Explain Azure Cloud Services.
Azure Cloud Services is a Paas (platform-as-a-service) product that intends to provide robust, efficient, and cost-effective applications. Azure Cloud Services are hosted on virtual machines, and they let one have a higher degree of control over the VMs by allowing software installation on the VMs and also making them remotely accessible.
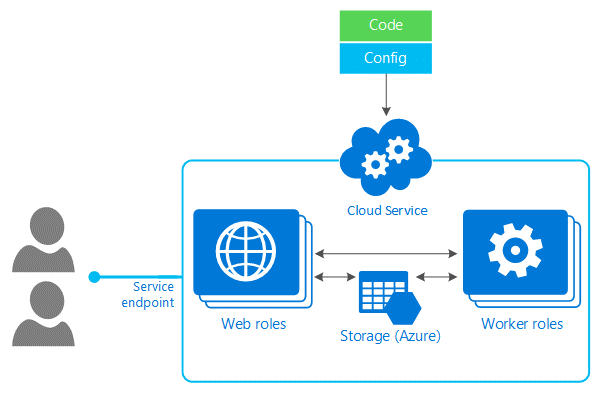
Source: Microsoft Azure docs
By launching a cloud service instance, Azure cloud services can be utilized to implement multi-tier web-based apps in Azure. Azure cloud services aid an application's scalability by making it easier and more adaptable. The two types of Azure Cloud Services roles are-
Web role (has a dedicated web server that uses IIS to automatically launch and host your app).
Worker role (allows apps to run by themselves without using IIS and helps run background processes).
What do you understand about the Azure SLA?
As the name suggests, Azure SLA (Service Level Agreement) is a service contract stating that when you deploy two or more role instances of a service on Azure, access to that cloud service is available for at least 99.9% of the time. It also indicates that if the role instance is not functioning, it will identify and resolve that role instance 99.9% of the time.
Suppose any of the points mentioned above fail to satisfy at any moment. In that case, Azure will credit the concerned user a certain percentage of their monthly payments based on the pricing model of the Azure services in question.
List the different cloud deployment models available in Azure.
Based on one's business requirements, there are three different cloud deployment models in which you can deploy any Azure cloud service -
Private Cloud- It comprises cloud computing resources owned entirely by a single company. This could mean hosting one's apps on their on-site servers or a dedicated server offered by the cloud service provider.
Public Cloud- The most common cloud deployment model, the public cloud, involves a third-party cloud service provider to manage and control the cloud resources distributed via the internet. The cloud provider owns all hardware, software, and other supporting facilities in this case. Example- Microsoft Azure.
Hybrid Cloud- A hybrid cloud is a blend of private and public clouds. These cloud deployment models employ private cloud service features such as processing confidential data and public cloud services such as hosting commercial applications.
Define IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
IaaS- IaaS stands for Infrastructure as a Service. It is a cloud computing service that hosts apps on the infrastructure and allows you to avail storage, networking resources, etc., on demand. Each resource is available as an individual service facility, and one has to only pay for it for as long as he needs to use it. Azure VM, VNET, etc., are some popularly known examples of IaaS.
PaaS- PaaS stands for Platform as a Service. It offers both- a cloud development and deployment environment, with facilities that enable users to produce simple cloud-based apps or even complex, cloud-enabled business systems. A user only pays for the resources he needs from a cloud service provider and accesses them over a secure Internet connection. Users are in charge of the applications and services they create, and the cloud service provider manages the rest. Azure web apps, Storage services, cloud services, and other services are all examples of PaaS.
SaaS- SaaS stands for Software as a Service. Organizations avail SaaS applications through a service delivery mechanism. This works by charging the organization for their use or by displaying advertisements. User interaction with cloud-based programs through the Internet can occur through software as a service (SaaS). The service provider's data center hosts the underlying infrastructure, software, and app data. Applications such as Office 365, Gmail, SharePoint Online, and others are examples of SaaS.
Explain Azure Redis Cache.
Azure Redis Cache is an in-memory data storage, or cache system, based on Redis that boosts the flexibility and efficiency of applications that rely significantly on backend data stores. It can handle massive numbers of application requests by storing highly trafficked data in server memory, where it can be written to and read fast. Redis open-source (OSS Redis) and Redis Enterprise (from Redis Labs) are both available as managed services through Azure Redis Cache. It offers safe and dedicated Redis server facilities and complete Redis API support. Microsoft runs this service, which can be helpful for any Azure-based or non-Azure-based application.
