Create a Batch account in the Azure portal
This article shows how to use the Azure portal to create an Azure Batch account that has account properties to fit your compute scenario. You see how to view account properties like access keys and account URLs. You also learn how to configure and create user subscription mode Batch accounts.
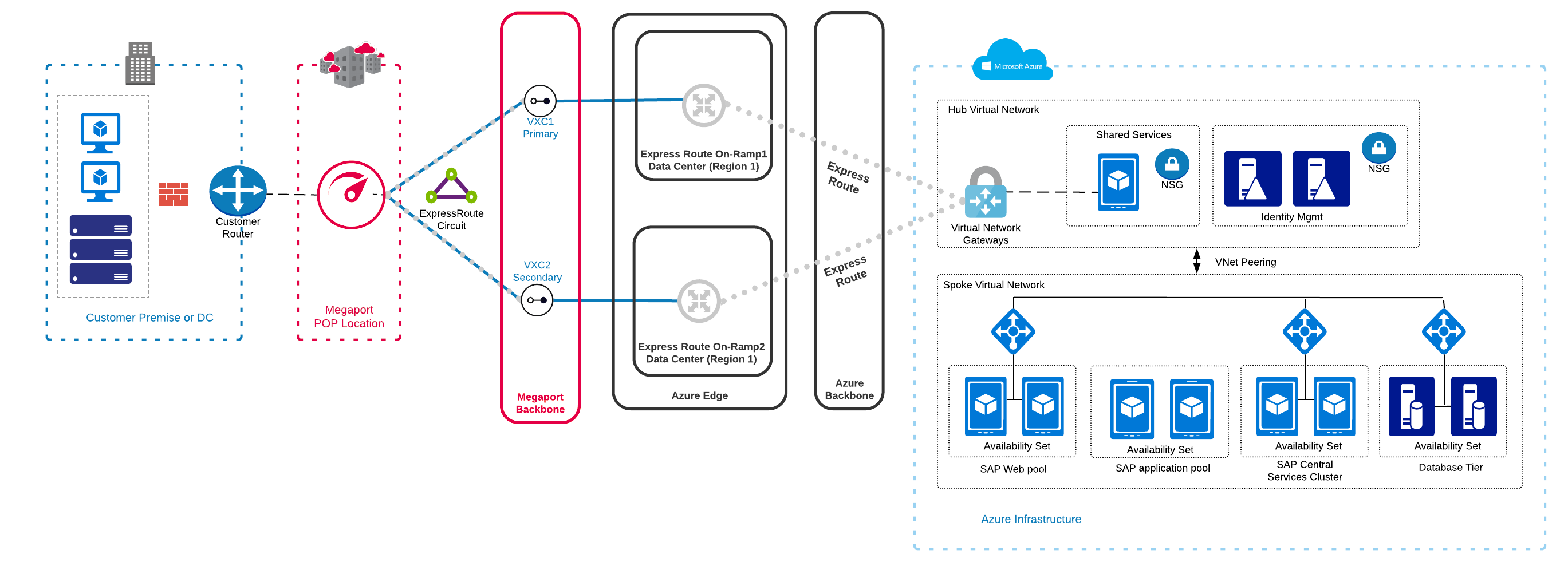
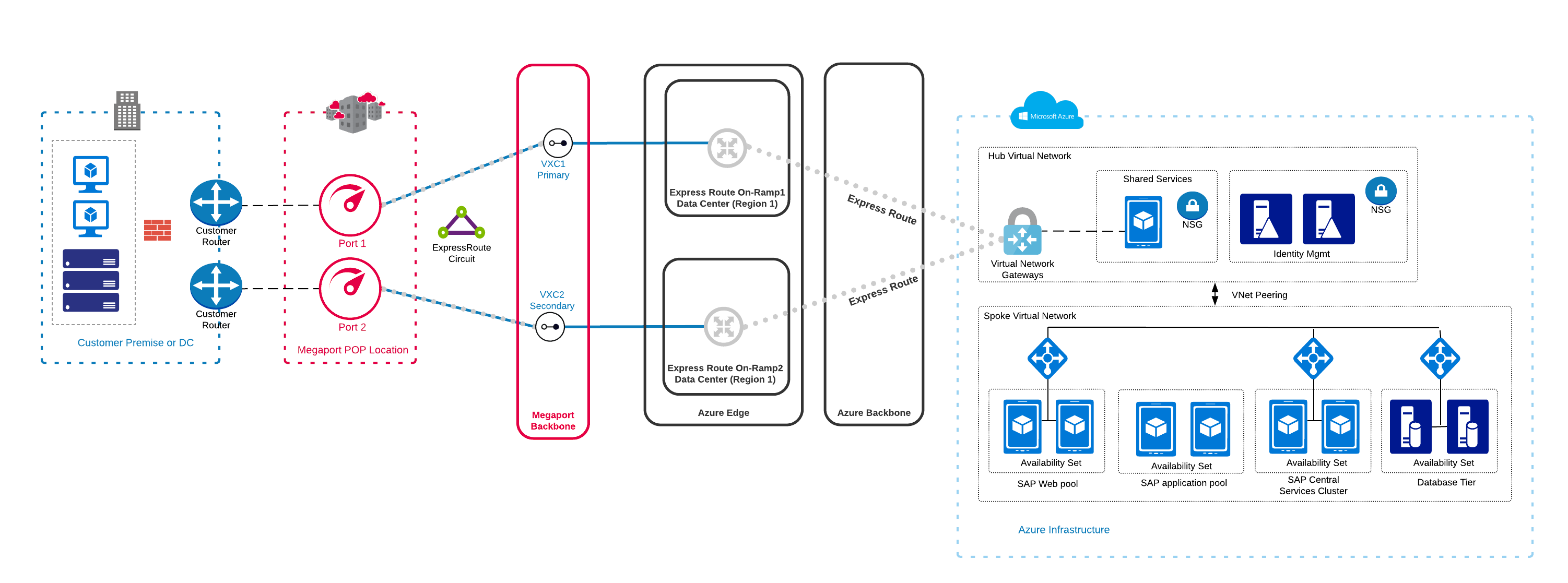
For background information about Batch accounts and scenarios, see Batch service workflow and resources.
Create a Batch account
When you create a Batch account, you can choose between user subscription and Batch service pool allocation modes. For most cases, you should use the default Batch service pool allocation mode. In Batch service mode, compute and virtual machine (VM)-related resources for pools are allocated on Batch service managed Azure subscriptions.
