In this video we will discuss azure deployment slots.
What is Azure App Service
We discussed App Service and the benefits it provides in Part 18 of azure tutorial. It is a Platform as a Service (PaaS) and we use it to host web applications, REST API's and backend services for mobile applications. It offers several benefits
- Scalability - both manual and auto-scaling
- Standards compliance like ISO, SOC, PCI etc
- Easy security implementation including support for external authentication providers like Google, Facebook, Twitter, or Microsoft.
- Support for Containerization and Docker
- DevOps optimization
- Deployment slots
What are azure deployment slots
Azure deployment slots are very useful. They allow you to run multiple versions of your application code on the same infrastructure. Let's understand the use of deployment slots with an example.
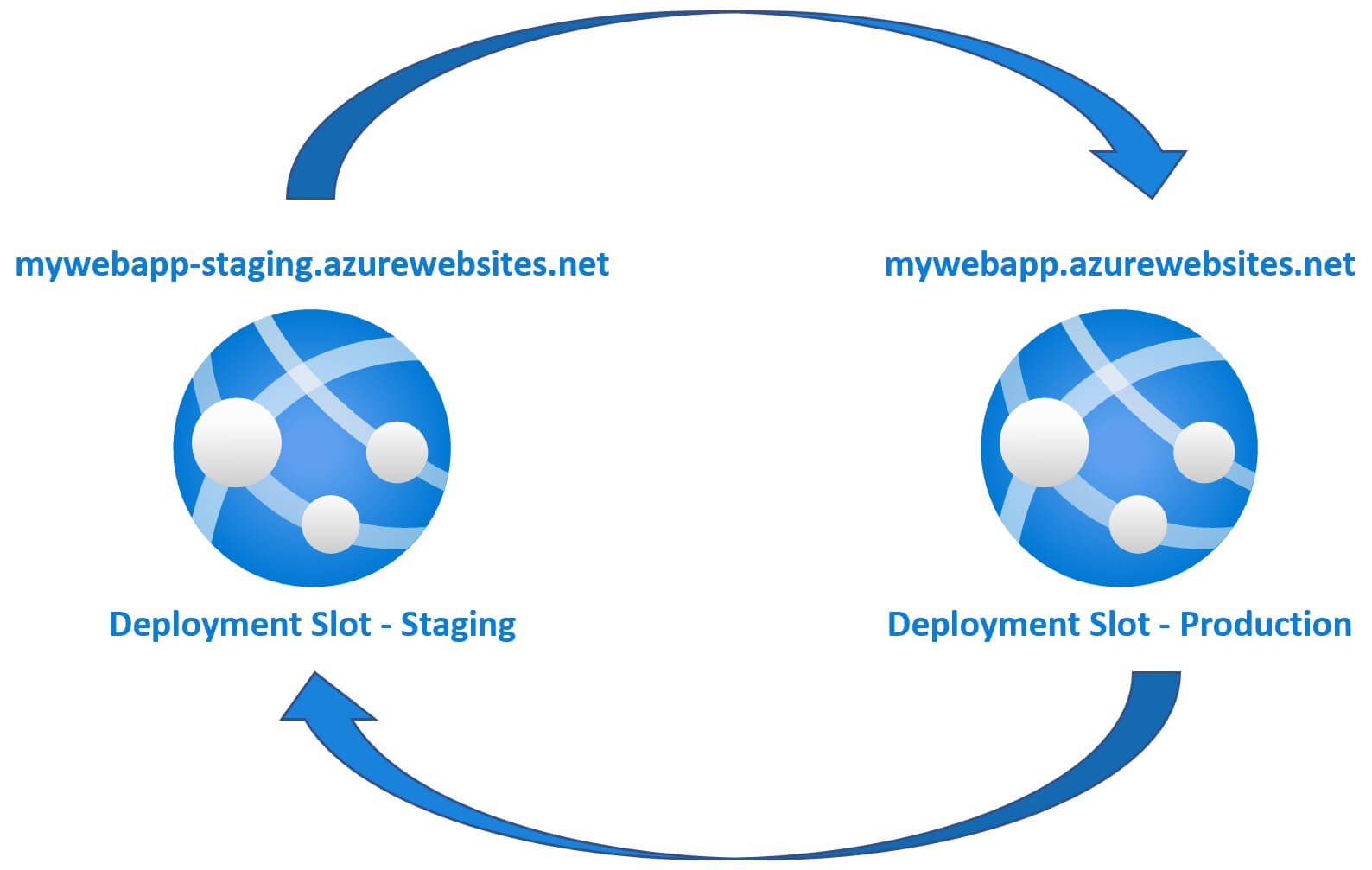
Let's say you have a web application (MyWebApp) deployed in azure. By default it gets the following URL. This is your production version of the application and your users are able to access and use it.
Now, let's say you have to make a change to your application. Maybe, there is a bug that you are fixing or you are adding a new feature. The point is you are making a change to your application code and you want to test these changes in your production like environment.
At this point, you might be wondering why can't we just test on our local machine. Why is there a need to test this changed version of the application on the same infrastructure as the production. Well, the simple answer is to test how your changed version of the application behaves on production environment. It's an opportunity for you to identify and fix any infrastructure or environment related issues.
We can create a deployment slot and deploy the changed version of our application. For example, if we name the deployment slot - staging, then we get the following URL.
How to create a deployment slot in azure
Not all azure app service plans support deployment slots. For example, the free app service plan does not support deployment slots. You have to upgrade to a standard or premium plan to add deployment slots. To see if your app service supports deployment slots, navigate to your app service in azure portal and click on Deployment Slots. If your current app service plan does not support deployment slots you will see the following screen.
