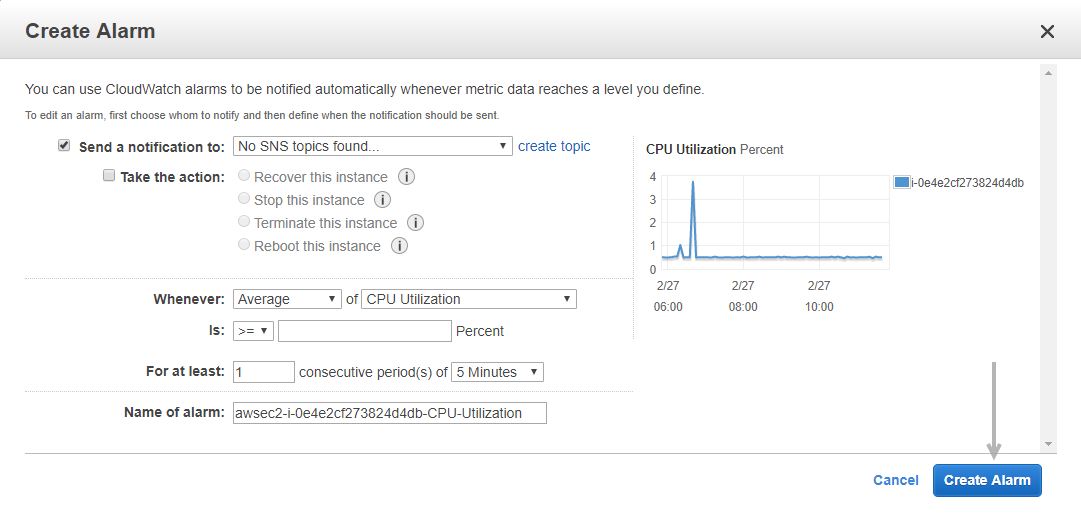
39. How does one set up CloudWatch to recover an EC2 instance?
Here’s how you can set them up:
- Using Amazon CloudWatch, create an alarm.
- Navigate to the Define Alarm -> Actions tab of the Alarm.
- Choose the Option to Recover This Instance
 40. How do you recover/log in to an EC2 instance for which you have lost the key?
40. How do you recover/log in to an EC2 instance for which you have lost the key?
If you have lost your key, follow the procedures below to recover an EC2 instance:
Step 1. Verify that the EC2Config service is operating.
Step 2. Detach the instance’s root volume.
Step 3. Connect the volume to a temporary instance
Step 4. Change the configuration file
Step 5. Restart the original instance.
Section 3: AWS interview questions for Amazon Storage
41. What exactly is Amazon S3?
Explanation S3 stands for Simple Storage Service, and Amazon S3 is the most extensively used storehouse platform. S3 is an object storehouse service that can store and recoup any volume of data from any position. Despite its rigidity, it’s basically measureless as well as cost-effective because it’s on- a demand storehouse. Away from these advantages, it provides new situations of continuity and vacuity. Amazon S3 aids in data operation for cost reduction, access control, and compliance.
42. What Storage Classes are available in Amazon S3?
Explanation: The following Storage Classes are accessible using Amazon S3:
- Storage class Amazon S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval
- Amazon S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval Storage Class (Formerly S3 Glacier)
- Glacier Deep Archive on Amazon S3 (S3 Glacier Deep Archive)
- Storage class S3 Outposts
- Amazon S3 Standard-Occasional Access (S3 Standard-IA)
- Amazon S3 One Zone-Only Occasional Access (S3 One Zone-IA)
- Amazon S3 Basic (S3 Standard)
- Amazon S3 Storage with Reduced Redundancy
- Intelligent-Tiering on Amazon S3 (S3 Intelligent-Tiering)
43. How do you auto-delete old snapshots?
Explanation: Here’s how to delete outdated photos automatically:
- Take snapshots of the EBS volumes on Amazon S3 in accordance with process and best practices.
- To manage all of the snapshots automatically, use AWS Ops Automator.
- You may use this to generate, copy, and remove Amazon EBS snapshots.
44. Another aws interview questions and answers for experienced scenario based. You need to configure an Amazon S3 bucket to serve static assets for your public-facing web application. Which method will ensure that all objects uploaded to the bucket are set to public read?
- Set permissions on the object to public read during upload.