In user subscription pool allocation mode, compute and VM-related resources for pools are created directly in the Batch account subscription when a pool is created. In scenarios where you create a Batch pool in a virtual network that you specify, certain networking related resources are created in the subscription of the virtual network.
To create a Batch account in user subscription pool allocation mode, you must also register your subscription with Azure Batch, and associate the account with Azure Key Vault. For more information about requirements for user subscription pool allocation mode, see Configure user subscription mode.
To create a Batch account in the default Batch service mode:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
In the Azure Search box, enter and then select batch accounts.
On the Batch accounts page, select Create.
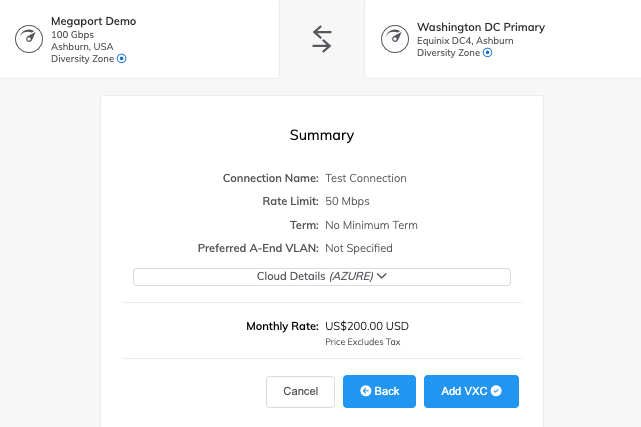
On the New Batch account page, enter or select the following details.
Subscription: Select the subscription to use if not already selected.
Resource group: Select the resource group for the Batch account, or create a new one.