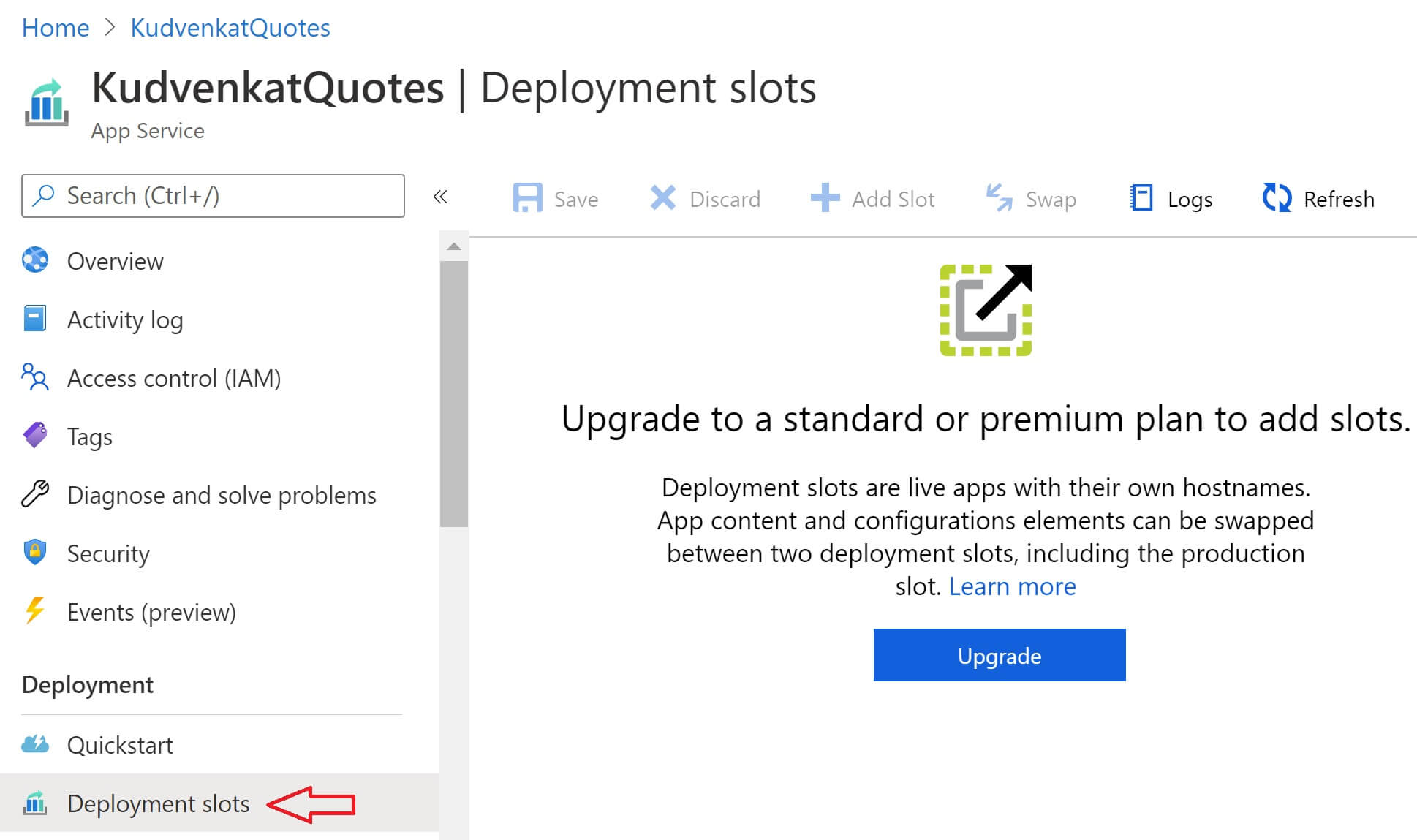
Click Upgrade button to upgrade to a plan that supports deployment slots. After you select a plan that supports deployment slots, navigate to your App Service and then click on Deployment Slots option. If your new plan supports deployment slots, you will see a screen similar to the one below. At the moment, we have only one deployment slot and it is the production slot. 100% of the traffic is going to this one production slot. To add a new deployment slot, click Add Slot button at the top.
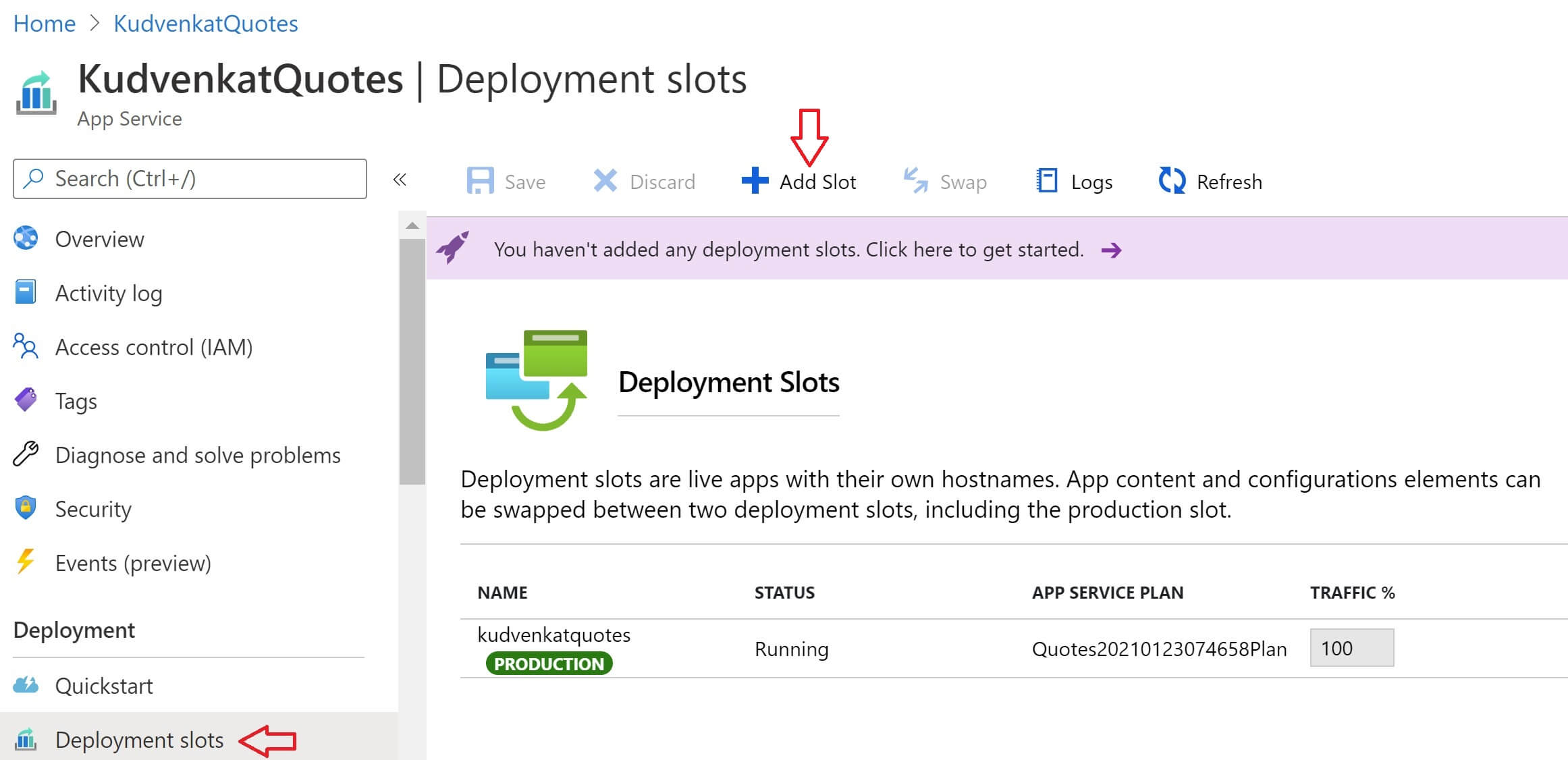
Provide name for the deployment slot. If the name is staging, azure generates the following URL. You can clone your application configuration settings from another already existing deployment slot if you want to. Click the Add button to add the new deployment slot.

