- An object storage service that stores data within buckets.
- Below is a sample Cloud Storage integration:
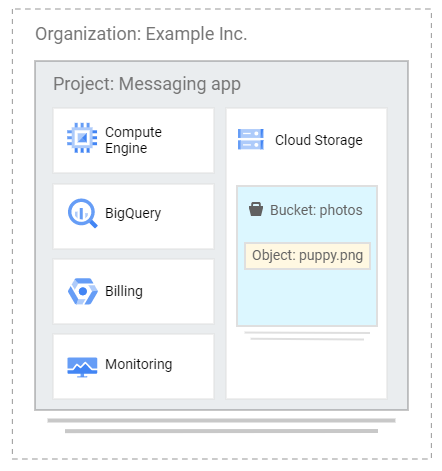
Buckets
- The data you upload on Cloud Storage are called objects.
- An object is an immutable piece of data consisting of a file in any format.
- You store objects inside containers called buckets.
- All buckets belong to a project.
- Each project can have multiple buckets.
- You can also configure a Cloud Storage bucket to host a static website for a domain you own.
Bucket Configurations
- Life Cycle Management
- You can define conditions that trigger data deletion, or transition to a cheaper storage class with object life cycle management.
- Versioning
- Continue to store old copies of objects you store when they are deleted or overwritten.
- Retention Policies
- Define minimum retention periods that objects must be stored.
- Object holds
- Place a hold on an object to prevent deletion.
- Encryption keys
- Customer-managed
- Customer-supplied
- Access Permissions
- Access Control List
- Uniform bucket level access
- Object and Bucket Level Permissions
Storage Classes
- Standard Storage
- Good for hot data that is accessed frequently.
- Nearline Storage
- Good for use cases that need to store objects for at least 30 days.
- Ideal for data that you plan to access once per month or less.
- Coldline Storage
- Is a low-cost storage option for storing infrequently accessed data within 90 days.
- Archive Storage
- Is the coldest storage among the storage classes.
- Designed for storing archive data and disaster recovery data that is expected to be accessed once per 365 days or less.
gsutil tool
- A Python application that enables you to manage your Cloud Storage from the command line.
- You can use gsutil to perform bucket and object management tasks like:
- creating and deleting buckets
- uploading, downloading, and deleting objects
- listing buckets and objects
- moving, copying, and renaming objects
- editing object and bucket ACL
- gsutil performs all operations using HTTPS and TLS
Uploading objects to GCS
You can send upload requests to Google Cloud Storage via the following methods:
- Simple Upload – utilize this if the file is small enough to upload again if the connection fails, and if there is no object metadata to send as part of the upload request.
- Multipart Upload – utilize this if the file is small enough to upload again if the connection fails, and you need to include object metadata as part of the upload request.
- Resumable Upload – utilize this for a more reliable transfer, which is especially important with large files.
- Parallel composite uploads – utilize if network and disk speed are not limiting factors. When doing parallel composite upload, a file is divided into up to 32 chunks and uploaded in parallel to temporary objects. The final object is recreated using the temporary objects, and the temporary objects are deleted.
- Alternatively, for uploading large volumes of data (from hundreds of terabytes up to 1 petabyte), you can utilize the Transfer Appliance. It is a hardware appliance you can use to securely migrate to Google Cloud Platform without disrupting business operations.
Pricing
- Pricing for Cloud Storage services is based on what you use, including:
- the amount of data you store,
- the duration for which you store it,
- the number of operations you perform on your data,
- the network resources used when moving or accessing your data.
- For “cold” storage classes meant to store long-term, infrequently accessed data, there are also charges for retrieving data and early deletion of data.
- You can require accessors of your data to include a project ID to bill for network charges, operation charges, and retrieval fees.

No comments:
Post a Comment