- Fully managed document database service designed to be fast, scalable, and highly available.
- Data is stored in JSON-like documents.
- Compatible with MongoDb.
- Flexible schema and indexing.
- Commonly used for content management, user profiles, and real-time big data.
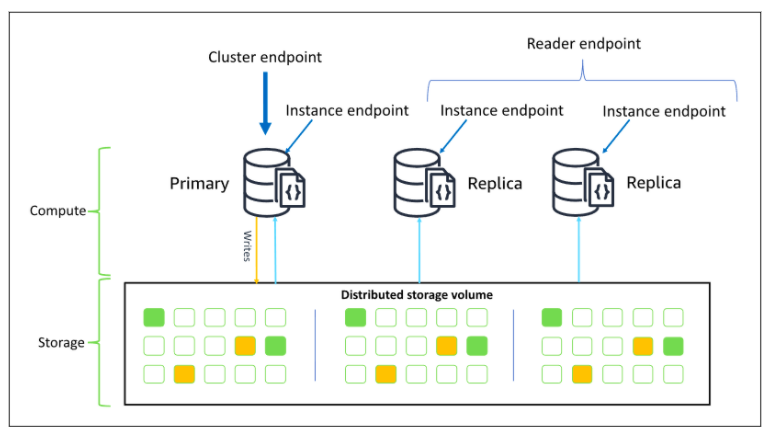
- An Amazon DocumentDB cluster decouples storage and compute.
- A cluster consists of Cluster volume and Instances
- Cluster volume refers to the storage layer that spans multiple Availability Zones. Each Availability Zone has a copy of the cluster data.
- Instances refers to the compute layer. It provides the processing power needed for the database to write data to, and read data from, the cluster volume.
- Amazon DocumentDB Endpoints
- Cluster endpoint
- Connects to cluster’s current primary instance.
- Can be used for both read and write operations.
- Cluster endpoint
- Reader endpoint
- Connects to one of the available replicas of the cluster.
- Use for read operations only.
- If the cluster has more than one replica, the reader endpoint will direct each request to DocumentDB replicas.
- Reader endpoint
- Instance endpoint
- Connects to a specific instance in the cluster.
- Use for specialized workloads that will only affect specific replica instances.
- Instance endpoint
- Provides millions of requests per second with millisecond latency and has twice the throughput of MongoDb.
- The minimum storage is 10GB. The Amazon DocumentDB storage will automatically scale up to 64 TB in 10 GB increments without affecting performance.
- The Amazon DocumentDB cluster can be scaled by modifying the instance class for each instance in the cluster.
- You can create up to 15 Amazon DocumentDB replicas in the cluster.
- The replication lag is usually less than 100 milliseconds after the primary instance has written an update.
- The cluster volume provides durability by maintaining six copies of all data across three Availability Zones.
- Amazon DocumentDB uses asynchronous replication to update the changes made to the primary instance to all of DocumentDB’s read replicas.
- In most cases, the DocumentDB’s restart time is less than a minute after a database crash.
- DocumentDB replicas can act as a failover target with no data loss.
- Supports automatic failover.
- Supports promotion priority within a cluster. Amazon DocumentDB will promote the replica with the highest priority tier to primary when the primary instance fails.
- To increase the cluster’s availability, create replicas in multiple Availability Zones. The Amazon DocumentDB will automatically include the replicas when selecting for a failover target in the event of an instance failure.
Cluster Volume | Local Storage | |
STORED DATA TYPE | Persistent data | Temporary data |
SCALABILITY | Automatically scales out when more space is required | Limited to the DB Instance class |
- Automated backups are always enabled.
- Supports Point-In-Time restoration, which can be up to 5 minutes in the past.
- You can restore from a cluster snapshot.
- Supports sharing of encrypted manual snapshots.
- Supports cross-region snapshot copying.
- You can authenticate a connection to a DocumentDB database through standard MongoDb tools with Salted Challenge Response Authentication Mechanism (SCRAM).
- You can authenticate and authorize the use of DocumentDB management APIs through the use of IAM users, roles, and policies.
- Data in transit is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS).
- Data at rest is encrypted using keys you manage through AWS KMS.
- Amazon DocumentDB supports role based access control ( RBAC ) with built-in roles to enforce the principle of least privileged access.
- You are billed based on four categories
- On-demand instances
- Pricing per second with a 10-minute minimum
- Database I/O
- Pricing per million I/Os
- Database Storage
- Pricing per GB/month
- Backup Storage
- Pricing per GB/month
- On-demand instances

No comments:
Post a Comment