A Comprehensive Introduction to Setting Up and Managing Your Web App in the Cloud
Azure App Services
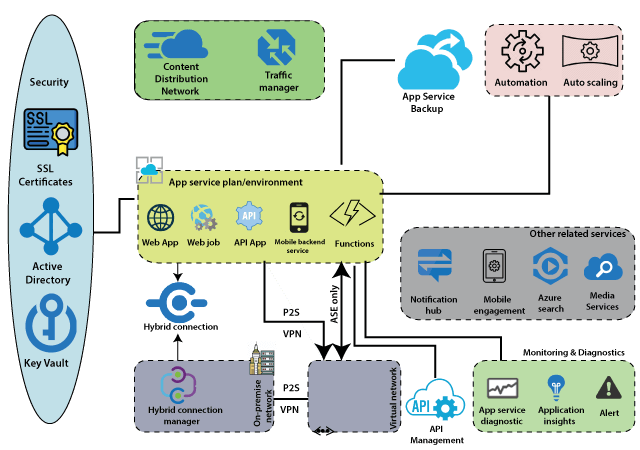
Azure App Services is a fully managed Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering from Microsoft that allows developers to host web-based services, including web apps, REST APIs, and mobile backends. This service is built on top of Azure and provides a wide range of features to help developers build and deploy their applications quickly and easily.
One of the key features of Azure App Services is its support for many different languages, including .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, and PowerShell. This makes it easy for developers to use their preferred language to build and deploy their applications. Additionally, the service also includes DevOps optimization tools, which allow developers to easily manage and scale their applications across multiple platforms.
Another key feature of Azure App Services is its support for containerization. This allows developers to easily deploy their applications using Docker containers, and also supports multi-container applications. This makes it easy to build and deploy applications in a consistent and repeatable way, regardless of the underlying infrastructure.
Azure App Services also includes built-in support for global scale and high availability. This allows applications to be easily scaled up or down as needed, either manually or automatically. Additionally, the service also supports serverless code, which allows developers to easily build and deploy functions as needed, without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure.
In addition to these features, Azure App Services also includes a wide range of application templates that can be used to quickly deploy common application scenarios. These templates can be found in the Azure Marketplace and can be used to quickly deploy applications, such as web apps, REST APIs, and more.
Security is another important aspect of Azure App Services. The service includes support for many compliance standards, and can be integrated with Azure Active Directory for additional security. Additionally, IP restrictions can be used to control access to the application.
Azure App Services also includes built-in support for connecting to SaaS platforms and on-premises data, as well as more than 50 connectors. This allows developers to easily connect their applications to other services, such as Azure Hybrid Connections and virtual networks, providing a seamless experience for their users. Payment for Azure App Services is determined by the subscription plan.
App Service Application Types
- Web App is the most common type of App Service application and it’s perfect for hosting web sites and web applications in an enterprise-grade environment. The service supports multiple languages such as .NET, Java, Node.js, Python, and PowerShell, making it easy for developers to use their preferred language for building and deploying applications. Web App also includes DevOps optimization tools, which allow developers to manage and scale their applications across different platforms.
- API App is designed for hosting RESTful APIs and it provides a simple and secure way to access and control access to the APIs. The service comes with automatic SDK generation and seamless integration with Logic Apps, allowing developers to build, test, and deploy APIs in a consistent and repeatable way. It also supports multiple languages such as .NET, Java, Node.js, and Python.
- Logic App is a powerful tool for automating business processes and system integration. It enables developers to share data across cloud services and automate workflows using a simple visual designer. This eliminates the need for custom code and makes it easy for developers to build and deploy complex business logic. Logic App also comes with built-in support for various connectors, including SharePoint, SQL Server, and Salesforce, making it easy to integrate with other systems.
- Mobile App is a powerful tool for hosting mobile app backends. It allows mobile apps to work with various Azure services, including Azure Storage, Azure Notification Hubs, and Azure Active Directory. This makes it easy for developers to build and deploy mobile apps that can take advantage of the full power of Azure. Mobile App also supports multiple languages such as .NET, Java, Node.js, and Python, making it easy for developers to build and deploy mobile apps in a wide range of languages.