How to deploy code to a deployment slot in azure
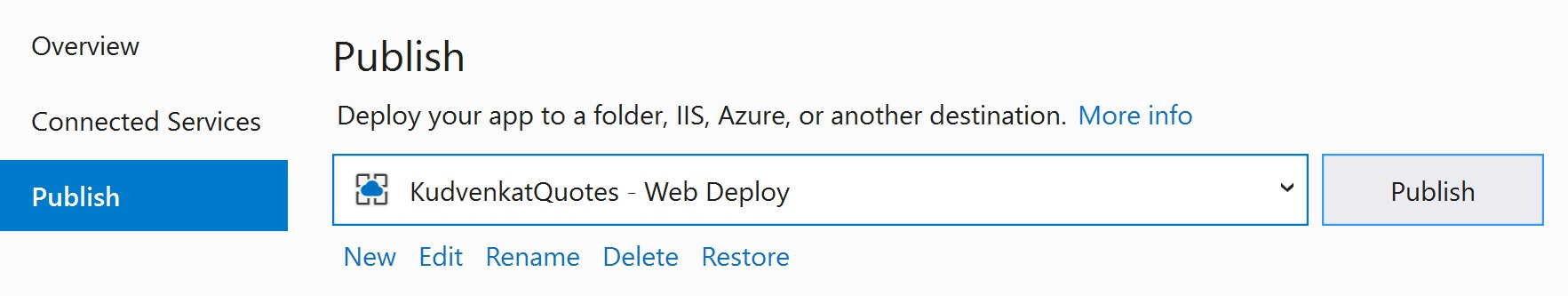
In Visual Stduio, right click on the project name in the Solution Explorer and select Publish to get to the Publish window. This publish page allows you to create several Publish profiles. At the moment, I already have a Publish profile that allows me to deploy directly to the Production slot in azure.
We now have a staging slot in azure. So, create a new publish profile and publish to the staging slot. Click the New link button.
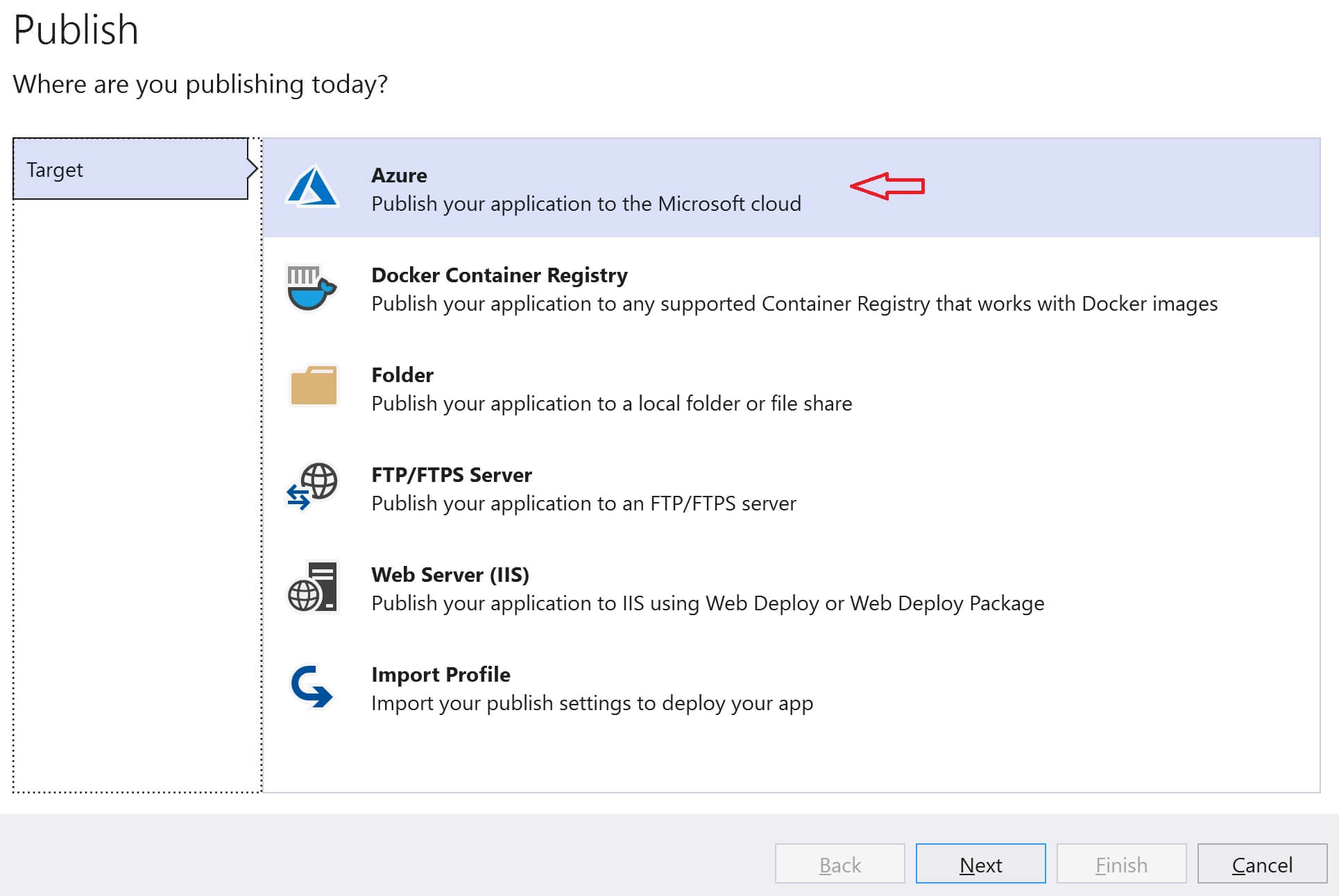
Select Azure and click Next.