Why isn't there an MSDN class library reference for Azure Redis Cache?
Microsoft Azure Redis Cache is built on the famous open source Redis Cache and can be accessible by several Redis clients written in various computer languages. Every client has its API for making Redis commands calls to the cache instance. There is no unified class reference on MSDN since each client is unique and keeps its reference data.
What are availability sets?
An availability set is a cluster of virtual machines that enables Azure to understand how an application offers redundancy and high accessibility. To provide a highly available application and achieve the 99.95 percent Azure SLA, creating two or more VMs within an availability set is safer. The two domains assigned to every VM in an availability set are- an update domain and a fault domain.
Update domains combine virtual machines and the underlying hardware that can reboot simultaneously. Before the maintenance on a different update domain, a restarted update domain takes 30 minutes to recover.
Fault domains are the set of virtual machines that share a common power source and a common network switch. Virtual machines specified in your availability set are split into up to three failure domains by default. Integrating virtual machines into an availability set helps mitigate the impact of hardware malfunctions, network outages, and power outages.
Define Azure Functions in detail.
The Azure Functions is a serverless code computation service that allows you to run code without a server on demand, such as Events and External-Invoke. They are stateless and short-lived, and azure Functions may automatically scale up in response to the request. They tend to speed up the development process by avoiding the need to perform any integration coding for you to connect to other services. They also offer Azure Application Insights for monitoring and evaluating code performance, which aids in the identification of bottlenecks and failure locations throughout the application's components. You can write Functions in C#, Node, Java, Python, and other languages.
What do you understand about Azure Active Directory?
Microsoft's Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is a cloud-based authentication and authorization service. It weaves application access management, core directory services, and identity protection into a single solution. It enables all employees in an organization to sign in and access resources in the following areas:
i) External resources such as Microsoft 365, the Azure gateway, and millions of other SaaS services.
ii) Internal resources, such as apps on your company's intranet and network and any cloud service apps built by your company.
Define CSPack in Azure.
CSPack is a command-line tool that generates package files for applications that must deploy in Azure. CSPack uses the data from the service definition and service configuration files to define the content within a package. You can upload an application package file (.cspkg) to Azure via the Azure site using CSPack. The package is named [ServiceDefinitionFileName].cspkg by default, but you can change it with the /out option of CSPack. Every cloud service project contains a cscfg file, essentially a cloud service configuration file generated by the cspack tool.
Explain Azure Blob storage.
Azure Blob storage is a Microsoft storage offering that is meant explicitly for cloud objects and is suitable for holding vast quantities of unstructured data. Unstructured data, such as text or binary data, does not correspond to a specific data model or description.
Blob storage is suitable for sharing images/docs directly to a browser, storing files meant for multiple access, streaming audio/video files, backing up data, creating log files, etc.
There are three types of resources available in blob storage:
A storage account- In Azure, a storage account gives your data its namespace.
A container in the storage account- A container manages a group of blobs, and there are no constraints on the number of blobs stored in a container.
A blob within the container- A blob is a Binary Large Object (BLOB), which can be any form of file or document of any size. Azure supports three different types of Blobs:
Block blobs: These are meant to store individual blocks of text and binary files and have a storage capacity of up to 195GB.
Append blobs: These are useful for append tasks like logging data in log files.
Page blobs: These store random access files up to 8 TiB and are intended for reading/writing operations that occur often.
In this section, we'll cover some of the popular Azure interview questions along with their answers suitable for the role of Azure Solution Architect.
Explain Service Bus Queue and Storage Queue.
Azure Service Bus Queues belong to the Azure messaging framework and include queuing, publishing, subscribing, etc. They are part of the Service Bus and can pass messages through to other Queues and Topics. The Azure Service Bus Queues feature a built-in dead-letter queue and allow you to choose a timeline for messages so they can last as long as you want them to! They connect applications or parts of applications that cover different communication protocols, data treaties, trust domains, or security protocols.
Azure Storage Queues belong to the Azure storage framework and are easy to use. They allow easy debugging by using the local Azure Storage Emulator. The set of Azure Storage Queue tools enables you to take a quick look at the top 32 messages and visualize the contents of those belonging to XML/JSON right from Visual Studio. Another feature of storage queues that ensures smooth development and QA operations is that the contents of these queues can be emptied when needed. Authenticated HTTP or HTTPS calls allow you to access the queue messages regardless of your geographical location. Queue messages have a maximum capacity of 64 KB and can hold millions of messages depending upon the storage account's overall capacity limit.