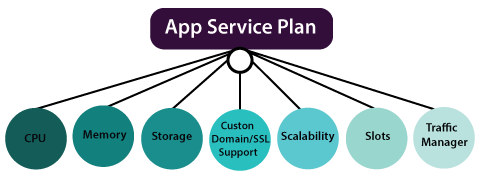
App Service Plans
There are two types of App Service Plans to choose from: Linux-based and Windows-based. The main difference between the two is the operating system that your app will run on. If you’re more familiar with Linux, you might want to choose the Linux-based plan, and if you’re more comfortable with Windows, you might want to choose the Windows-based plan.
Once you’ve chosen an App Service Plan, you can then create an app service. An app service is the actual place where your app will run, and it’s created within the context of an App Service Plan. This means that the resources and features of your app service are determined by the App Service Plan you’ve chosen.
One of the key features of Azure App Services is the ability to have multiple app services within a single App Service Plan. Each app service can have different deployment slots, which are essentially different versions of your app that you can test and deploy. This allows you to easily test and deploy new features and updates to your app without disrupting the main version of your app.
When you create an App Service Plan, you specify the region where you want the compute resources to be created, so all the apps you put in that App Service Plan are hosted on those resources. Additionally, you also choose the Operating System and the number and size of VM instances that you need. The pricing tier and region are also chosen when creating an App Service Plan. With deployment slots, it is easy to test new updates and features in a staging environment before making them live in production.
Deployment slot
A deployment slot is a feature of Azure App Service that allows you to run different versions of your app, called slots, in different environments. Each slot is exposed through a publicly available endpoint and you can swap instances assigned to the slot on demand. This feature allows you to test new updates and features in a staging environment before making them live in production.
Scale Applications
Azure App Service provides several options to scale your applications as per your requirements. The two main options for scaling your apps are Scale Up and Scale Out.
- Scale Up is the process of increasing the amount of resources like RAM, CPU, or storage that your app service uses. This option is best for monolithic applications that have a high demand for resources. By scaling up, you are increasing the amount of resources available to your app, which can help it to handle more traffic or perform more complex tasks.
- Scale Out on the other hand, is the process of adding more instances of your app service to handle more traffic. This option is best for apps that can adopt to auto-scaling. By scaling out, you are increasing the number of instances of your app service, which can help it to handle more traffic by distributing the load among multiple instances.
Pricing Tiers
Azure App Service offers different pricing tiers for your app service plans to help you choose the right one based on your needs. The three main pricing tiers are:
- Shared Compute: This is the most basic and cost-effective pricing tier. It is best for small or low-traffic apps that don’t require a lot of resources. In this tier, your app shares the resources with other apps on the same machine.
- Dedicated Compute: This pricing tier provides your app with dedicated resources and is best for medium or high-traffic apps that require more resources. In this tier, your app has its own machine and resources that are not shared with other apps.
- Isolated: This pricing tier provides the highest level of isolation and resources for your app. It’s best for large, high-traffic apps or apps that require a high level of security. In this tier, your app is hosted in a dedicated virtual network, and you have control over the underlying infrastructure.
Hands-On Demonstration
In this demonstration, you will learn how to host a web application using Azure App Service and Visual Studio Code. To start, you will need to create an App Service Plan in Azure which will provide the compute resources for your web application. Once the App Service Plan is created, you can use Visual Studio Code to create a new web application project. Then, you can use the Azure App Service extension in Visual Studio Code to deploy the application to the App Service Plan.
After deploying the application, you can then test it by visiting the publicly available endpoint for your App Service Plan. By the end of this demonstration, you will have a basic understanding of how to use Azure App Service and Visual Studio Code to host a web application.