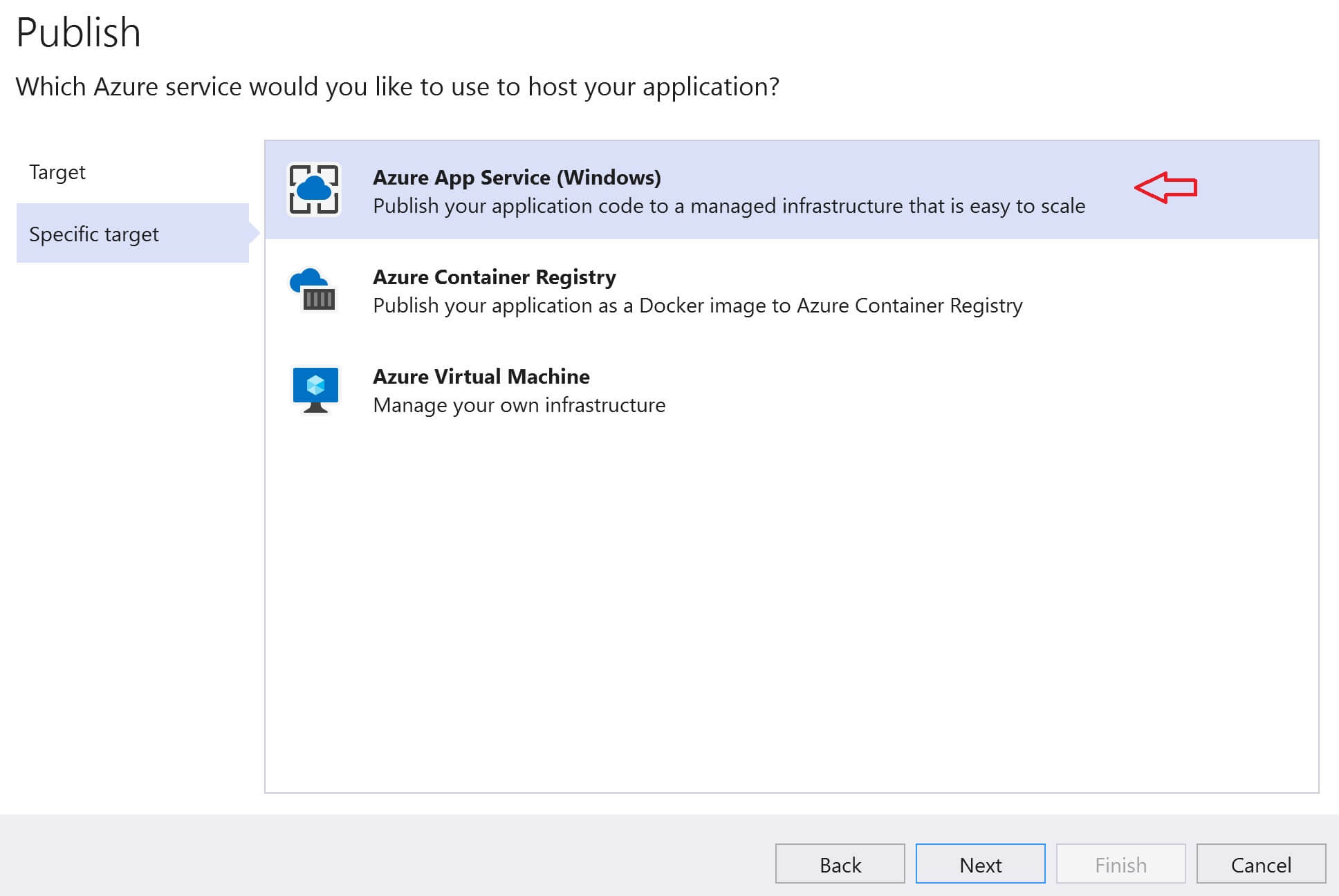
Select Azure App Service and click Next
Select Staging deployment slot and click Finish.
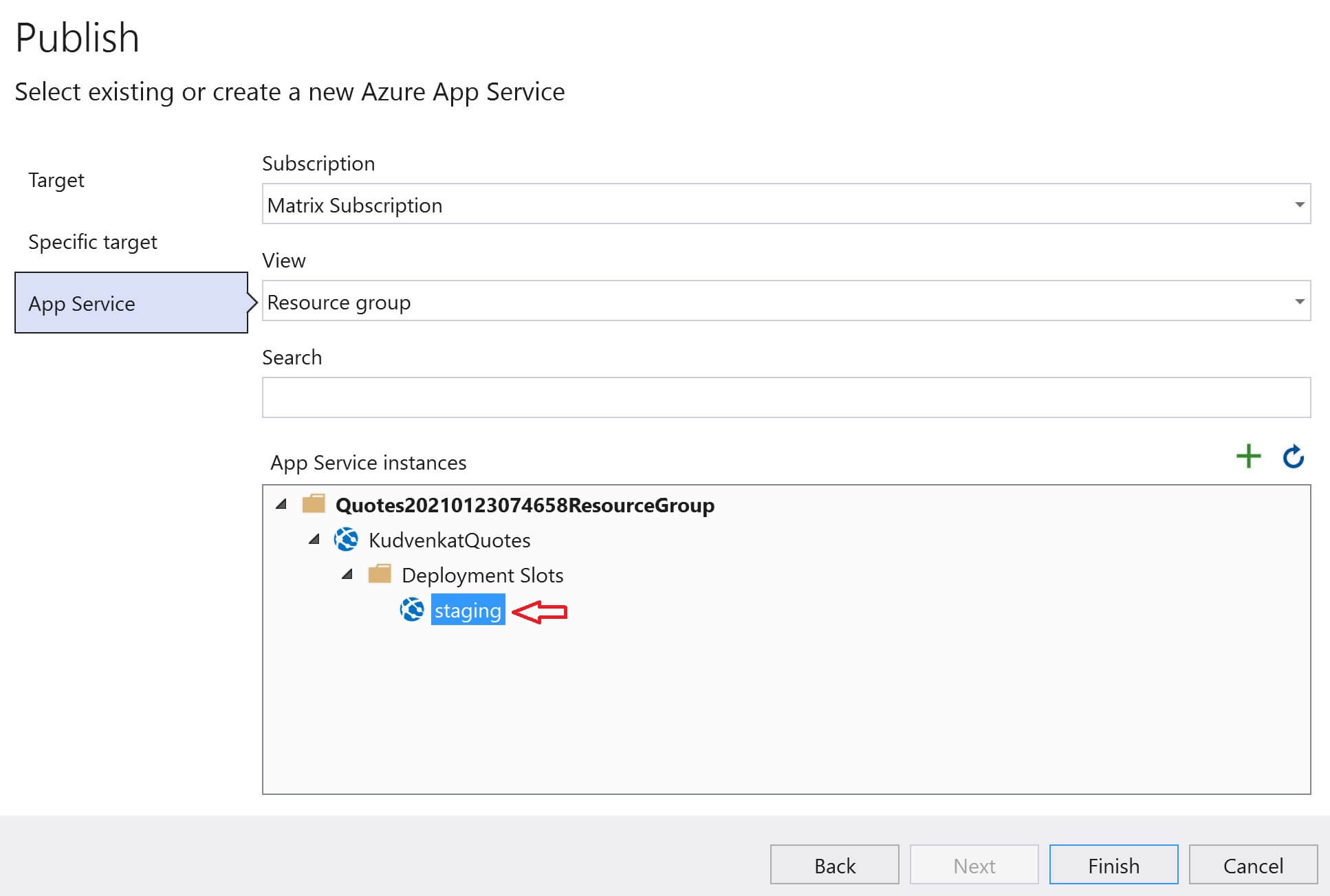
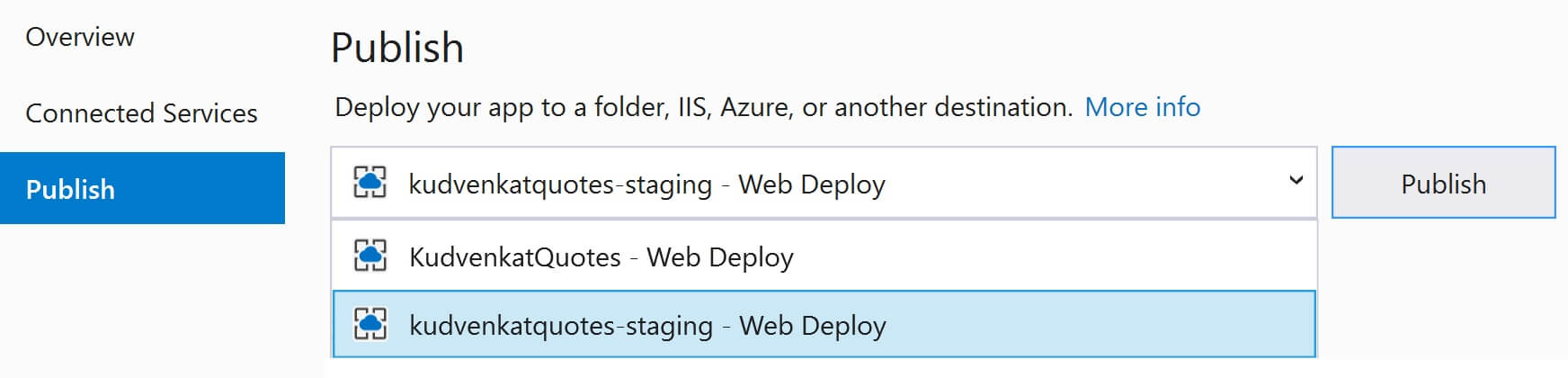
Finally, select the staging publish profile from the dropdownlist and click the Publish button to deploy the code to the Staging slot in Azure
We now have 2 versions of our application code in azure. One version is the production version in the production slot and the second version is the staging version in the staging slot. You can even divert a percentage of your