Can you specify the storage limit associated with a virtual machine?
When it comes to the storage limit associated with virtual machines, each data disk has a maximum capacity of 1 TB. The amount of data disks one can use is determined by the virtual machine's size. Azure Managed Disks is a new and highly recommended disk storage option for Azure Virtual Machines for long-term data storage. Each Virtual Machine can have many Managed Disks. Premium and Standard Managed Disks are two types of long-term storage options offered by Managed Disks. Also, storage for the OS disk and any data disks can be provided via Azure storage accounts. Each disk is a page blob that is stored in a .vhd file format.
What is meant by Azure Cognitive Search?
Azure Cognitive Search is a cloud search solution that entrusts server and infrastructure maintenance to Microsoft. It provides developers with platforms, APIs, and tools for creating ready-to-use advanced search experiences in web, mobile, and corporate applications over private, diverse content. By using a simple REST API or.NET SDK, you can easily add a powerful search experience to your applications without having to manage search infrastructure or become a search specialist. For apps that depend exclusively on the search for both feature extraction and content navigation, Azure Cognitive Search is the ideal cloud provider for full-text search operations over content repositories and databases on Azure.
What is Azure CosmosDB?
Azure CosmosDB is one of the PaaS features offered by Microsoft. It is a cloud-based NoSQL database that deals mainly with modern app development. CosmosDB data can be easily shared and replicated anywhere in the world, which ensures faster and more efficient app development. Capacity management, automatic scaling, and serverless databases aid in matching demand with storage capacity.
Azure Cosmos DB takes care of database administration for you, including auto-management, updates, etc., and also includes features such as single-digit millisecond response times, rapid scalability, SLA-backed availability, and enterprise-grade privacy.
Which Cosmos DB component will you use if you need to provide your application temporary access to Cosmos DB?
The two URLs, Read and Read-Write, allow you to share your Azure Cosmos DB account with other people for a specified duration of time. Since the account access has an expiration time window of 24 hours, you can regain access by using a newly-generated access URL or the connection string.
Read URL- Other users can browse the databases, collections, queries, and other resources linked with that specific account, provided you share the read-only URL with them.
Read-Write URL- Other users can read and alter the databases, collections, queries, and other resources linked with that specific account if you share the Read-Write URL with them.
What Azure feature may be used to prevent high application load in the case of no-man assistance on the flow?
The solution to this problem involves using VM Scale sets, which define the necessary configuration and requirements for provisioning a new VM whenever there is an escalation in the application load. Developers can use Azure VM Scale Sets to build and manage a load-balanced collection of VMs. The number of virtual machine instances can be increased or decreased automatically in response to demand or a set timeline. Scale sets enable developers to facilitate the construction of large-scale applications that support huge data, massive workloads, and compute loads. They ensure the high availability of the applications and allow developers to manage, update, and configure large VMs centrally.
Is sticky session support available in Traffic Manager?
Since the Traffic Manager works at the DNS level, clients are directed to the ideal service endpoint using DNS responses. This also means that clients manage to connect directly to the service endpoint, bypassing Traffic Manager, which results in the HTTP traffic between the client and the server remaining unknown to the Traffic Manager. Furthermore, the recursive DNS service owns the source IP address of the DNS query received by the Traffic Manager instead of the client. As a result, Traffic Manager is unable to track individual clients or create sticky sessions. This constraint exists in the case of all DNS-based traffic control solutions, including Traffic Manager.
Explain the Site Recovery feature of Azure.
Site Recovery is a service that keeps corporate apps and workloads operational during outages, assuring smooth business processes. This feature offered by Azure works in such a way that it copies activities from a primary location to a secondary location with the help of physical and virtual machines (VMs). When your primary location goes down, you switch to the secondary location, where you can access the apps. You can roll back to the principal location once it has been restored. Site Recovery ensures replication for Azure VMs, on-site VMs, Azure Stack VMs, and physical servers.
What is meant by Azure Service Fabric?