STEPS:
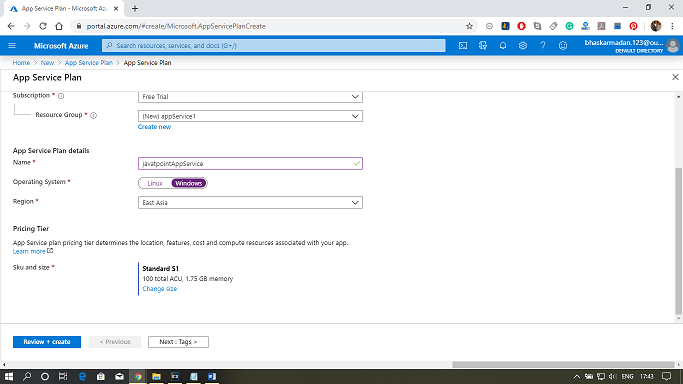
Step 1: Create an App Service Plan in Azure
- Log in to the Azure portal and navigate to the App Service Plans section
- Click on the “+ Create” button to create a new App Service Plan
- Provide a name and select the appropriate subscription, resource group, and operating system for your plan
- Choose a pricing tier that fits your needs, and select the desired region for your App Service Plan
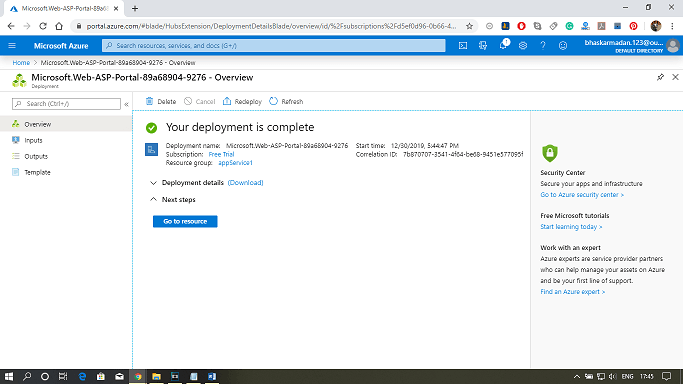
- Click on the “Review + create” button to review your App Service Plan settings and then click on “Create” button to create it.
