- AWS offering for a managed message broker service for Apache ActiveMQ. Message brokers allow different software systems–often using different programming languages, and on different platforms–to communicate and exchange information.
- Amazon MQ also supports RabbitMQ, a popular open-source message broker. Migrate your existing RabbitMQ message brokers to AWS without having to rewrite code.
- Amazon MQ uses industry-standard APIs and protocols for messaging, including Java Message Service (JMS), .NET Message Service (NMS), AMQP, STOMP, MQTT, OpenWire, and WebSocket.
- Amazon MQ manages administrative tasks such as hardware provisioning, broker setup, software upgrades, and failure detection and recovery.
- Amazon MQ stores your messages redundantly across multiple Availability Zones (AZs).
- Amazon MQ supports both single-instance brokers, suitable for evaluation and testing, and active/standby brokers for high availability in production. In the event of a failure of the broker, or even a full AZ outage, Amazon MQ automatically fails over to the standby broker.
- ActiveMQ messaging features
- ActiveMQ provides all the standard JMS features including:
- point-to-point (message queues),
- publish-subscribe (topics),
- request/reply,
- persistent and non-persistent modes,
- JMS transactions,
- and distributed (XA) transactions.
- ActiveMQ also supports more complex patterns such as:
- composite destinations (producers can send the same message to multiple destinations)
- virtual destinations (publishers broadcast messages via a topic to a pool of receivers subscribing through queues)
- ActiveMQ preserves the order of messages sent by a single producer to all consumers on a topic.
- ActiveMQ supports message groups, which enable multiple consumers on a queue to process messages within a group in first-in, first-out (FIFO) order.
- ActiveMQ also supports message redelivery and dead letter queues when a message cannot be delivered to its destination.
- ActiveMQ provides all the standard JMS features including:
- A message broker environment running on Amazon MQ. It is the basic building block of Amazon MQ.
- Brokers created without public accessibility can’t be accessed from outside of your VPC.
- Broker Types
- A Single-instance broker is comprised of one broker in one Availability Zone. The broker communicates with your application and with an AWS storage location.

- A Single-instance broker is comprised of one broker in one Availability Zone. The broker communicates with your application and with an AWS storage location.
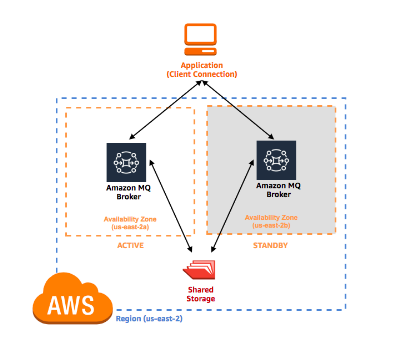
- An Active/standby broker for high availability is comprised of two brokers in two different Availability Zones, configured in a redundant pair. These brokers communicate synchronously with your application, and with a shared storage location.
- Broker instance types
- Mq.t2.micro
- mq.t2.micro instances are designed for initial product evaluation
- Mq.m4.large
- Mq.m5.large
- mq.m5.large instance for default production usage
- Mq.m5.xlarge
- Mq.m5.2xlarge
- Mq.m5.4xlarge
- Mq.t2.micro
- A network of brokers is comprised of multiple simultaneously active single-instance brokers or active/standby brokers. You can configure networks of brokers in a variety of topologies (for example, concentrator, hub-and-spokes, tree, or mesh).
- Broker instance types
- A configuration contains all of the settings for your ActiveMQ broker, in XML format.
- Making changes to a configuration does NOT apply the changes to the broker immediately. To apply your changes, you must wait for the next maintenance window or reboot the broker.
- Amazon MQ provides encryption of your messages at rest and in transit.
- Connections to the broker use SSL, and access can be restricted to a private endpoint within your Amazon VPC.
- Authentication from applications to the ActiveMQ broker itself is provided using username and password-based authentication.
- Amazon MQ supports LDAP authentication and authorization with directory services like Microsoft Active Directory.
- Amazon MQ is HIPAA eligible and meets standards for PCI, SOC, and ISO compliance.
- You can configure Amazon MQ to publish general and audit logs to Amazon CloudWatch Logs.
- You pay for the time your message broker instance runs (price varies depending on the size of the instance used), the storage you use monthly, and standard data transfer fees.
IBM MQ
- IBM MQ is messaging middleware that simplifies and accelerates the integration of diverse applications and business data across multiple platforms.
- It uses message queues to facilitate the exchange of information.
- Features
- It offers a single messaging solution for cloud, mobile, IoT, and on-premises environments.
- The IBM MQ service on AWS supports client messaging applications from
- within your virtual private cloud (VPC),
- from trusted addresses on the internet,
- and via a VPN from your on-premises environment.
- Secure message delivery with end-to-end encryption.
- Dynamic scaling via auto scaling groups since IBM MQ runs on an EC2 instance running on a pre-built AMI.
- The IBM MQ server is typically placed in a private subnet, spanning across two availability zones for high availability. The only ways to access it are through two ports exposed by a public facing elastic load balancer (ELB) or, if you need to SSH to the host, via a Bastion server from the public subnet.
- All the queue manager data is stored on Amazon EFS.

No comments:
Post a Comment