Azure Service Fabric is a parallel processing platform that ensures simple packaging, smooth deployment, and efficient handling of robust and reliable microservices and containers. Service Fabric allows you to create microservice-based applications. The major constraints in designing and administering cloud-native apps are also handled by Service Fabric. It has a huge emphasis on designing stateful services. You can run container-based stateful services written in any language or code using the Service Fabric computing architecture. Also, you can create Service Fabric clusters in the private clouds with Windows Server and Linux, as well as in other public clouds.
How does Azure Traffic Manager differ from Azure Load Balancer?
Azure Traffic Manager is mainly responsible for sending traffic globally on the basis of dynamic principles. This leads to an enhanced user experience that reflects how your application is distributed worldwide. Your public endpoints will also experience benefits such as high accessibility and responsiveness. For diverse application objectives and spontaneous recovery systems, Traffic Manager offers a variety of traffic-routing mechanisms and endpoint tracking solutions.
The Azure Load Balancer handles the routing of traffic within a certain region. It is used together with Azure Traffic Manager, which directs traffic to a region between virtual machines. When the two are coupled, you get global traffic control with local backup. The Azure Load Balancer service offers a high-performance, low bandwidth Layer 4 load-balancing solution for all UDP and TCP protocols. It can ensure the smooth handling of millions of queries per second while maintaining high availability.
Distinguish between an Azure SQL Database and a SQL managed instance.
Azure SQL Database is a fully managed PaaS database server that keeps track of most database management tasks like data upgradations, patching, data backups, etc., without the need for human intervention. Azure SQL Database always runs on the most recent stable version of the Microsoft SQL Server database system, and its built-in PaaS capabilities allow you to concentrate on the domain-specific database management and performance activities that play a major role in upscaling your business. It also enables you to develop a highly accessible and rich in performance data storage layer for Azure apps and solutions.
Azure SQL Managed Instance is an efficient, highly scalable database solution by Microsoft. It is fully compatible with the latest SQL Server (Enterprise Edition) database system and offers a native VNet implementation that resolves basic safety issues, as well as a commercial model that is appealing to existing SQL Server users. Existing SQL Server users are enabled to migrate their local workloads to the cloud with minimal changes. Simultaneously, SQL Managed Instance retains all PaaS functionalities, including automated upgrades, automated backups, and high accessibility, thereby lowering administration expenses.
In Azure Synapse Analytics, what does a dedicated SQL pool mean?
The enterprise data warehousing solutions included in Azure Synapse Analytics are referred to as a dedicated SQL pool. When using Synapse SQL, a dedicated SQL pool constitutes a group of analytic tools that are deployed. Data Warehousing Units are solely responsible for determining the size of a dedicated SQL pool. Once the dedicated SQL pool is established, you can use basic PolyBase T-SQL queries to import massive amounts of data and then leverage the distributed data processor to run high-performance analyses. As data gets merged and analyzed, a dedicated SQL pool becomes the only source your company can rely on for reliable high-speed insights.
What are the steps to link SQL Management Studio to an Azure database?
i. The Connect to Server dialogue box automatically appears when you launch SQL Server Management Studio for the first time. Alternatively, you can also go to Object Explorer > Connect > Database Engine.
ii. Then, in the Connect to Server window, input the following information-
Server Type- Here, you need to enter the database engine
Server Name- Enter the name of the Azure SQL Database or Azure Managed Instance you want to use.
Authentication- Enter the SQL Server Authentication
Login- Enter the user ID for the server account.
Password- Enter the password for the server account.
iii. Once you've filled all the required fields, click on Connect.
If the firewall settings aren't configured, a popup occurs to do so. Provide the Azure account login credentials once you've signed in. After that, click OK.
iv. Select and browse Object Explorer for the hostname, SQL Server version, and username to see whether your Azure Database connection is successful.
Explain Azure Backup. Mention some of its advantages.
Azure Backup is a cloud-based solution offered by Microsoft that allows you to backup Azure Windows VMs, Azure Managed Disks, Azure File shares, SQL Server databases, SAP HANA databases, Azure PostgreSQL databases, etc.
Some primary benefits of Azure Backup include-
Azure Backup is a convenient way to back up your on-premises data to the cloud. Without building extensive on-premises backup solutions, you may get short and long-term backup.
Azure Backup enables separate backups to protect original data from unexpected damage. Backups are retained in a Recovery Services storage with built-in recovery point management.
Azure Backup delivers high availability with minimal maintenance or monitoring overhead by leveraging the Azure cloud's core ability and infinite capacity.