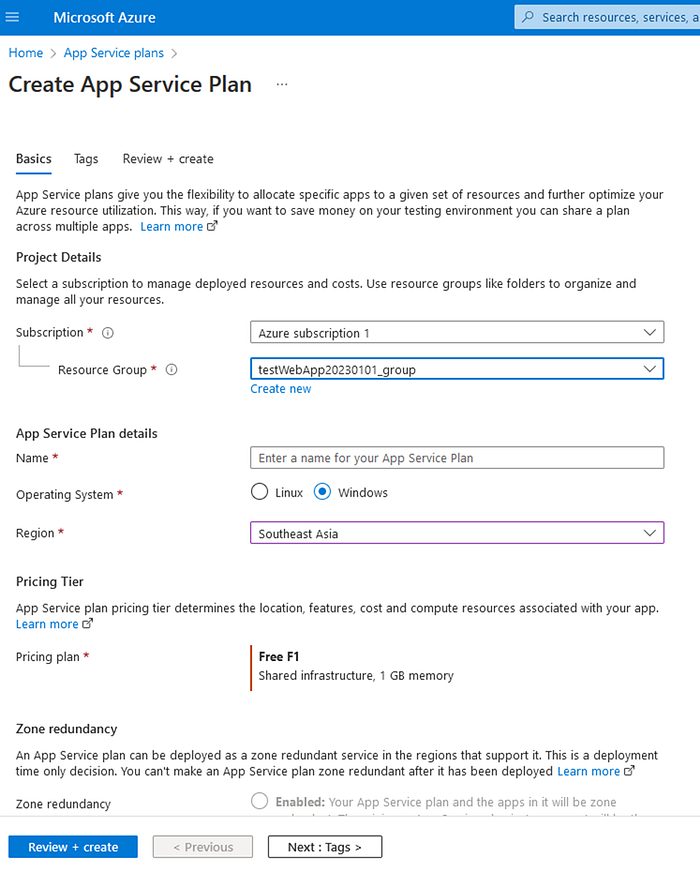
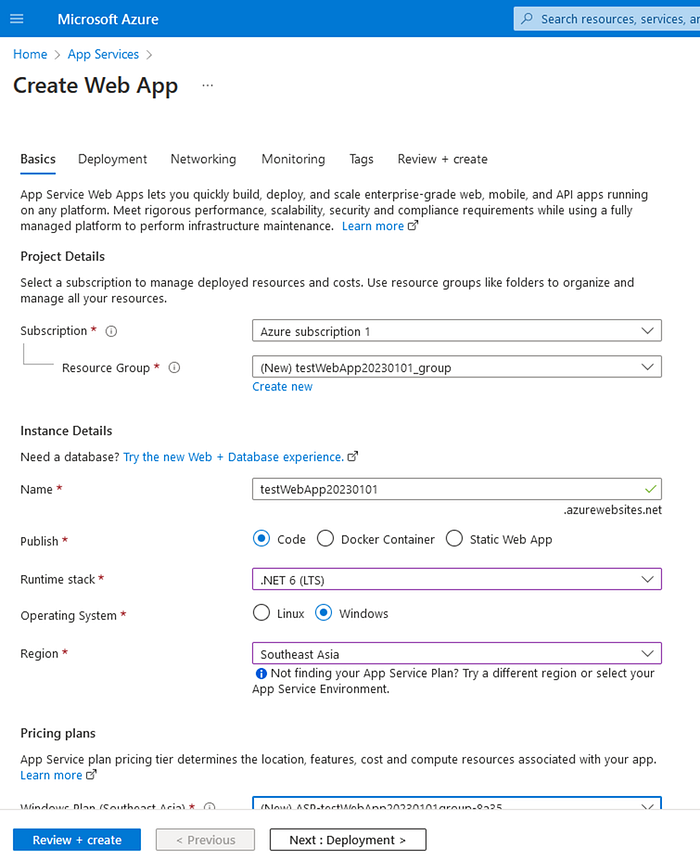
- Once the App Service Plan is created, navigate to the App Services section in the Azure portal.
- Click on the “Create” button to create a new App Service
- Provide a name for the App Service, select the subscription, resource group, and App Service Plan that you created in step 1. Click next with the default values.
- In the “Review + Create” tab, click on “Create” button to create it. Refer below screenshots.
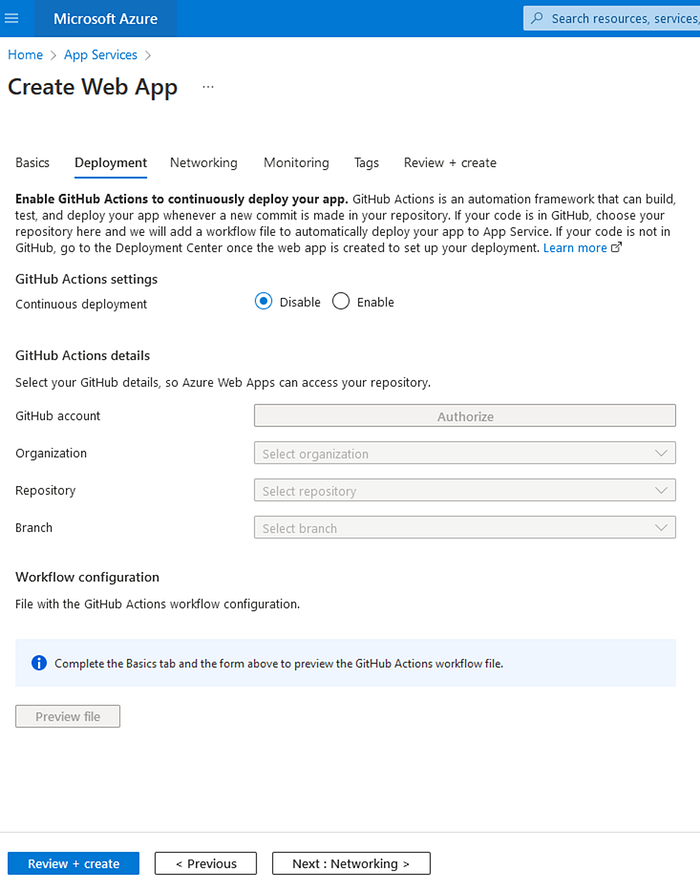
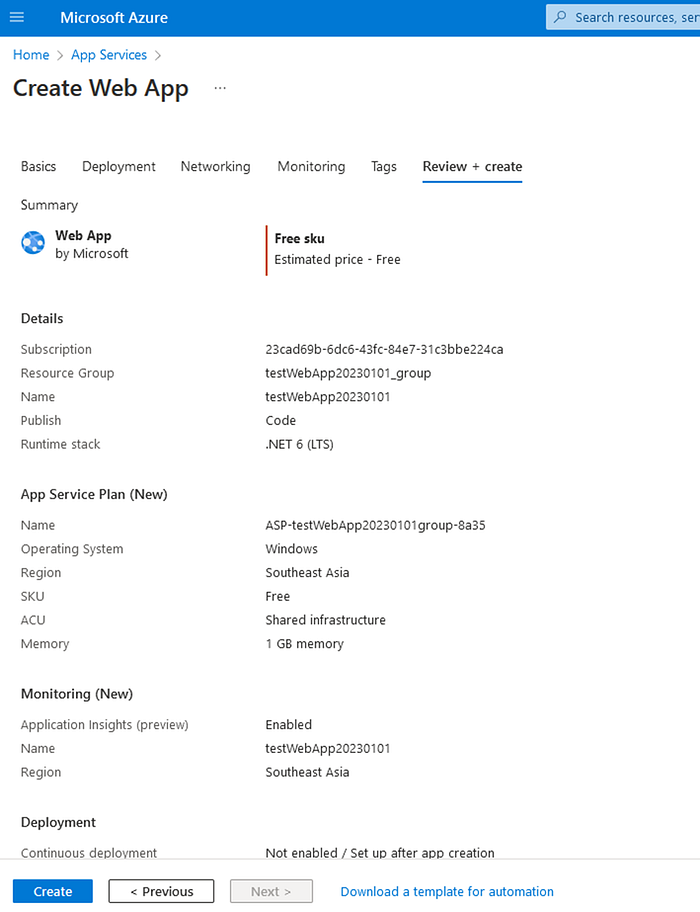
