Aws vs Azure vs Google Cloud
Amazon Web Service, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are the top cloud service providers that dominate the worldwide cloud market. Each of them has its own advantages. AWS is known for its large global presence and scalability options, while Azure is better at integrating with other services and providing better security. Whereas, GCP's advanced data management and machine learning features set it apart.
Whether to opt for Cloud Computing has become an irrelevant question today; now, the question arises, which cloud platform to go for? So, how will you decide which one to choose? How do you conclude the big AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud debate? To give answers to all such questions, we are here with a detailed comparison of all these giant cloud service providers.
| Read More: Top 50 Azure Interview Questions and Answers |
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing is the on-demand availability of computer resources like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence through the internet or cloud medium. It eliminates the need for individuals and businesses to self-manage physical resources themselves, and only pay for what they use.
Cloud computing uses a network (most often, the internet) to connect users to a cloud platform where they request and access rented computing services. A central server handles all the communication between client devices and servers to facilitate the data exchange.
| Read More: What is Cloud Computing? A Beginner’s Guide to Microsoft Azure |
There are three different cloud computing deployment models:
| Read More: Azure Roadmap to Become Azure Developer |
Benefits of Cloud Computing
- Decreased CapEx
No matter which cloud computing service model is used, enterprises only pay for the computing resources they use. It lets you offload some or all of the expense and effort of purchasing, installing, configuring, and managing mainframe computers and other on-premises infrastructure.
- Reduced Infrastructure Maintenance
As cloud computing provides all the resources through the internet it eliminates the need for physical storage and maintenance. It helps the businesses to focus on other goals and initiatives.
- Increased Availability
Due to cloud computing, any organization can now use enterprise applications in minutes instead of waiting weeks or months for IT to respond to a request, purchase and configure supporting hardware, and install software. This feature empowers users—specifically DevOps and other development teams—to help leverage cloud-based software and support infrastructure.
- Scalability
Cloud computing provides elasticity and self-service provisioning, so instead of purchasing excess capacity that sits unused during slow periods, you can scale capacity up and down in response to spikes and dips in traffic. You can also use your cloud provider’s global network to spread your applications closer to users worldwide.
Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services (AWS), a subsidiary of Amazon.com is the world’s most comprehensive and broadly adopted cloud platform. It offers nearly 200 fully featured services to individual developers, large enterprises, and even governments. With AWS, you can leverage the latest technologies to experiment and innovate more quickly. The AWS Partner Network (APN) includes thousands of systems integrators specialized in AWS services and tens of thousands of independent software vendors (ISVs) who adapt their technology to work on AWS.
Below is the list of popular AWS Users:
- Coursera
- Expedia
- Netflix
- Coinbase
- Formula 1
- Intuit
- Airbnb
- Lyft
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- Coca Cola
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is the second-largest cloud platform. It not only provides Windows-based services but also supports open-source languages, technologies, and platforms, giving anyone the freedom to build and support any application. It offers almost 200+ services in 78 regions available in 140 countries.
Below is the list of popular Azure Users:
- Bosch
- Audi
- ASOS
- HSBC
- Starbucks
- Walgreens
- 3M
- FedEx
- Walmart
- HP
- Mitsubishi Electric
- Renault
| Read More: AWS vs. Azure: Key Differences between AWS and Azure |
Google Cloud
- Toyota
- Equifax
- Nintendo
- Spotify
- The Home Depot
- Target
- Paypal
- UPS
Aws vs Azure vs Google Cloud
Now, we'll compare the three cloud providers in terms of various parameters.