Discuss the different types of backups available in Azure?
To maintain the high availability of your data as well as storage, Azure Backup supports three methods of backup-
i. Locally redundant storage (LRS) copies your data three times in a centralized storage unit within the same region. LRS is a cost-effective option for safeguarding data against local hardware breakdowns.
ii. Geo-redundant storage (GRS) is the standard and preferred backup mode that replicates your data to a secondary region far away from the primary location of the source data. GRS is more expensive than LRS, but it provides greater data resilience, even in the event of a local disruption.
iii. Zone-redundant storage (ZRS) backs up data in availability zones, ensuring data retention and durability in the same zone. You can back up your essential activities that involve data retention and must run without disruption since ZRS has zero latency.
What types of storage services does Azure provide?
The following data options are provided on the Azure Storage platform:
i. Azure Blob Storage- Text and binary data can be stored in Azure Blobs, which is highly scalable object storage. It stores arbitrary data and allows them to be retrieved as block blobs on a huge scale.
ii. Azure File Storage- Managed file sharing for cloud and on-premises operations can be done with Azure Files. Using the standard Server Message Block (SMB) protocol, you can access fully managed cloud file shares from just about anywhere.
iii. Azure Queue Storage- Azure Queues is a messaging repository that allows application modules to communicate reliably. Asynchronous message queueing between software modules is supported.
iv. Azure Table Storage- Azure Tables is a NoSQL database for storing structured data without a schema. It lets you store organized NoSQL data in the cloud and provides a schemaless key/attribute storage.
v. Azure Disk Storage- Block-level storage units for Azure VMs are called Azure Disks. They allow data to be kept and retrieved from an associated virtual hard disk continuously.
How does a Classic Subscription Administrator role differ from a Directory Administrator role?
When you sign up for an Azure subscription, you are automatically assigned the Classic Subscription Administrator position. You have full access to the Azure subscription and can log in with a Microsoft account or an office/a personal account from the Azure subscription's directory. This job has access to the Azure interface and can manage services there with the help of the Azure site, Azure Resource Manager APIs, etc. You can add others as co-admins if they need to sign in and access services using the same Azure subscription. Both the owner and the co-admins have the same access.
Azure AD offers a set of various different admin roles that are responsible for governing different features. These administrators will be able to use the Azure portal to access a wide range of capabilities. The admin's status dictates the functions they can perform, such as modifying users, assigning administrative duties to others, handling domains, and all other tasks that belong to Azure AD resources in a directory.
What are Network Security Groups in Azure?
A network security group is a group of security rules (Access Control List of rules) that allow or prohibit incoming and outgoing network traffic for various Azure resources. Subnets or specific NICs connected to a subnet can be linked with NSGs in such a way that the rules apply to every single VM in that particular subnet. You can define the sender and receiver address, as well as the host and protocol, for each rule.
Define application partitions in Azure Active Directory.
The application partitions are directory partitions that are copied to domain controllers and belong to the Azure Active Directory system. These domain controllers that are involved in the partitioning procedure keep a copy of the partition. Application partitions have the advantage of being able to be cloned to any individual domain controller, potentially leading to traffic reduction. Although domain directory partitions can transport their entire data to all the domains, application partitions in the domain area can only target one. This minimizes the need for application partitions and thereby increases their availability.
What do you mean by Azure Resource Manager Templates (ARM)?
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates are JSON files mainly used to implement infrastructure as code for your Azure solutions. The template outlines your project's infrastructure and configuration. A declarative syntax is used in the template, which allows you to declare what you want to deliver without the use of any actual programming/coding. The template must include the resources to launch as well as their attributes.
Briefly discuss the Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) aims at the easy installation of a hosted Kubernetes cluster on Azure. It is solely responsible for managing containerized applications. It's an open-source solution for scaling, automatic deployment, and managing traffic. Azure deals with important functions like health diagnosis and management as a managed Kubernetes service. You solely manage and maintain the agent nodes because the Kubernetes masters are controlled by Azure. As a result, AKS is completely free; you only have to pay for the agent nodes in your clusters.
What is the procedure for adding an administrator to the Azure portal?