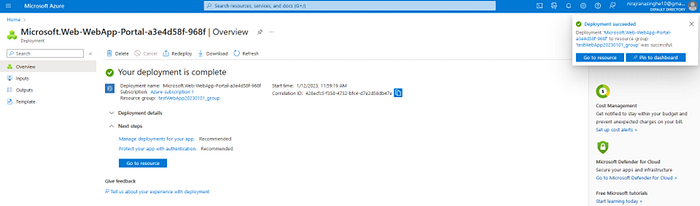
Step 2: Create a new web application project in Visual Studio Code
- Open Visual Studio Code and create a new project by selecting “File” -> “DOTNET_TEST”
- Open the terminal in Visual Studio Code by selecting “View” -> “Terminal”
- Create a new web application by running below commands:
dotnet new mvcdotnet run(Once you run above command you can check the created sample web app in local host too.)
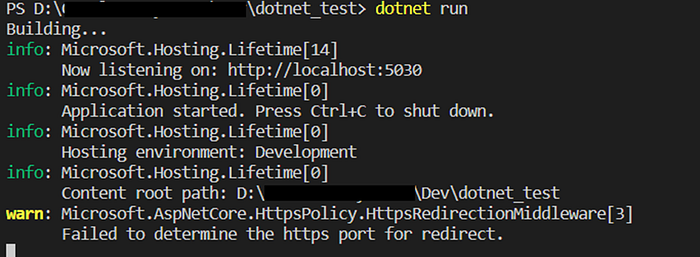
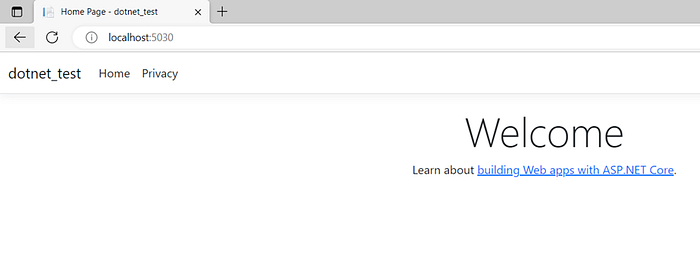
Step 3: Deploy the application to Azure App Service
