Amazon Detective
- The service automatically collects log data from your AWS resources and uses machine learning, statistical analysis, and graph theory to build a linked set of data that enables you to easily conduct faster and more efficient security investigations.
- Can be integrated with AWS security services like Amazon GuardDuty, Amazon Macie, and AWS Security Hub as well as partner security products to identify potential security issues, or findings.
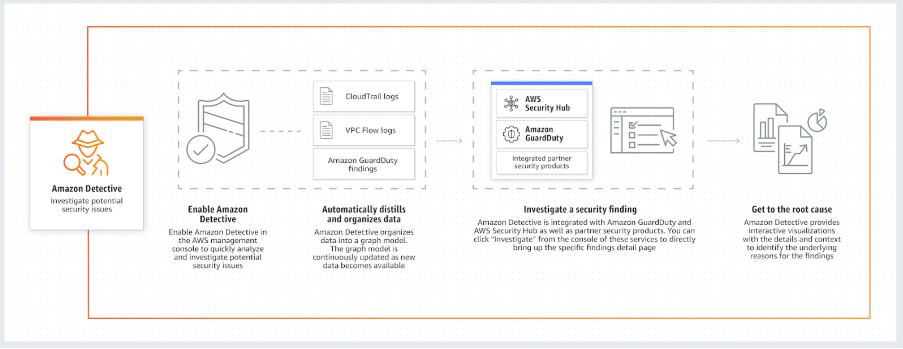
- Amazon Detective can analyze trillions of events from multiple data sources such as VPC Flow Logs, AWS CloudTrail, and Amazon GuardDuty, and automatically creates a unified, interactive view of your resources, users, and the interactions between them over time. This allows you to identify the underlying reasons for the findings, drill down into relevant historical activities, and quickly determine the root cause of a security concern.
- Amazon Detective’s prebuilt data aggregations, summaries, and context help you to quickly analyze and determine the nature and extent of possible security issues.
- How It Works
Concepts
- Investigation – The process of performing triage on suspicious or interesting activity, determining the scope, getting to its underlying source or cause, and then determining how to proceed.
- Behavior graph – A linked set of data generated from incoming source data that is associated with one or more AWS accounts. Each behavior graph uses the same structure of findings, entities, and relationships.
- Management account – The AWS account that owns a behavior graph and that uses the behavior graph for investigation. The management account invites member accounts to contribute their data to the behavior graph. Management accounts can also view data usage for the behavior graph, and remove member accounts from the behavior graph.
- Member account – An AWS account that a management account invited to contribute data to a behavior graph. Member accounts can respond to the behavior graph invitation and remove their account from the behavior graph. They have no other access to the behavior graph.
- Finding – A security issue detected by Amazon GuardDuty.
- Entity – An item extracted from the incoming data. Each entity has a type, which identifies the type of object it represents. Examples include IP addresses, Amazon EC2 instances, and AWS users.
- For each entity, the source data is also used to populate entity properties. Property values can be extracted directly from source records or aggregated across multiple records.
- Relationship – Activity that occurs between individual entities. Relationships are also extracted from the incoming source data.
- Similar to an entity, a relationship has a type, which identifies the types of entities involved and the direction of the connection. An example of a relationship type is an IP address connecting to an Amazon EC2 instance.
- Profile – For a finding or an entity, a single page that provides a collection of data visualizations plus supporting guidance.
- For findings, profiles help analysts to determine whether the finding is of genuine concern or a false positive.
- For entities, profiles provide supporting details for an investigation into a finding or for a general hunt for suspicious activity.
- Scope time – The time window that is used to scope the data displayed on finding and entity profiles. The default scope time for a finding profile reflects the first and last times when the suspicious activity was observed. The default scope time for an entity profile is the previous 24 hours.
- Amazon Detective needs to be enabled on a per region basis and enables you to quickly analyze activity across all your accounts within each region.
- Amazon Detective is a multi-account service that aggregates data from monitored member accounts under a single management account within the same region. You can configure multi-account monitoring deployments in the same way that you configure management and member accounts in Amazon GuardDuty and AWS Security Hub.
- If you cannot use the same management accounts across all of the services, then after you enable Detective, you can optionally create a cross-account role.
- If you are using Amazon GuardDuty, Amazon Detective will automatically ingest and process two weeks of historical log data upon activation.
- The management account for a behavior graph can disable Amazon Detective. When you disable Detective, the behavior graph and its associated Detective data are deleted. Deleted behavior graphs cannot be restored.
- Amazon Detective is able to analyze IAM role sessions by processing VPC flow records and CloudTrail management events from across a customer’s enabled accounts, collating data about activity performed under an IAM Role into role sessions. This lets you visualize and understand the actions that users and apps have performed using the assumed roles.
- Amazon Detective vs Amazon GuardDuty vs AWS Security Hub
- Amazon GuardDuty is a threat detection service that continuously monitors for malicious activity and unauthorized behavior to protect your AWS accounts and workloads.
- With Security Hub, you have a single place that aggregates, organizes, and prioritizes your security alerts, or findings, from multiple AWS services, such as Amazon GuardDuty, Amazon Inspector, and Amazon Macie, as well as from AWS Partner solutions.
- Amazon Detective simplifies the process of investigating security findings and identifying the root cause.
Limits
- You can maintain up to a year of aggregated findings for analysis
Common Use Cases
- Triage security findings
- Incident investigation
- Hunting for hidden security threats


No comments:
Post a Comment