1.What is Linux?
Answer: Linux is an operating system based on UNIX, and was first introduced by Linus Torvalds. It is based on the Linux Kernel, and can run on different hardware platforms manufactured by Intel, MIPS, HP, IBM, SPARC and Motorola. Another popular element in Linux is its mascot, a penguin figure named Tux.
2. What is the difference between UNIX and LINUX?
Answer :Unix originally began as a propriety operating system from Bell Laboratories, which later on spawned into different commercial versions. On the other hand, Linux is free, open source and intended as a non-propriety operating system for the masses.
3. Give me 15 commands which you use frequently.
Answer :Depends on the environment you work. Some examples are
mkdir – For creating folders( use -p option to create multiple folders at a time)
ls – List folders/files( check what ls -1 do)
top – To monitor system activities
To check whats happening on the server and which process open which file.
netstat -tcp –Gives you complete picture about network connection details.
vnstat –Gives you Network band width statics
sh –For running shell scripts
history –For monitoring the commands executed by users
cd –For changing directories
vi –-For editing configuration files.
chmod–To change permissions of folders and files.
Mount –For mounting formatted partitions.
service –For start/restart/stop a service.
chkconfig –For permanent on/off a service.
fdisk -l –To list all the partitions
This is my own list, you can have your list.
4. Give me some commands for user management.
Answer: last, chage, chsh, lsof, chown, chmod, useradd, userdel, newusers.
5. Give me syntax checking commands for following services
Answer: DNS, SAMBA, Apache etc
6. What is the command to do password less logins to other machines.
Answer: expect and ssh-keygen
7. Give me some security monitoring related commands.
Answer: lsof, netstat, top, ps -ef, tail, last, tcpdump, sestatus, history, w.
8. What is the difference between man, info, whatis commands and a –help option for a command?
Answer: man command gives you medium size info.
info command gives full details about a commands, lots and lots of information about a command. Please share your interview questions with us, we post them here so that others can get help from this.
9. What is Kerberos used for?
Answer: Kerberos is used for secure network logon.
10. Which partition store system configuration files in Linux system?
Answer: /etc partition stores system configuration files in Linux.
11. What is the purpose of the MD5 option on passwords?
Answer : MD5 is an encryption method that encrypts the password before saving.
Name any four general password rules for user account.
Answer:
- Include at least eight total characters
- Use the string in an unrepeated way
- Avoid use words that can be found in the dictionary
- Avoid use dates of significance, such as a birthday or anniversary A better method of password security is to create difficult-to-break passwords that are easy for the users to remember.
12. What is the alternative method to a GUI installation in Linux?
Answer : Linux provides text base installation as the alternative method of GUI installation.
13. What is the purpose of the swapon command?
Answer : swapon command is used to activate a already created swap partition. It cannot be used to create a new swap partition.
14. What is gzip?
Answer: gzip is a compression utility created by the GNU project.
15. What is tar?
Answer : tar is an archive utility that is used to create tape backups.
16. Which is the standard command used to uncompress gzip files?
Answer : The standard command used to uncompress gzip files is gunzip.
17. What is the RPM switch for only installing packages?
Answer : The command line switch for installing an RPM is -i.
18. What is the command used to install an RPM package named demofilename2.2- 2.i386.rpm?
Answer : The most common command used to install an RPM package is rpm -ivh. Following command will install the given package
#rpm -ivh demofilename2.2-2.i386.rpm
19. What is the command used to remove an RPM package named demofilename2.2- 2.i386.rpm?
Answer : The most common command used to remove an RPM package is rpm -evh. Following command will remove the given package
#rpm -evh demofilename2.2-2.i386.rpm
20. What is the command used to update an RPM package named demofilename2.2- 2.i386.rpm?
Answer : The most common command used to update an RPM package is rpm -Uvh. Following command will update the given package and remove the old.
#rpm -Uvh demofilename2.2-2.i386.rpm
21. PPP is most often used to create?
Answer: PPP is most often used to create serial point-to-point connections.
22. What fstab file do?
Answer : The fstab file is used to automatically mount file systems.
23. What inittab file do?
Answer : The /etc/inittab file is used to perform the default state and terminal connections for a Linux system.