- Configure the bucket policy to set all objects to public read.
- Use AWS Identity and Access Management roles to set the bucket to public read.
- Amazon S3 objects default to public read, so no action is needed.
Answer B.
Explanation: Rather than making changes to every object, its better to set the policy for the whole bucket. IAM is used to give more granular permissions, since this is a website, all objects would be public by default.
45. A customer wants to leverage Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) and Amazon Glacier as part of their backup and archive infrastructure. The customer plans to use third-party software to support this integration. Which approach will limit the access of the third party software to only the Amazon S3 bucket named “company-backup”?
- A custom bucket policy limited to the Amazon S3 API in three Amazon Glacier archive “company-backup”
- A custom bucket policy limited to the Amazon S3 API in “company-backup”
- A custom IAM user policy limited to the Amazon S3 API for the Amazon Glacier archive “company-backup”.
- A custom IAM user policy limited to the Amazon S3 API in “company-backup”.
Answer D.
Explanation: Taking queue from the previous questions, this use case involves more granular permissions, hence IAM would be used here.
45. Can S3 be used with EC2 instances, if yes, how?
Yes, it can be used for instances with root devices backed by local instance storage. By using Amazon S3, developers have access to the same highly scalable, reliable, fast, inexpensive data storage infrastructure that Amazon uses to run its own global network of web sites. In order to execute systems in the Amazon EC2 environment, developers use the tools provided to load their Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) into Amazon S3 and to move them between Amazon S3 and Amazon EC2.
Another use case could be for websites hosted on EC2 to load their static content from S3.
For a detailed discussion on S3, please refer our S3 AWS blog.
46. A customer implemented AWS Storage Gateway with a gateway-cached volume at their main office. An event takes the link between the main and branch office offline. Which methods will enable the branch office to access their data?
- Restore by implementing a lifecycle policy on the Amazon S3 bucket.
- Make an Amazon Glacier Restore API call to load the files into another Amazon S3 bucket within four to six hours.
- Launch a new AWS Storage Gateway instance AMI in Amazon EC2, and restore from a gateway snapshot.
- Create an Amazon EBS volume from a gateway snapshot, and mount it to an Amazon EC2 instance.
Answer C.
Explanation: The fastest way to do it would be launching a new storage gateway instance. Why? Since time is the key factor which drives every business, troubleshooting this problem will take more time. Rather than we can just restore the previous working state of the storage gateway on a new instance.
47. When you need to move data over long distances using the internet, for instance across countries or continents to your Amazon S3 bucket, which method or service will you use?
- Amazon Glacier
- Amazon CloudFront
- Amazon Transfer Acceleration
- Amazon Snowball
Answer C.
Explanation: You would not use Snowball, because for now, the snowball service does not support cross region data transfer, and since, we are transferring across countries, Snowball cannot be used. Transfer Acceleration shall be the right choice here as it throttles your data transfer with the use of optimized network paths and Amazon’s content delivery network upto 300% compared to normal data transfer speed.
48. How can you speed up data transfer in Snowball?
The data transfer can be increased in the following way:
- By performing multiple copy operations at one time i.e. if the workstation is powerful enough, you can initiate multiple cp commands each from different terminals, on the same Snowball device.
- Copying from multiple workstations to the same snowball.
- Transferring large files or by creating a batch of small file, this will reduce the encryption overhead.
- Eliminating unnecessary hops i.e. make a setup where the source machine(s) and the snowball are the only machines active on the switch being used, this can hugely improve performance.
49. What’s the distinction between EBS and Instance Store?
EBS is a type of persistent storage that allows data to be recovered at a later time. When you save data to the EBS, it remains long after the EC2 instance has been terminated. Instance Store, on the other hand, is temporary storage that is physically tied to a host system. You cannot remove one instance and attach it to another using an Instance Store. Data in an Instance Store, unlike EBS, is lost if any instance is stopped or terminated.
50. How can you use EBS to automate EC2 backup?
To automate EC2 backups using EBS, perform the following steps:
Step 1. Get a list of instances and connect to AWS through API to get a list of Amazon EBS volumes that are associated to the instance locally.
Step 2. List each volume’s snapshots and give a retention time to each snapshot. Create a snapshot of each volume afterwards.
Step 3. Remove any snapshots that are older than the retention term.


No comments:
Post a Comment