What are containers and how are they different from virtual machines
In this video we will discuss, what are containers and how are they different from virtual machines.
In our previous video, we discussed what are virtual machines and how they allow us to run multiple applications on a single physical server. However, with each virtual machine that we create, there is a lot of overhead, both in terms of cost and maintainability. Let's understand this with an example.
Virtual Machines and Multiple applications
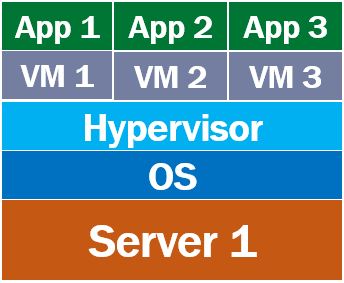
Let's say we have 4 applications - App 1, App 2, App 3, and App 4. We want to be able to run all these 4 apps on one physical server - Server 1. Obviously, we cannot run applications directly on the server hardware. We need an operating system like windows or linux. This is the Host OS i.e the operating system at the server level. On top this we install a piece of software called Hypervisor. It is the Hypervisor, that creates and manages virtual machines. We have 4 apps that we want to run in isolation on this physical server, so we create 4 virtual machines.
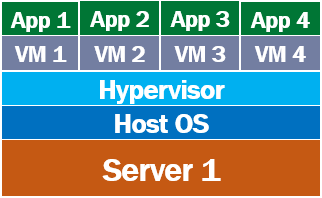
As we discussed in our previous video, a virtual machine virtualises the hardware of the physical server. This means each virtual machine that is created, gets a slice of the the server hardware. In our case we created 4 virtual machines, so each VM gets 25% of memory, disk space, processor and other server hardware resources.
Virtual Machine Disadvantages
Applications, i.e App 1 to App 4 cannot directly run on a virtual machine. Keep in mind, a virtual machine virtualises the server hardware. This means, in simple terms, a virtual machine is a slice of the underlying server hardware and an application cannot run directly on the hardware. So for a virtual machine to be able run a software application, it needs a full copy of its own operating system.
We have 4 virtual machines, so this means we need to install 4 operating systems, one on each virtual machine. Usually, windows or linux. This operating system that is installed on a virtual machine is usually called Guest Operating System. So, on top of this guest OS on the VM, we install our business application and any dependencies it might need.
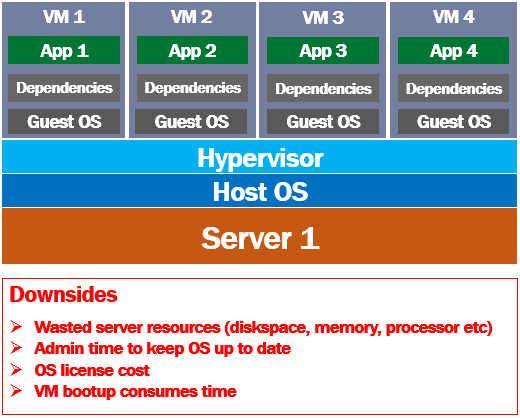
Now, just imagine the, amount of server resouces required to install and run 4 operating systems. So much of server resources like disk space, memory and processor time are wasted just to keep these VMs up and running. In addition to the wated server resources, each installation of the operating system also needs admin time. For example if there is an update or a security patch available for the OS, the admin needs to download and install it on all the VMs that has that operating system. In addition to this, we also need to pay for 4 operating system licenses.
Remember a virtual machine is like a computer with in a computer. It has it's own OS. So for a virtual machine to be up and running it's operating system must also be booted up. Booting up an entire operating system obviously consumes a lot of time.
In our example, if we want App 1 to be up and running, VM 1 operating system must be booted up, in addition to booting up the host operating system i.e the operating system at the physical server level.
What are containers
A virtual machine virtualises the server hardware where as containers virtualises the operating system, i.e it's an abstraction at the operating system level. Multiple containers can run on the same machine and share the host operating system kernel. Unlike a VM, a container does not required it's own operating system. Straight away you can see the amount of disk space, ram and processor time that is saved.
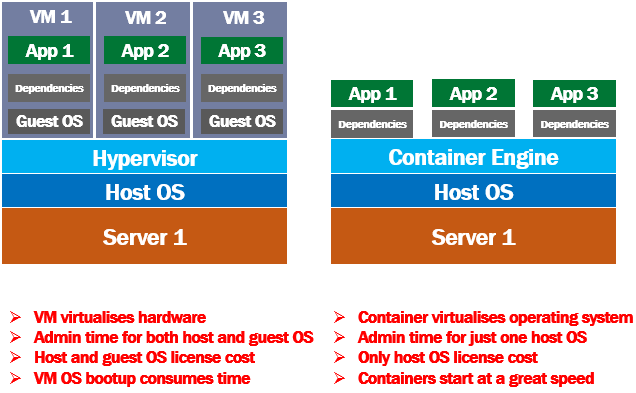
Each conatiner packages your application code and it's dependencies together. If you have 3 apps to run on a single physical server, you create 3 containers. Each application thinks, it is running on a dedicated OS and a dedicated server hardware. In reality all the container apps are sharing the same host operating system and hardware.
In case of VMs, admin time is required to install security patches and keep up to date host operating system and the guest operating systems on all the VMs. No matter how many containers we have on our server, there is just one host operating system that demands admin time.
From the cost standpoint, in case of VMs, we have to pay for host and the guest operating systems of all the VMS, where as in case of containers, we have to pay just for the 1 host operating system.
A container is very small compared to a VM. Since a container does not have it's own operating system to bootup, it can usually be brought online in a very less time compared to booting up and entire VM and it's operating system.


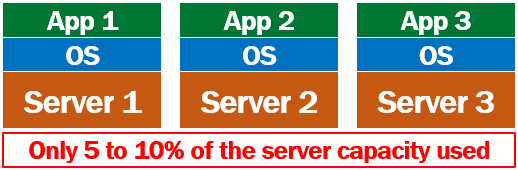

 At this point, you might be wondering, can't we install this new application on our existing physical server, because the first application is only using a fraction of the server capacity anyway. Well, in most cases, we can't. This may be because this new application has different dependencies than the first application. May be it needs a differnt version of the framework installed. May be it needs a different operating system altogether. May be both applications need access to the same resources or devices which obviously results in resource conflicts.
At this point, you might be wondering, can't we install this new application on our existing physical server, because the first application is only using a fraction of the server capacity anyway. Well, in most cases, we can't. This may be because this new application has different dependencies than the first application. May be it needs a differnt version of the framework installed. May be it needs a different operating system altogether. May be both applications need access to the same resources or devices which obviously results in resource conflicts.