24. What command can you use to verify the current active shell?
Answer : The env command will display the current active shell.
25. Where is the file. bashrc located?
Answer : The. bashrc file is usually located in the /home/username directory.
26. What function does the .bash_profile file perform?
Answer : The function of the .bash_profile file is to provide login initialization commands.
27. What function does the .bash_logout file perform?
Answer : The function of the .bash_logout is to provide logout functions
28. What function does the .bashrc file perform?
Answer : The function of the .bashrc file is to provide shell configuration commands.
29. What command would you use to shut down the system in 100 seconds?
Answer : #shutdown -h 100
30. What daemon controls the print spooling process?
Answer : The Line Printing Daemon (lpd) controls the print spooling process.
31. What configuration file defines the default runlevel for the init process?
Answer :/etc/inittab file defines the default runlevel for the init process.
32. Which command can you use to shut down and halt a Linux System?
Answer : The halt command will shut down a Linux system without rebooting
33. What init level should you set to bring the system to single-user mode?
Answer : init 1 will bring the system to single-user mode
34. A user wants to restart the NFS server because they want to enable changes made in the configuration file. What command accomplishes this task?
Answer : #service nfs reload
The reload command will tell the system to stop the service, reload the configuration file, and restart the service
35. What command can you use to reboot a Linux system?
Answer : The command to reboot a Linux system is reboot
36. What mode must you be in when using vi editor to input text into a file?
Answer : To insert text in the vi editor, you must be in insert mode
37. What is BASH?
Answer : BASH is short for Bourne Again SHell. It was written by Steve Bourne as a replacement to the original Bourne Shell (represented by /bin/sh). It combines all the features from the original version
of Bourne Shell, plus additional functions to make it easier and more convenient to use. It has since been adapted as the default shell for most systems running Linux.
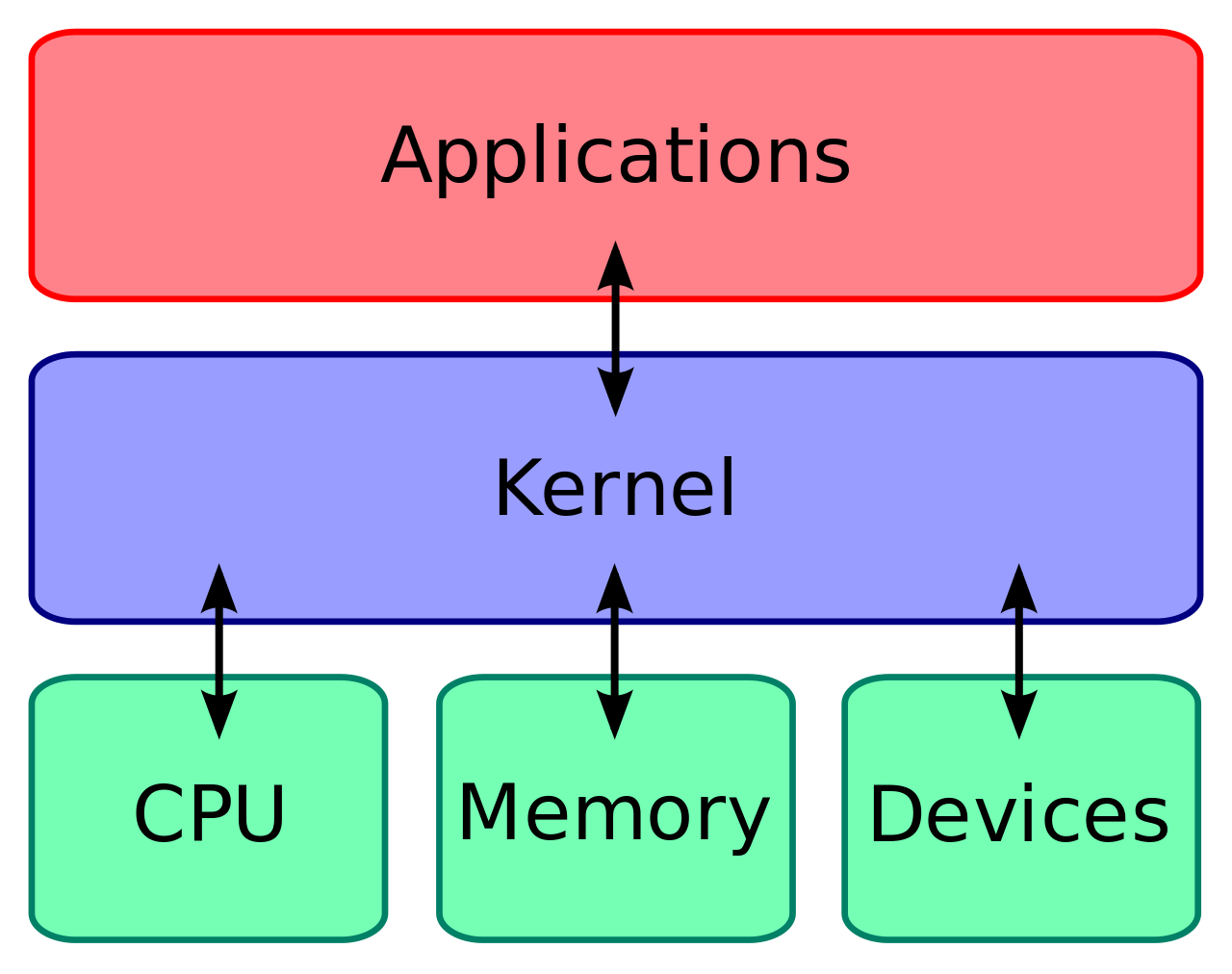
38. What is Linux Kernel?
Answer : The Linux Kernel is a low-level systems software whose main role is to manage hardware resources for the user. It is also used to provide an interface for user-level interaction.
39. What is LILO?
Answer : LILO is a boot loader for Linux. It is used mainly to load the Linux operating system into main memory so that it can begin its operations.
40. What is a swap space?