1. Common Services
1. Compute Services
| Services | AWS | AZURE | GCP |
| IaaS | Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) | Azure Virtual Machine | Google Compute Engine |
| PaaS | AWS Elastic Beanstalk | App Service | Google App Engine |
| Container | AWS Elastic Container/Kubernetes Service | Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) | Google Kubernetes Engine |
| Serverless Functions | AWS Lambda | Azure Function | Google Cloud Functions |
Read More: An Introduction to Azure App Services
2. Database Services
| Services | AWS | AZURE | GCP |
| RDBMS | Amazon Relational Database Service | Azure SQL/ Database for MySQL/PostgreSQL | Google Cloud SQL |
| NoSQL | DynamoDB, Simple DB | Azure Cosmos DB, Table Storage | BigTable, Cloud Datastore |
3. Storage Services
| Services | AWS | Azure | GCP |
| Object Storage | Amazon Simple Storage Service | Blob Storage | Google Cloud Storage |
| File Storage | Elastic File System | Azure File Storage | Google Filestore |
| Cold Storage | Amazon Glacier | Azure Archive Blob Storage | Google Cloud Storage Nearline |
| Virtual Server Disks | Amazon Elastic Block Store | Managed Disks | Google Compute Engine Persistent Disks |
| Data Warehouse/Data Lake | Amazon Redshift | Azure Synapse Analytics | Google BigQuery |
4. Networking Services
| Services | AWS | Azure | GCP |
| Virtual Network | Amazon Virtual Private Cloud(VPC) | Virtual Networks (VNets) | Virtual Private Cloud |
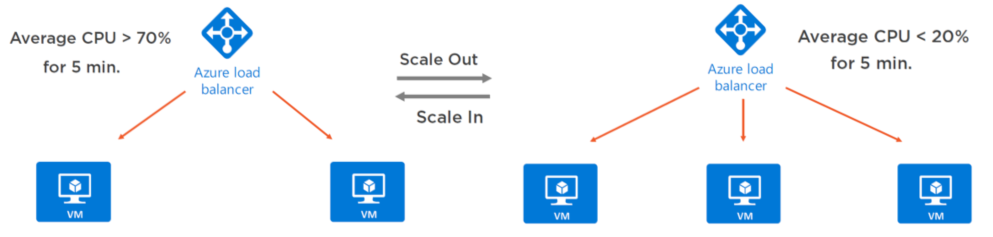
| Load Balancing | Elastic Load Balancer | Azure Load Balancer | Google Cloud Load Balancing |
| Firewall | AWS Firewall / Web Application Firewall | Azure Firewall | Google Cloud firewalls |
| DNS | Amazon Route 53 | Azure DNS | Google Cloud DNS |
| CDN | Amazon CloudFront | Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) | Cloud CDN |
| Peering | Direct Connect | ExpressRoute | Google Cloud Interconnect |
5. Specialized Services
| Services | AWS | Azure | GCP |
| DevOps | CodePipeline, CodeBuild, CodeDeploy, CodeStar | Azure Boards, Pipelines, Repos, Test Plans, Artifacts | GCP DevOps CloudBuild, Artifact Registry |
| AI & ML | Amazon SageMaker, Amazon Comprehend, Amazon Lex, Amazon Polly | Azure Machine Learning, Azure Databricks, Azure Cognitive Search, Azure Bot Service, Cognitive Services | Vertex AI, AutoML, Dataflow CX, Cloud Vision, Virtual Agents |
| IoT | FreeRTOS, IoT Core, Greengrass, IoT Analytics, SiteWise | Azure IoT Hub/Central, IoT Edge, Azure Sphere, Azure RTOS | Google Cloud IoT Core |
| AR & VR | Amazon Sumerian | Azure Mixed Reality (Spatial Anchors/Remote Rendering) | ARCore |
| Game Development | Amazon GameLift | Azure PlayFab | |
| Business Analytics | Amazon Quicksight | Azure Power BI | Looker |
| End-User Computing | Amazon Workspaces | Azure Virtual Desktop |
Read More: Top 10 Most Used Microsoft Azure Services
2. History And Open Source
| AWS | Azure | GCP |
| AWS came into the market in 2006 | Azure started services in 2010 | GCP launched in 2008 |
| AWS has been friendly with the open-source model from the beginning | Azure has not so good a relationship with the open-source community | GCP offers managed open-source services that are tightly integrated into Google Cloud |
| Large and complex scale offerings of services that can potentially be manipulated. | Low-Quality Support | Quite costly support fee of about $150/month for the silver class, which is the most basic of services |
3. Availability Zones
| AWS | Azure | GCP |
| 105 availability zones across 33 regions in 245 countries | 113 availability zones across 69 regions in 215 countries | 109 availability zones across 69 regions in 215 countries |
4. Pricing
There are some factors affecting the cost of the cloud platform They are:
- Customer specifications
- Usage
- The services utilized
| Machine Type | AWS | Azure | GCP |
| Smallest Instance | AWS charges roughly US$69 per month for a primary instance with two virtual CPUs and eight gigabytes of RAM. | In Azure, an instance with 2 CPUs and 8 GB of RAM, will cost roughly US$70 per month. | GCP will supply you with the most basic instance, including two virtual CPUs and eight gigabytes of RAM, at a 25% lower cost. As a result, it will cost you around US$52 every month. |
| Largest Instance | The most expensive AWS instance, with 3.84 TB of RAM and 128 CPUs, will cost you roughly US$3.97/hour. | Azure's largest instance includes 3.89 TB of RAM and 128 CPUs. It costs about $6.79 per hour. | GCP's largest instance is 3.75 TB of RAM and 160 CPUs. It will cost you approximately US$5.32/hour. |
5. Managing Packages
| AWS | Azure | GCP |
| You need to integrate external software or third-party software like Artifactory | Azure has a package manager tool called Azure Artifacts to manage packages like Nuget, Maven, etc. | Artifact Registry is used to manage container images and language packages (such as Maven and npm) |
6. Service Integration
| AWS | Azure | GCP |
| Users can easily integrate services with Amazon EC2, Amazon S3, Beanstalk, etc. | Users can easily integrate services with Azure VM, Azure App Service, SQL databases, etc | Users can easily integrate services Compute Engine, Cloud Storage, Cloud SQL, etc. |
7. Hybrid and Multicloud Options
A hybrid cloud merges one or more public clouds with an organization's existing infrastructure and a private cloud, offering a versatile and integrated solution.