Account name: Enter a name for the Batch account. The name must be unique within the Azure region, can contain only lowercase characters or numbers, and must be 3-24 characters long.
Note
The Batch account name is part of its ID and can't be changed after creation.
Location: Select the Azure region for the Batch account if not already selected.
Storage account: Optionally, select Select a storage account to associate an Azure Storage account with the Batch account.
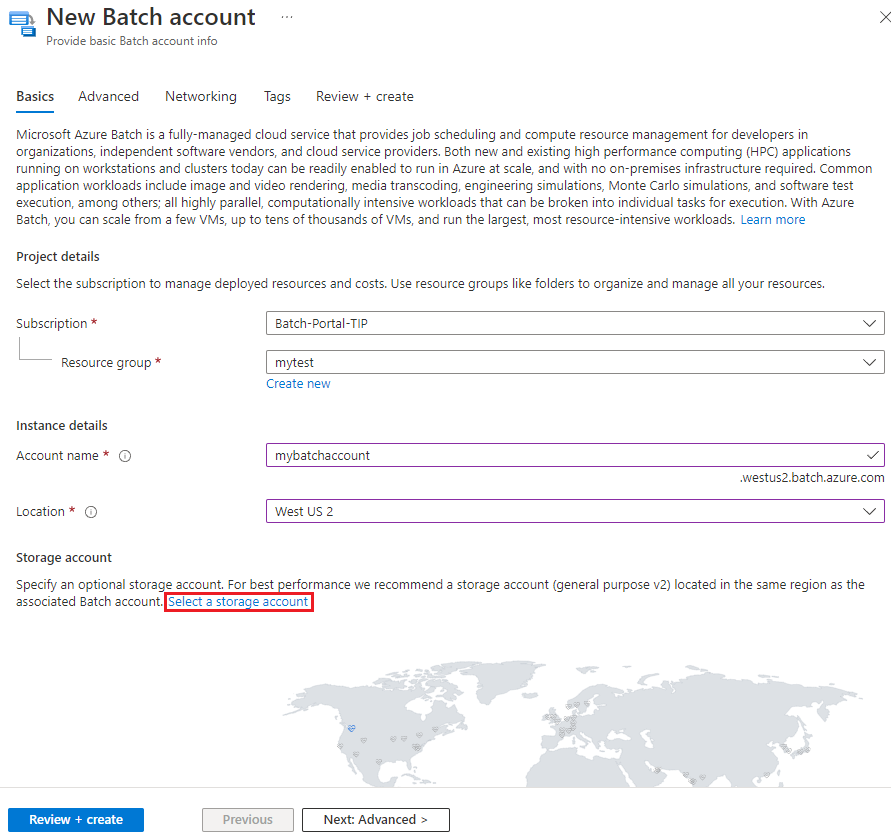
On the Choose storage account screen, select an existing storage account or select Create new to create a new one. A general-purpose v2 storage account is recommended for the best performance.
Optionally, select Next: Advanced or the Advanced tab to specify Identity type, Pool allocation mode, and Authentication mode. The default options work for most scenarios. To create the account in User subscription mode, see Configure user subscription mode.
Optionally, select Next: Networking or the Networking tab to configure public network access for your Batch account.
Select Review + create, and when validation passes, select Create to create the Batch account.
View Batch account properties
Once the account is created, select Go to resource to access its settings and properties. Or search for and select batch accounts in the portal Search box, and select your account from the list on the Batch accounts page.