production traffic and see how your application behaves. You can configure to redirect a certain percentage of live traffic to the staging slot. You do this on the Deployment slots blade of your App Service instance in the azure portal. In the example below, 50% of the live traffic is being diverted to the staging slot.
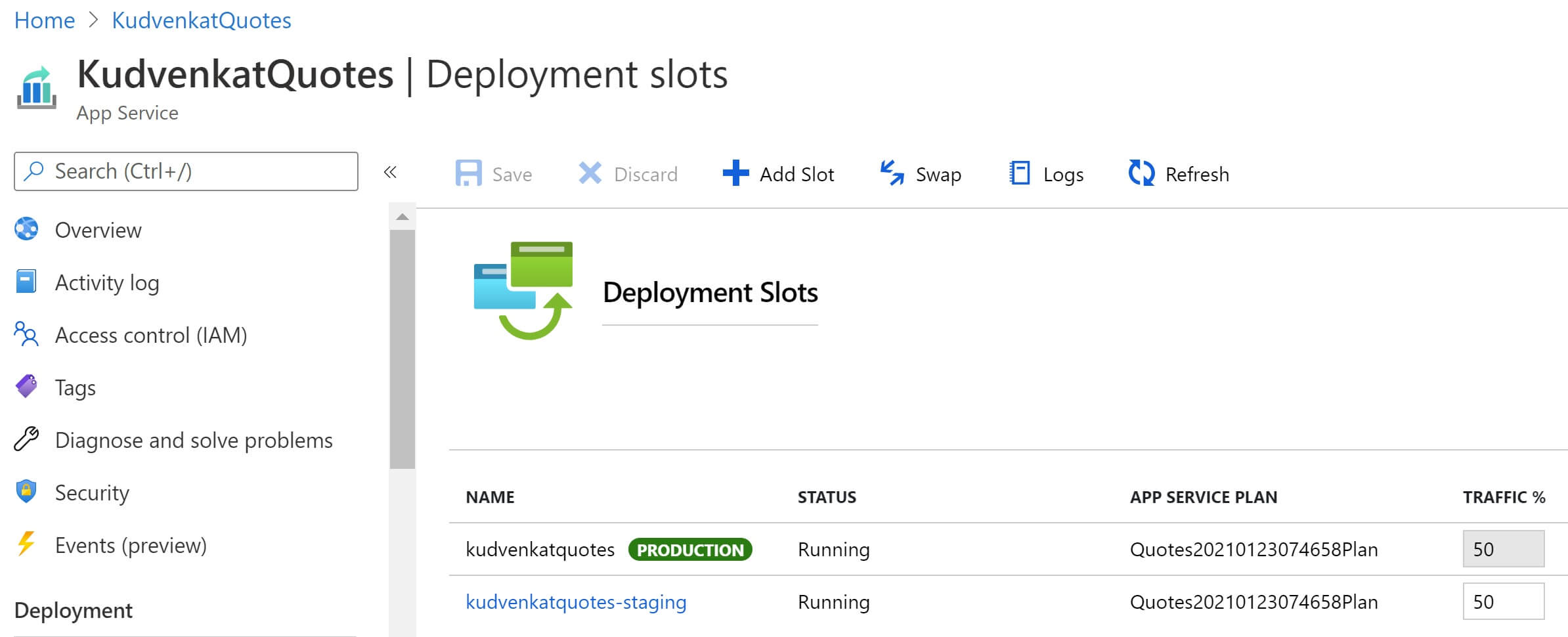
The new version of the app is now in the staging slot. It gives you an opportunity to test your application. If you are happy with the changes, you simply swap the staging deployment slot with the production deployment slot.