| AWS | Azure | GCP |
|
|
|
8. Pros and Cons
1. Pros
| AWS | Azure | GCP |
| AWS is an established market leader. | Azure is Open to Hybrid Cloud systems. | GCP specializes in highly high-competitive offerings like Big data and machine Learning. |
| High Transfer Stability: Minimal data loss during server and storage transfer. | Easy integration with Microsoft tools and software. | Easy integration with other GCP Services like Compute Engine, Kubernetes Engine, or App Engine. |
| Easy Availability of Data: users can choose to store data close to their location | Azure has a more profound knowledge of enterprise needs. | Well-detailed documentation, including an API reference guide. |
| AWS has a vast global infrastructure with data centers located in multiple regions worldwide | Azure has a significant global footprint with data centers distributed across multiple regions worldwide. | It offers a vast global network of data centers, ensuring low latency and high-performance services across regions. |
2. Cons
| AWS | Azure | GCP |
| Incomplete and weak Hybrid Strategy | Integration with non-Microsoft is complex. | Google’s App Engine is limited to Java, Python, PHP, and Google Go. |
| Support for hybrid cloud outputs is still in its early stages, lacking demonstrated maturity. | Restrictive Platform, Less flexible with non-windows server platforms | The cost of downloading data from Google Cloud Storage is relatively high |
| Large and Complex scale offerings that can potentially be manipulated. | Low-Quality Support | Quite costly support fee of about $150 per month for the silver class, which is the most basic of services |
Read More: Top 50 Azure Administrator Interview Questions and Answers
How to Decide Which Cloud Provider is Best?
We saw a detailed comparison of all three major cloud providers. Now which cloud provider best suits your needs? How to know which is the best for our business? To answer all these questions, we'll look at some major positive and negative points of these cloud providers. After that, you decide which of the three best suits your needs.
- Establishment: AWS has been providing its services for five years. So, in this category, AWS wins.
- Availability zones: AWS has the highest number of regions and availability zones. Here, again AWS is leading.
- Market shares: AWS spans one-third of the cloud market emerging as the winner in this parameter.
- Growth rate: AWS has a nearly 100 percent growth rate.
- Users: A large number of high-end customers are using all three cloud platforms. So here, there's a tie between them.
- Services: AWS offers the largest number of services i.e. at least 200. Hence, it leads from the front in terms of services. But here, in terms of integration with open-source and on-premise systems, such as MS tools, that are mostly used in almost all organizations, the winner is Azure.
- Pricing Models: In this criteria, Google Cloud fits the best as it offers various customer-friendly pricing models and discount models.
We can see that in this battle, AWS wins in almost all the parameters. But this doesn't make the other two irrelevant. Even though AWS is the current market leader in terms of capacity and service, Microsoft and Google are also rapidly growing to compete with AWS. Azure and GCP each have their own set of advantages.
Hence, we can conclude that you should not go for the best cloud service provider but select the best-suited provider according to the needs of your business or organization.
ScholarHat has come up with the following Certification Programs and Courses to help you upskill your cloud-computing skills.
- Microsoft Azure Cloud Architect
- Microsoft Azure Training
- Azure Developer Certification (Az-204) Training
- Azure DevOps Training
- Azure Solution Architect Certification Training
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Certification Course
- Azure Developer Certification Course (Az-204)
- Azure Fundamentals Course | AZ 900 Certification