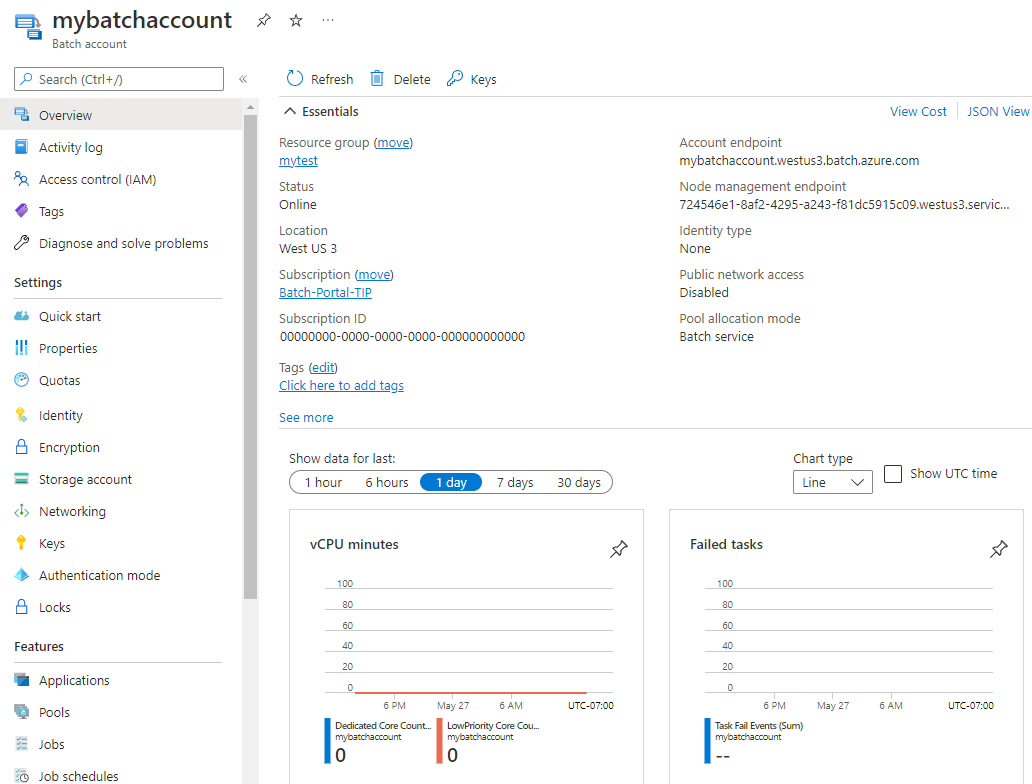
On your Batch account page, you can access all account settings and properties from the left navigation menu.
When you develop an application by using the Batch APIs, you use an account URL and key to access your Batch resources. To view the Batch account access information, select Keys.
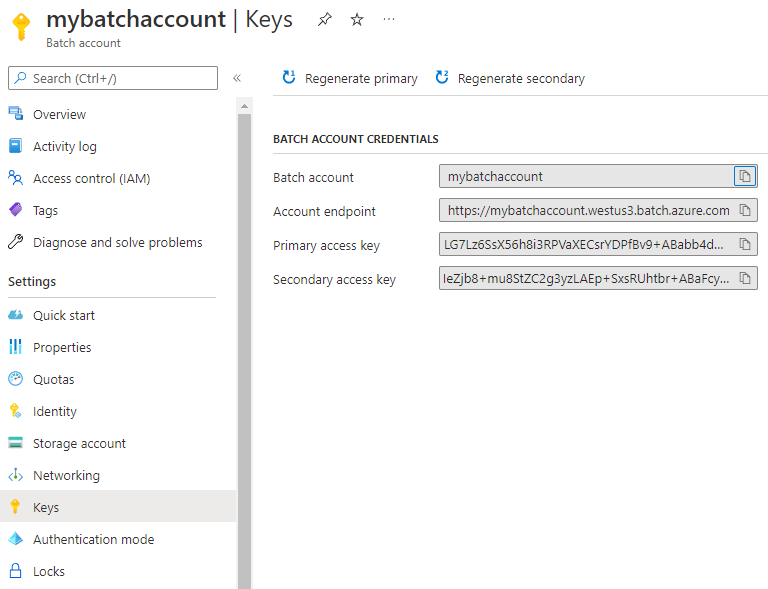
Batch also supports Microsoft Entra authentication. User subscription mode Batch accounts must be accessed by using Microsoft Entra ID. For more information, see Authenticate Azure Batch services with Microsoft Entra ID.
To view the name and keys of the storage account associated with your Batch account, select Storage account.
To view the resource quotas that apply to the Batch account, select Quotas.
Configure user subscription mode
You must take several steps before you can create a Batch account in user subscription mode.