The owner role must be assigned to an administrator before it may be added to the Azure portal. It will only be able to control the subscription's resources that have been assigned to it. These are the steps to add an administrator:
i. Firstly, to use the Azure portal, go to https://azure.microsoft.com/en-in/features/azure-portal/ and sign in.
ii. Then, select the Hub menu followed by Subscription, and select the subscription that the administrator will need access to.
iii. In the subscription blade, select Access control (IAM) and then click Add.
iv. Select Owner from the drop-down menu under Select a role.
v. In this field, enter the email address of the user who will be designated as the owner.
vi. Select the user by clicking on his or her name.
Define table storage in Azure.
Huge quantities of structured data are stored in the Windows Azure Table storage service.
It is a NoSQL service that takes calls from both inside and outside the Windows Azure cloud.
Table: A table is a grouping of objects. Tables do not impose a format on entities; therefore, a single table can contain entities with various sets of characteristics. Many tables can be found in a single account.
Entity: Similar to a database entry, an entity is a collection of attributes. A single entity can be 1MB in size.
Properties: A name-value pair is referred to as a property. Each object can have up to 252 properties. In addition, each entity has three system properties: a partition key, a row key, and a timestamp.
Azure Cloud Engineer Interview Questions
Below are some of the popular Azure cloud engineer interview questions, along with their suitable answers.
Why do we use Profilers in Azure?
Azure Profilers are used to trace and assess the performance of applications that are under production in Azure. This is usually done to ensure that the application is stable and capable of handling high traffic. Profiler automatically collects data at scale without causing any inconvenience to your consumers. In order to address a certain web request, Profiler can assist you in finding the "hot" code route that takes up the longest time duration.
Define Content Delivery Networks in Azure.
A content delivery network (CDN) is a decentralized network of servers that delivers web information to users quickly and effectively. In order to reduce latency, CDNs keep buffer data on edge nodes in point-of-presence (POP) locations close to target users. Whether you are building or maintaining websites or mobile apps, encrypting and delivering streaming services, system updates, etc., the Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) can help you minimize the page load time, reduce bandwidth, and improve responsiveness.
What do you mean by Azure HDInsight?
Azure HDInsight is a Hadoop feature distribution on the cloud. It is responsible for faster and cost-effective processing of vast amounts of data in a configurable framework. You can deploy Hadoop, Spark, Hive, LLAP, Kafka, Storm, R, and other popular open-source frameworks. You can use these frameworks to allow situations that deal with extract, transform, and load (ETL), data warehousing, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
What do you mean by Azure File Sync?
Azure File Sync is a Microsoft service that enables you to centralize your organization's file shares in Azure Files in a way that does not hamper the flexibility, scalability, and consistency of a local file server. Your Windows Server machines become a rapid cache of your Azure file sharing, and to access your data locally, you can use any method supported by Windows Server, including SMB, Network File System (NFS), and File Transfer Protocol Service (FTPS).
Which Azure service allows users to identify email messages that should be regulated from a safety point of view through authentication, encryption, and identity regulations, and why?
The answer is the Azure Information Protection service.
When the Azure Information Protection client is installed, it interacts with the operations of end-users. Users and admins can access a file tracking website once a file has been protected. This gives them insight into who accesses the files and when these materials are accessed. Users have the opportunity to withdraw access to the file(s) in question if they detect any type of violation.
Explain Azure Virtual Networks (VNet).
The Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is the most basic component of your Azure private network. With the help of VNet, many types of Azure resources, such as Azure Virtual Machines (VM), can connect anonymously with one other, the internet, and even local networks. VNet works just like any standard network in a locally-owned data center, but in addition to a standard network's features, it offers Azure's operational features like scalability, availability, and exclusion. Interaction of Azure resources with the internet, connection with Azure resources, communication with local resources, screening and directing network traffic, and connection with Azure services are all scenarios that can be executed with a virtual network.
Mention the key segments of Windows Azure.
Windows Azure Compute: It provides a code that the hosting environment can control. A key benefit of using Azure Compute is that it is able to calculate through sections. Web Role, Worker Role, and VM Role are the three sorts of roles available.
Windows Azure Storage (VHD): Queue, Tables, Blobs, and Windows Azure Drives are the four types of storage services provided by Windows Azure Storage (VHD)
Windows Azure AppFabric: Service bus, Access, Caching, Integration, and Composite are the five services provided by Windows Azure AppFabric.
What is meant by autoscaling in Azure?