Answer : A swap space is a certain amount of space used by Linux to temporarily hold some programs that are running concurrently. This happens when RAM does not have enough memory to hold all programs that are executing.
41. What is the advantage of open source?
Answer : Open source allows you to distribute your software, including source codes freely to anyone who is interested. People would then be able to add features and even debug and correct errors that are in the source code. They can even make it run better, and then redistribute these enhanced source code freely again. This eventually benefits everyone in the community.
42. What are the basic components of Linux?
Answer : Just like any other typical operating system, Linux has all of these components: kernel, shells and GUIs, system utilities, and application program. What makes Linux advantageous over other operating system is that every aspect comes with additional features and all codes for these are downloadable for free.
43. Does it help for a Linux system to have multiple desktop environments installed?
Answer : In general, one desktop environment, like KDE or Gnome, is good enough to operate without issues. It’s all a matter of preference for the user, although the system allows switching from one environment to another. Some programs will work on one environment and not work on the other, so it could also be considered a factor in selecting which environment to use.
44. A newbie enabled the root session for FTP server. is it ok?
Answer : No, he has put the security of entire server on risk. You should disable to root session as soon as possible.
45. A user complains you that he is unable to set ‘123’ as his password. Why would not the system allow this password?
Answer : There would be a minimum length rule for password, which is blocking user to use this password. Default minimum length rule for password is six characters. It means a user cannot have password less than six characters.
46. Your company is running Web Server. One dedicate account holder customer complains that his visitors are able to scan the directory tree. Which directive would you configure to stop web server from listing the directory?
Answer : You should remove/ comment the “Options Indexes” directive from the main configuration file ‘ httpd.conf’ of the web server. This is a security measure so that remote users can’t scan the directory tree of the server looking for security holes. Server won’t show directory listings if requested by a user.
47.What type of backup strategy can you use to fully back up a system every night?
Answer : You can use full backup strategy that will always perform a full backup of all files. This takes much more time and space than other methods, but is it the most complete method and allows for easy file restoration.