Important
To create a Batch account in user subscription mode, you must have Contributor or Owner role in the subscription.
Accept legal terms
You must accept the legal terms for the image before you use a subscription with a Batch account in user subscription mode. If you haven't done this action, you might get the error Allocation failed due to marketplace purchase eligibility when you try to allocate Batch nodes.
To accept the legal terms, run the commands Get-AzMarketplaceTerms and Set-AzMarketplaceTerms in PowerShell. Set the following parameters based on your Batch pool's configuration:
Publisher: The image's publisherProduct: The image offerName: The offer SKU
For example:
Get-AzMarketplaceTerms -Publisher 'microsoft-azure-batch' -Product 'ubuntu-server-container' -Name '20-04-lts' | Set-AzMarketplaceTerms -Accept
Important
If you've enabled Private Azure Marketplace, you must follow the steps in Add new collection to add a new collection to allow the selected image.
Allow Batch to access the subscription
When you create the first user subscription mode Batch account in an Azure subscription, you must register your subscription with Batch. You need to do this registration only once per subscription.
Important
You need Owner permissions in the subscription to take this action.
In the Azure portal, search for and select subscriptions.
On the Subscriptions page, select the subscription you want to use for the Batch account.
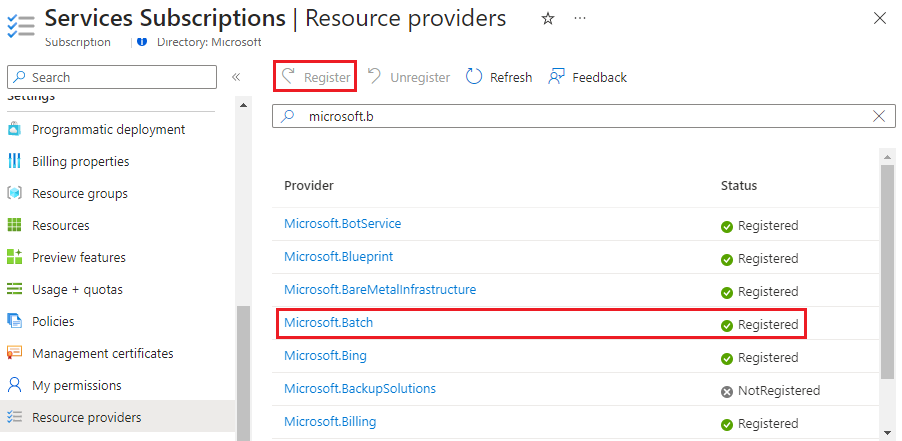
On the Subscription page, select Resource providers from the left navigation.
On the Resource providers page, search for Microsoft.Batch. If Microsoft.Batch resource provider appears as NotRegistered, select it and then select Register at the top of the screen.
Return to the Subscription page and select Access control (IAM) from the left navigation.
At the top of the Access control (IAM) page, select Add > Add role assignment.
On the Add role assignment screen, under Assignment type, select Privileged administrator role, and then select Next.
On the Role tab, select either the Contributor or Owner role for the Batch account, and then select Next.
On the Members tab, select Select members. On the Select members screen, search for and select Microsoft Azure Batch, and then select Select.
For detailed steps, see Assign Azure roles by using the Azure portal.
Create a key vault
User subscription mode requires Azure Key Vault. The key vault must be in the same subscription and region as the Batch account and use a Vault Access Policy.
To create a new key vault:
- Search for and select key vaults from the Azure Search box, and then select Create on the Key vaults page.
- On the Create a key vault page, enter a name for the key vault, and choose an existing resource group or create a new one in the same region as your Batch account.
- On the Access configuration tab, select Vault access policy under Permission model.
- Leave the remaining settings at default values, select Review + create, and then select Create.
Create a Batch account in user subscription mode
To create a Batch account in user subscription mode:
- Follow the preceding instructions to create a Batch account, but select User subscription for Pool allocation mode on the Advanced tab of the New Batch account page.
- You must then select Select a key vault to select an existing key vault or create a new one.
- After you select the key vault, select the checkbox next to I agree to grant Azure Batch access to this key vault.