Autoscale is an inbuilt feature of Cloud Services, Virtual Machine Scale Sets, and Websites that enables applications to expand to adapt to changing demand. Scaling out refers to increasing the number of instances in a system. Scaling up in Windows Azure is also possible by using larger role instances rather than additional role instances. You may balance the performance of your Windows Azure application against its operational costs by adding and removing role instances while it is running. The amount of manual work necessary in dynamically scaling an application is reduced with an autoscaling solution.
Password resets are frequently required when users are shut out of their accounts. You opt to use Azure Self-Service to reset your password. What are your options for deploying this service? What types of authentication are accepted?
First, you need to select the total number of authentication techniques for a password reset, and the number of authentication techniques users can access once you've enabled password reset for all. Ideally, you should keep multiple authentication options even though there's a need for just one. You can either send an email notification to the user's registered email address, a text or security code to the user's phone, or a series of security questions. Security questions can be customized to mandate a specified number of questions to be submitted for users in your Active Directory tenant (3-5). In addition, you must specify the number of correctly answered security questions that must be answered in order for an effective password reset.
In case of a missing server, how will you use Azure to execute code?
Azure Functions may run code without the need for a server. These services make complicated operations and issues easier to manage. They let clients access other services without having to manually code integrations, which accelerates development. Azure Application Insights can assist with code performance analysis and monitoring, as well as identifying inefficiencies and problem areas across multiple application modules.
In what way will you manage the Azure connectivity if an application's front-end hosting is done on Azure, but the user requires database hosting on a local server owing to safety reasons?
There are different ways to deal with this:
i. In case of fewer resources to be connected, a local database can be connected to such an application using the Azure VNET-based point-to-site service.
ii. Site-to-site or express routes are the solutions if more resources need to be connected. Due to the VPN's reliance on public infrastructures, such as the internet, response time may get delayed from site to site. Alternatively, express routes can be used in this scenario because they have a dedicated leased line that overcomes lag constraints.
iii. In case none of the above options are suitable, a Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) service can be built and hosted locally. The CRUD operations in the service would remain specific to the local database.
Suppose ‘Acc1' is the name of your Azure Cosmos DB account. Acc1 has a database associated with it called DB1. The database again consists of a container named Cont1, which has its partition key set to /city. What should you do if you wish to modify Container1's partition key?
Certain features offered by Azure Cosmos DB, such as Change Feed Processor and Bulk Executor Library, can be used to perform a live data transfer between containers. This enables data redistribution to meet the intended new partition key strategy, as well as subsequent application updates. As a result, you'll be able to update your partition key.
Suppose you're working on building an Azure web app as part of a solution for your business. The web app must allow users to sign in with their Facebook login credentials. What would you suggest, and why?
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) functionalities offered by the Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) can be linked into applications. Azure AD B2C uses OpenID Connect, which is supported by a wide network of services, including Twitter, Google, and several others. Azure AD B2C safeguards your applications from denial-of-service and password threats and features user interface customizations that make it simple to deploy into your existing applications.
Your company acquires customer purchase data from a variety of retail outlets, and you're working on a system that will analyze the data and forecast future customer purchases for each retailer. Which Azure service do you recommend?
Azure Machine Learning is a data analytics service offered by Microsoft that provides end-to-end solutions for data science problems. It is a data science method that enables computers to predict future actions, results, and trends on the basis of given data. Computers that implement the machine learning technology can operate without any specific hard-core programming. Azure Machine Learning offers many open-source features that allow users to design, implement, and manage predictive models across a variety of environments.
A company has multiple virtual machines (VMs) that were generated using the standard deployment approach. To improve administration, you should transfer the standard VMs to Azure Resource Groups. What are your alternatives for resolving this?
When resources were produced under the old deployment model, there was no provision for resource group management, resulting in the management of higher numbers of resources and the difficulty of executing easy resource management in a unified manner. The latest Azure Resource Manager deployment approach, on the other hand, allows you to move resources like virtual machines between resources, even VMs produced using the classic deployment style. To migrate standard VMs to resource groups, you can try using the Azure portal, Azure PowerShell, or the Azure CLI.
You've decided to use Multiple Stage Builds to improve the accessibility and management of the Dockerfile. What are the points to consider for having multiple-stage builds?
You should consider using Container Modularity, avoiding Application Data, avoiding any extra modules, and adopting an Appropriate Base. Multi-stage builds are a recently updated feature that requires at least Docker 17.05 on both the daemon and the client. Those who are willing to improve Dockerfiles while making them comprehensible and manageable would benefit from multi-stage builds.