To perform the swap operation, click the Swap link in the Azure portal.
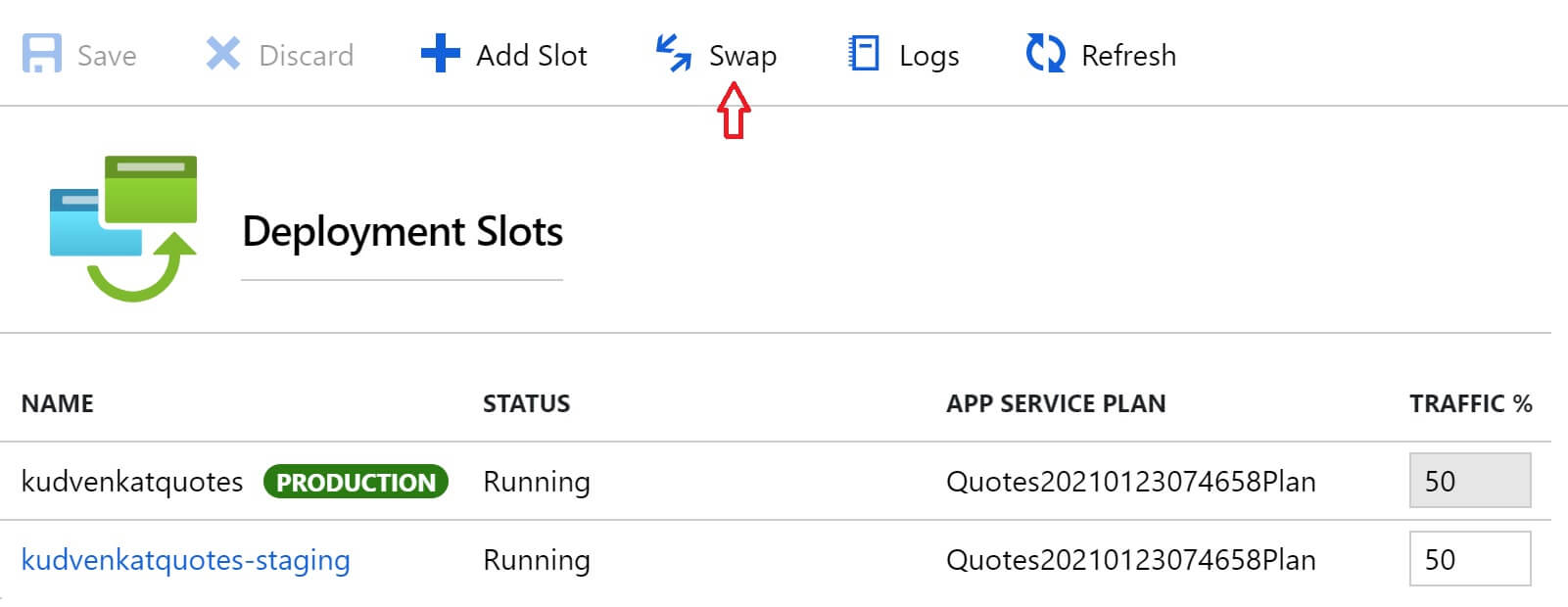 So your new version of the app is now in production and the version that was in production, is now in staging slot. The important point to keep in mind is, Azure warms up the production slot before the swap operation. So this means we get ZERO downtime deployments. How great is that?
So your new version of the app is now in production and the version that was in production, is now in staging slot. The important point to keep in mind is, Azure warms up the production slot before the swap operation. So this means we get ZERO downtime deployments. How great is that?
You can even undo the swap anytime you want. If for whatever reason, you change your mind and want to revert the deployment to a previous version, you can simply swap back again, staging to production and production to staging.