- Select Review + create, and then select Create to create the Batch account.
Create a Batch account with designated authentication mode
To create a Batch account with authentication mode settings:
Follow the preceding instructions to create a Batch account, but select Batch Service for Authentication mode on the Advanced tab of the New Batch account page.
You must then select Authentication mode to define which authentication mode that a Batch account can use by authentication mode property key.
You can select either of the 3 "Microsoft Entra ID, Shared Key, Task Authentication Token authentication mode for the Batch account to support or leave the settings at default values.
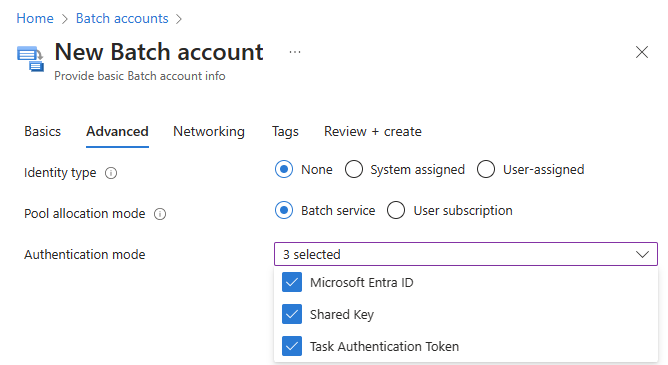
Leave the remaining settings at default values, select Review + create, and then select Create.
Tip
For enhanced security, it is advised to confine the authentication mode of the Batch account solely to Microsoft Entra ID. This measure mitigates the risk of shared key exposure and introduces additional RBAC controls. For more details, see Batch security best practices.
Warning
The Task Authentication Token will retire on September 30, 2024. Should you require this feature, it is recommended to use User assigned managed identity in the Batch pool as an alternative.
Grant access to the key vault manually
You can also grant access to the key vault manually.
Select Access policies from the left navigation of the key vault page.
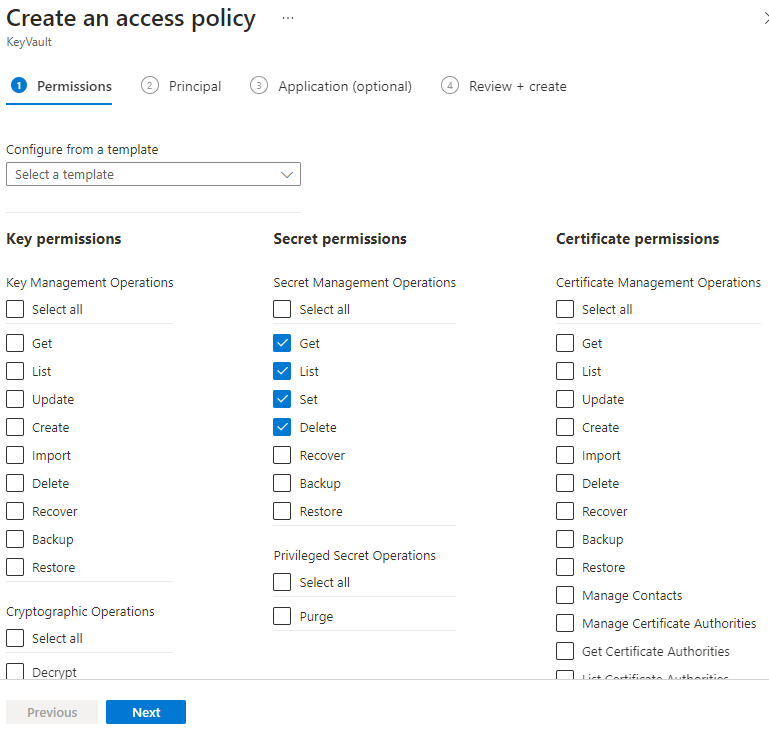
On the Access policies page, select Create.
On the Create an access policy screen, select a minimum of Get, List, Set, and Delete permissions under Secret permissions. For key vaults with soft-delete enabled, also select Recover.
Select Next.
On the Principal tab, search for and select Microsoft Azure Batch.
Select the Review + create tab, and then select Create.