NGINX (Pronounced as Engine-X) is an open source, lightweight, high-performance web server or proxy server. Nginx used as reverse proxy server for HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP, IMAP, POP3 protocols, on the other hand, it is also used for servers load balancing and HTTP Cache. Nginx accelerates content and application delivery, improves security, facilitates availability and scalability for the busiest websites on the Internet.

In easy term, Nginx is just a kind of software which is used in web servers to serve the concurrent requests. Previously we used to install Apache in web servers to handle these functions; but as the world is growing and demanding more things at one time the term concurrency comes into the picture and Nginx launched for the same thing.
Why Apache is Slow? How Nginx Came in Action?
Apache introduced in 1995; when there was no concept multitasking. Later when the need of multitasking required then MPM (Multi-Processing Module) was added in Apache to overcome this issue. But with this new feature memory consumption starts increasing with the coming years; where giant sites like Google and Facebook getting millions of hits every day. So the need of new platform or change in Apache was required.
This issue was named as C10K (Concurrent 10 Thousand) Problem.
Then Igor Sysoev started the development of Nginx in 2002 to overcome the same issue, and the first time Nginx was publicly released in 2004.
Now (in 2014) Nginx hosts nearly over 12% (22+ Million) of active sites across all domains.
How Does Nginx Work?
Nginx follows event-based process; it does not create individual thread of request for each process like Apache does, but smartly follows events of a process. Below is the demonstration of a Nginx server handling concurrent MP3 and MP4 file requests.
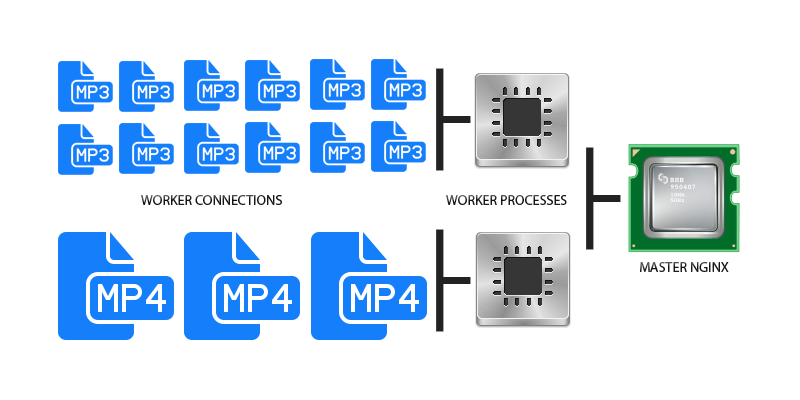
Nginx divided its job into Worker Connections and Worker Process. Here worker connections are managing the request made and the response obtained by users on the web server; in the same time these request are passed to its parent process which is Worker Process.
A single worker connection (See in Diagram: Worker Connections) can handle around 1024 connections at a time. It is the greatest ability of a worker connection.
There can “n” numbers of the worker process in Nginx based on the type of server you have and each worker process handle different jobs so that it can handle more numbers of concurrent requests.
Finally, the worker process transfers the requests to Nginx Master Process which quickly responds to the unique requests only.
Nginx is Asynchronous; that means each request in Nginx can be executed concurrently without blocking each other like a water pipe. So this way Nginx enhances the virtually shared resources without being dedicated and blocked to one connection.
That is why Nginx is able to do the same work with less amount of memory and utilizes that memory in an optimized way.

No comments:
Post a Comment