48. How can you enhance the security of password file?
Answer : Linux keep user account information in a text file called /etc/passwd. This file also store one way encrypted password. This file is accessed by several tools to get user information, so file need to world readable. This is a security risk. To minimize the security risk you can use shadow password format. This method save account information in regular file /etc/passwd. However, the password is stored as a single “x” character (not actually stored in this file). A second file, called “/etc/shadow”, contains encrypted password as well as other information such as account or password expiration values, etc. The /etc/shadow file is readable only by the root account and is therefore less of a security risk
49. What command should be used to make a tar archive to a disk file system located in /mnt/backup?
Answer : The correct command is tar -cvf /mnt/backup. The /mnt/backup directory should be on another machine to be fully effective as a backup strategy.
50. You have just finished the installation of sever. This server is going to be use as file server. Default installation have send mail service running, while this server will never send any e-mails. How should you deal with send mail service?
Answer : You should disable the send mail service if server is not being used for mail purpose. Leaving them running can increase the chance of a security vulnerability being exploited, and unauthorized use of sendmail relay.
51. What command can you use to back up an entire file system most efficiently?
Answer : The easiest command to use to back up an entire file system is the dump command. Files can
be restored from a dump operation by using the restore command.
52. Which necessary steps should you take to enhance the security of server just after the initial installation?
Answer:
- Kernel and packages should be upgraded to the latest versions.
- Unnecessary services and daemons should be disable.
- Enable and configure firewall
- Set a complex password policy
53. While auditing user accounts, an administrator notices that one of the users has a blank password. What should he do to the account?
Answer : To prevent further use of the account, which is an immediate security risk, disable it and set a temporary password for the user for the next time they login.
54. Which backup strategy backs up all files that have changed since the last backup?
Answer : An incremental backup will only back up files that have changed since the last backup.
55. Your company has terminated a server administrator. What is first thing as an administrator should you do to enhance the security?
Answer : Because the server administrator knows the root password for the server, it should be changed immediately to prevent them from tampering with the system.
56. You are setting up an FTP server. Only company employees are allowed to use the FTP services. What should you configure on the FTP server to enhance security?
Answer : You should disable the anonymous FTP account, so that only users with a username and password can access the system.
57. What is the location of system configuration files that should be backed up on a regular basis?
Answer : The /etc directory contains most of the Linux system configuration files.
58. Which permission allows a user to run an executable with the permissions of the owner of that file?
Answer : The Set-User-ID is a special permission that allows a user to run an executable with the permissions of the owner of that file.
59. What command can you use to make a tape archive file of a /home directory, and send it to the /dev/tape device?
Answer : The correct command is tar -cvf /dev/tape /home.
The -xvf option is used to extract files from an archive.
60. Employees at your company are lazy in changing the password. As a system administrator what can you do to minimize the security risk?
Answer : You can setup a password policy which enforce user to change his password after a specific time periods.
61. Which program should you use to connect a system remotely?
Answer : You should always use SSH to connect a system remotely. SSH is a secure method that encrypts the entire session.
62. To save disk space, an administrator wants to backup files, and then remove them from the server permanently. What kind of backup operation is this?
Answer : An archive operation will take the files, back them up to a device, and then remove the files from the original server.
63. What does firewall do?
Answer : Firewall is a device or service which can be used to protect the network or system from other outside networks.
64. Due to power fluctuation, your system starts up from a powered off state. You receive a warning error stating that the machine was not shut down properly, and fsck will be run. What is the cause of this message?
Answer : If your hard drive file systems are not unmounted properly, the fsck utility will automatically run the next time the system is started to fix any inconsistencies before they are mounted again. If they are not fixed, the file system can quickly become corrupt.
65. A junior system administrator is trying to read through a large log file using the cat command. Because it is so large, the cat command scrolls the file right to the end without allowing the start of the file to be read. What command can he be used to more easily read the file?
Answer : He can use less command instead of using cat command, which allows him to scroll through the file.
66. When you try to boot a Linux system, you receive a message stating that it canot mount the /home partition because of errors. While debugging, you found that it occur due to data error. What can you do to fix the problem?
Answer : You can use fsck utility that enable you to recover from the errors.
67. During the bootup of a Linux system, there is no output on the monitor, the machine beeps, and then halts the boot-up process. What is the most likely cause of the problem?
Answer : If the system would not even get to the POST stage, the problem is most likely with the motherboard itself. You should count and compare the number of beeps to the BIOS manual in order to determine which specific component failed.