Azure deployment slots - Important points
- With deployment slots you can run multiple versions of application code on the same infrastructure
- Provides a great way to test your builds before promoting to production
- By default you get one deployment slot - Production
- You can create multiple deployment slots - Development, Staging, Testing etc
- You can also route a percentage of live traffic to deployment slots other than production
- Not all app service plans support deployment slots
- Production deployment slot is automatically warmed up just before the swap operation
- Zero downtime deployments
- Traffic redirection is seamless and no requests are dropped because of swap operation
- Swap manually through the azure portal or configure auto swap
- You can rollback a swap
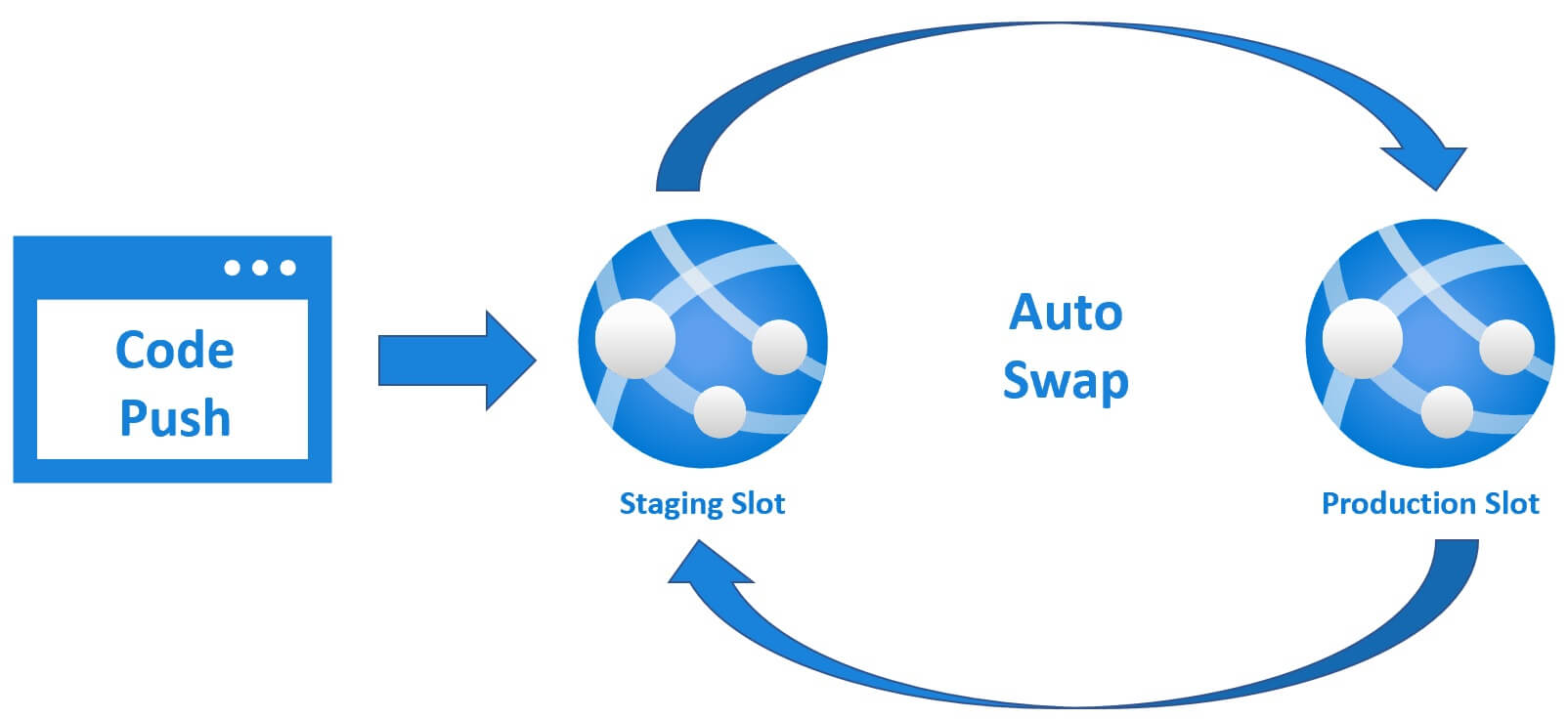


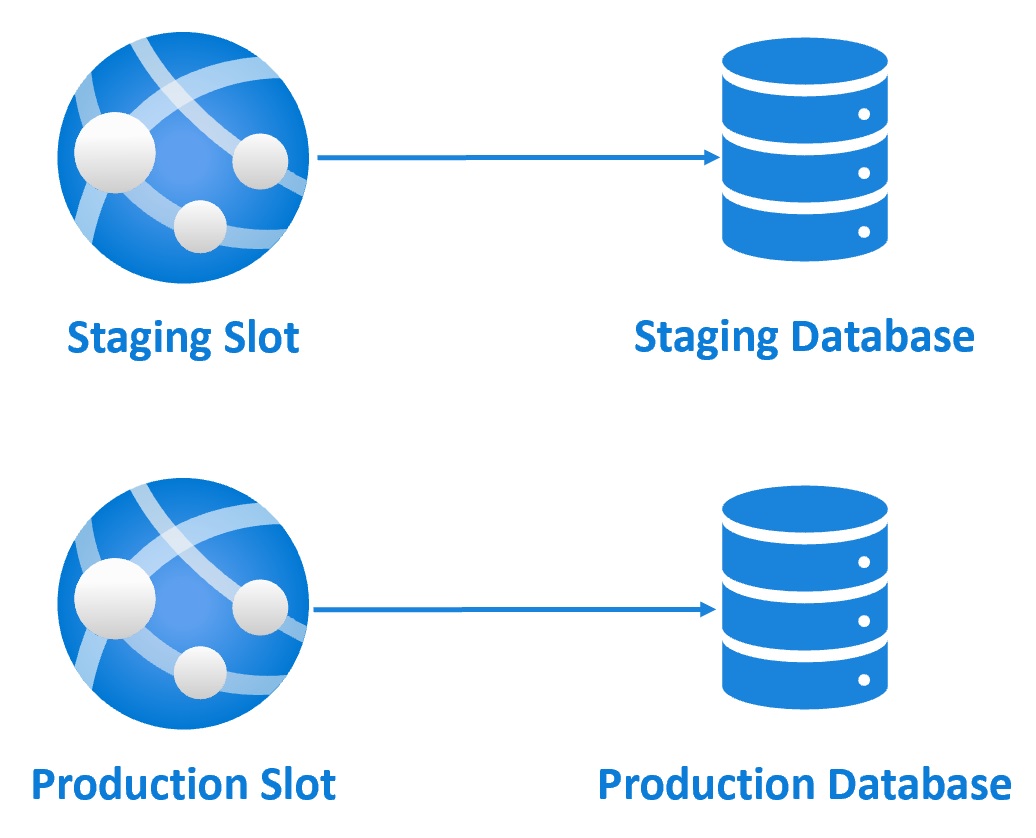
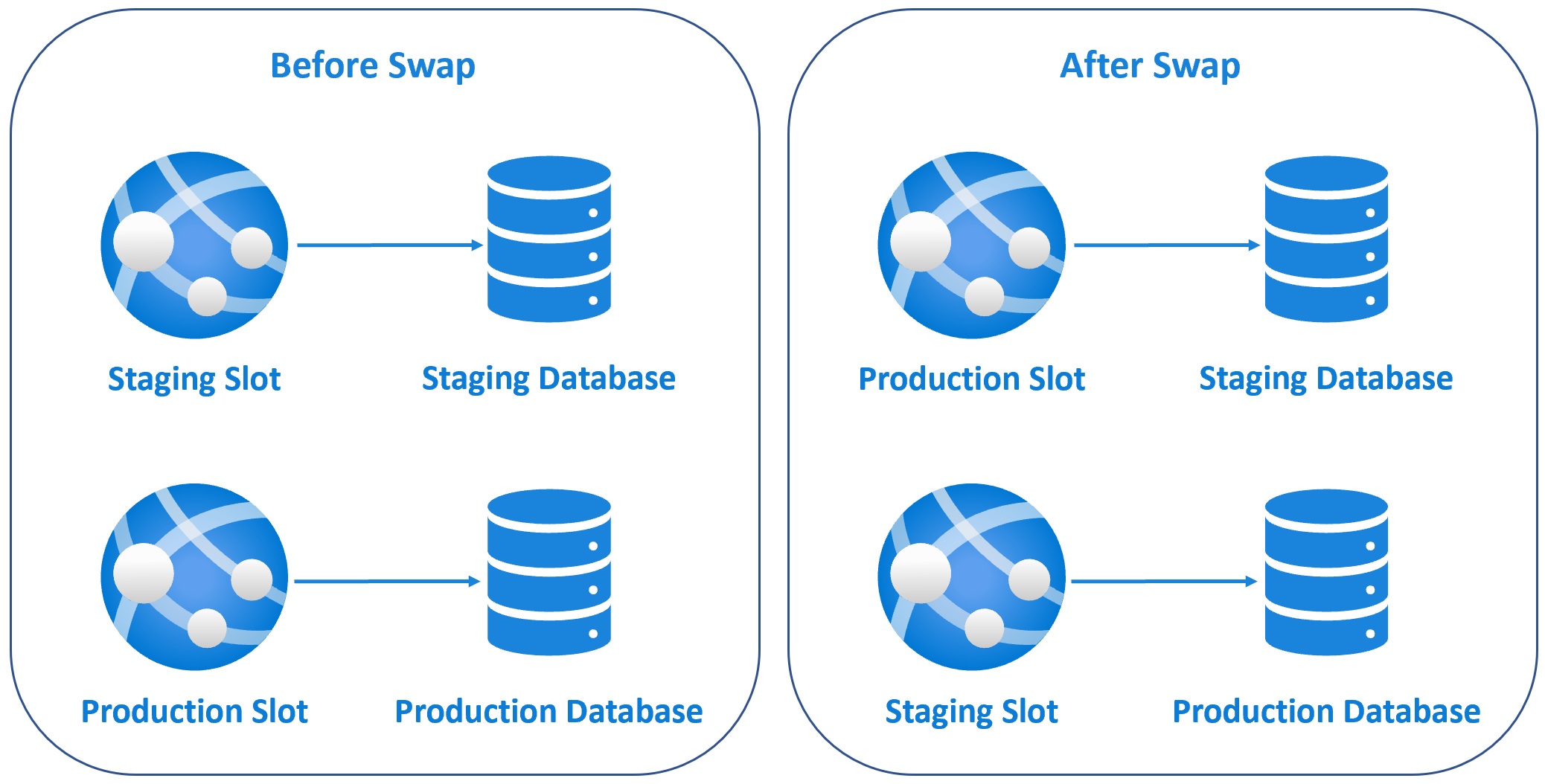
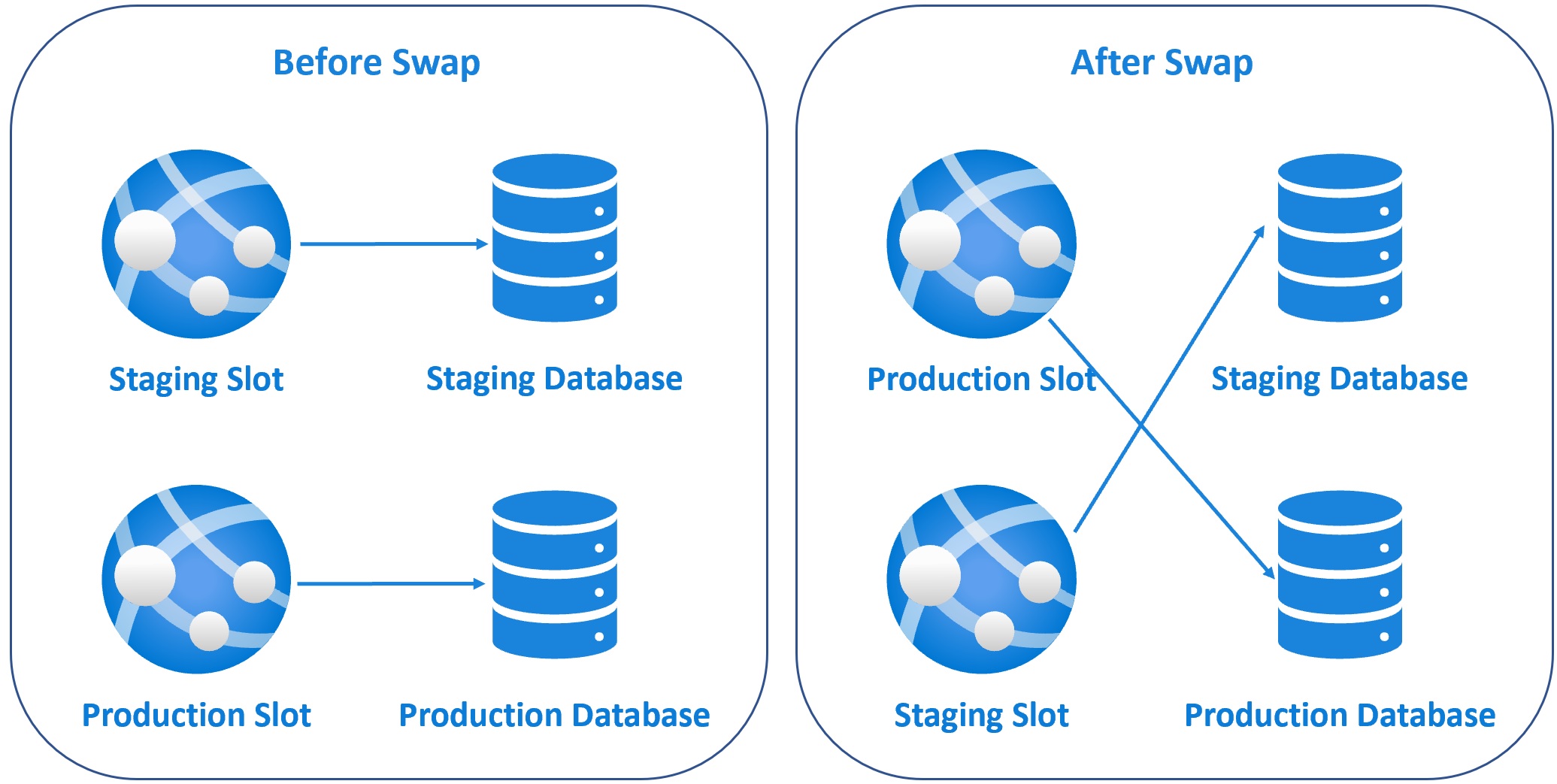










 So your new version of the app is now in production and the version that was in production, is now in staging slot. The important point to keep in mind is, Azure warms up the production slot before the swap operation. So this means we get ZERO downtime deployments. How great is that?
So your new version of the app is now in production and the version that was in production, is now in staging slot. The important point to keep in mind is, Azure warms up the production slot before the swap operation. So this means we get ZERO downtime deployments. How great is that?