- Install the Azure App Service extension and azure account in Visual Studio Code by searching for “Azure” in the Extensions marketplace
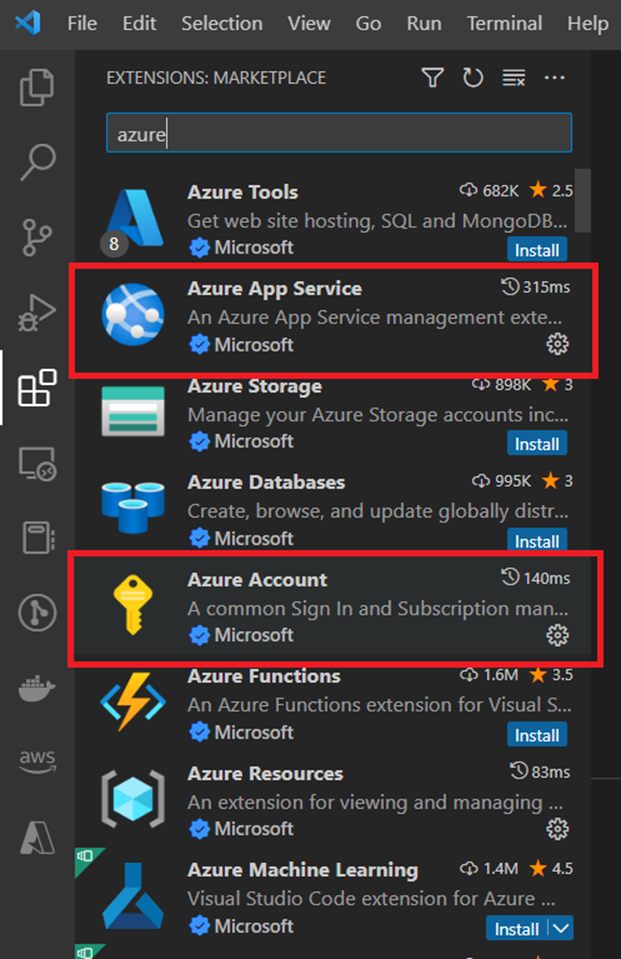
- Right-click on the project in the Explorer pane and select “Deploy to Web App”
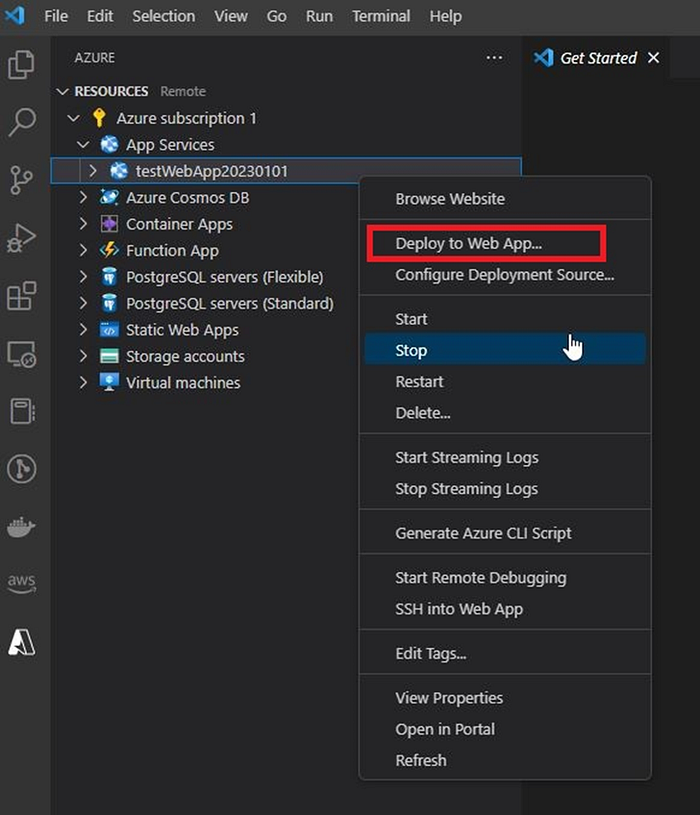
- In the next pop up window click on “Deploy” button to start the deployment process
Step 4: Test the application
- Once the deployment is complete, you will be provided with a publicly available endpoint for your App Service Plan
- Open your browser and navigate to the endpoint to test your application