68. Which utility could you use to repair the corrupted file system?
Answer : You can use fsck to repair the corrupted file system.
69. What is the core of Linux Operating System?
- Shell
- Kernel
- Command
- Script
- Terminal
Answer: 3. Kernel is the core of Linux Operating System. Shell is a command Line Interpreter, Command is user Instruction to Computer, Script is collection of commands stored in a file and Terminal is a command Line Interface
70. What Linus Torvalds Created?
- Fedora
- Slackware
- Debian
- Gentoo
- Linux
Answer: Linux Torvalds created Linux, which is the kernel (heart) of all of the above Operating System and all other Linux Operating System.
71. Torvalds, Wrote most of the Linux Kernel in C++ programming Language, do you agree?
Answer: No! Linux Kernel contains 12,020,528 Lines of codes out of which 2,151,595 Lines are comments. So remaining 9,868,933 lines are codes and out of 9,868,933 Lines of codes 7,896,318 are written in C Programming Language.
The remaining Lines of code 1,972,615 is written in C++, Assembly, Perl, Shell Script, Python, Bash Script, HTML, awk, yacc, lex, sed, etc.
Note: The Number of Lines of codes varies on daily basis and an average of more than 3,509 lines are being added to Kernel.
72. Linux initially was developed for intel X86 architecture but has been ported to other hardware platform than any other Operating System. Do you agree?
Answer: Yes, I do agree. Linux was written for x86 machine, and has been ported to all kind of platform. Today’s more than 90% of supercomputers are using Linux. Linux made a very promising future in mobile phone, Tablets. In-fact we are surrounded by Linux in remote controls, space science, Research, Web, Desktop Computing. The list is endless.
73. Is it legal to edit Linux Kernel?
Answer: Yes, Kernel is released under General Public Licence (GPL), and anyone can edit Linux Kernel to the extent permitted under GPL. Linux Kernel comes under the category of Free and Open Source Software (FOSS).
74. What is the basic difference between UNIX and Linux Operating System.
Answer: Linux Operating System is Free and Open Source Software, the kernel of which is created by Linus Torvalds and community. Well you can not say UNIX Operating System doesn’t comes under the category of Free and Open Source Software, BSD, is a variant of UNIX which comes under the category of FOSS. Moreover Big companies like Apple, IBM, Oracle, HP, etc. are contributing to UNIX Kernel.
75. What is the difference between service and process?
Answer: A process is any piece of software that is running on a computer. For example, your anti-virus software runs in the background as a process, which was automatically started when the computer booted. Some processes start when your computer boots, others are started manually when needed. Some processes are services that publish methods to access them, so other programs can call them as needed. Printing services would be an example of a service type of process, where your email program can just call the print services process to say it wants to print, and the service does the actual work.
76. How to view crond status?If it’s show service is not found.
Answer: Service crond restart
77. My clients are getting services from servers but how to know which client is using which service. is there any files to keep information about these? Clients used ftp, nis, samba, apache, squid, nfs and mail services how to know how many users got service from server side with date, time and client system ip?
Answer :
Mail server – /var/log/mail/maillog [RedHat,centos]
ssh – /var/log/secure
Apache – /var/log/http/access.log
nfs – /var/lib/nfs/rmtab
78. How to FTP user access other directory except his own home directory?
Answer :
vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
Chroot_list_enable=yes
79. What are the Linux-based security tools?
Answer:
- Selinux
- Firewall
- iptables
- Tcp-wrappers
80. What are the basic elements of firewall?
Answer: A firewall should be able to filter packets (drop/pass them) based on certain rules specified by the user. The rules may be used to identify an incoming packet to the computer or outgoing packet from the computer, it can be based on target port number/ip add, traffic from a particular Network card etc…
The firewall rules can be in a tabular form (saved on the disk) from where the firewall software can read them and implement it. iptables firewall on Linux is a great example
81. What is a command to display top 10 users who are using huge space?
Answer: du -sh /home/* | sort -r | head -10
82. How do find all failed login attempts via ssh?
Answer: tail -f /var/log/secure | grep Failed
83. How do you configure Linux system as a router?
Answer:
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
system-config-network
eth0 192.168.1.120 eth0:1 172.24.0.1
255.255.255.0 255.255.0.0
172.24.0.1 192.168.1.120
84. What is the UID and GID of root user? Can a normal user can change the ownership of a file? What is the command to change ownership of a file?
Answer: The root UID/GID is 0 (zero). Which is why he can able to intervene in all normal users files even though he don’t had permission. A normal user will don’t have the permission to change ownership of file. The command to change ownership is < chown user.user file >
85. What is the diff b/w ext2 and ext3?
Answer : Ext3 is a tiny bit slower than ext2 is, but it holds tremendous advantages. There is really only one difference between ext2 and ext3, and that is that ext3 uses a journal to prevent filesystem corruption in the case of an unclean shutdown (ie. before the filesystem is synced to disk). That makes ext3 a bit slower than ext2 since all metadata changes are written to the journal, and then flushed to disk, but on the other hand you don’t risk having the entire filesystem destroyed at power failure or if an unwitted person turns the computer off uncleanly. You don’t have to check the filesystem after an unclean shutdown either. Ext3 has three levels of journalling. Metadata (ie. internal filesystem structures) are always journalled, so that the filesystem itself is never corrupted. How ordinary data is written to the file system is controllable, though. The default option is the “ordered” mode, which causes file contents to be written to the filesystem before metadata is even committed to the journal. The highest reliable mode is called the “journal” mode, which causes file data to be committed to the journal before it is flushed to its final place, like the metadata. The least reliable mode, but rumoured to be the fastest, is called the “writeback” mode, which makes no promises at all regarding the consistency of file data. Only metadata is output reliably in writeback mode. So as for anything else, it’s mainly a matter of priority. If you don’t want ultimate speed, go with ext3. If you need the highest speed that is theoratically aquirable though, then go with ext2. For that to be effective you’ll probably need a really advanced hard drive controller, though.
86. As the system administrator you need to review Bob’s cronjobs. What command would you use?
Answer: crontab –lu Bob
87. What command is used to remove the password assigned to a group?
Answer: gpasswd –r groupname
88. What are the different RAID levels?
Answer:
- RAID level 0
- RAID level RAID level 1
- RAID level 2
- RAID level 3
- RAID level 4
- RAID level 5
- RAID level 6
- RAID level 10
- RAID level 50
89. How do you create a swapfile?
Answer:
dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1024 count=200M
mkswap /swapfile
swapon /swapfile
90. What does nslookup do?
Answer: Nslookup is a program used to find information about internet Domain Name server. The two modes of nslookup are: Interactive and non-interactive. Using ‘interactive mode’ user can query the name servers for the information pertaining to hosts and domains.
Using ‘non-interactive mode’ the user can just print the name and requested information of a host.
91. What is Linux and why is it so popular?
Answer : Linux is an operating system that uses UNIX like Operating system.
Unix interview questions with answers
92. How we can configure data hard derive during redhat 9 installation.
Answer : Have the data driver on a floppy drive. At the start of installation, when u boot from the CD/DVD, on the prompt, write “dd”. It will ask for the driver floppy later on and will load the sata driver. Then you can configure/partition the drive using disk druid or fdisk.
93. What is LILO?
Answer: LILO is Linux Loader is a boot loader for Linux. It is used to load Linux into the memory and start the Operating system.
94. What is the difference between home directory and working directory?
Answer : Home directory is the default working directory when a user logs in. On the other hand, working directory is the user’s current directory.
95. What is the difference between internal and external commands?
Answer : Internal commands are commands that are already loaded in the system. They can be executed any time and are independent.
96. Explain the difference between a static library and a dynamic library.
Answer: Static libraries are loaded when the program is compiled and dynamically-linked libraries are loaded in while.
97. What is LD_LIBRARY_PATH?
Answer : LD_LIBRARY_PATH is an environment variable. It is used for debugging a new library or a non standard library.
98.What is the file server in Linux server?
Answer : File server is used for file sharing. It enables the processes required for sharing.
99. What is NFS? What is its purpose?
Answer : NFS is Network File system. It is a file system used for sharing of files over a network.
100. How do I send email with linux?
Answer : Email can be sent in Linux using the mail command.