Basic AWS Interview Questions
1. Define and explain the three basic types of cloud services and the AWS products that are built based on them?
The three basic types of cloud services are:
- Computing
- Storage
- Networking
Here are some of the AWS products that are built based on the three cloud service types:
Computing - These include EC2, Elastic Beanstalk, Lambda, Auto-Scaling, and Lightsat.
Storage - These include S3, Glacier, Elastic Block Storage, Elastic File System.
Networking - These include VPC, Amazon CloudFront, Route53
The three basic types of cloud services are:
- Computing
- Storage
- Networking
Here are some of the AWS products that are built based on the three cloud service types:
Computing - These include EC2, Elastic Beanstalk, Lambda, Auto-Scaling, and Lightsat.
Storage - These include S3, Glacier, Elastic Block Storage, Elastic File System.
Networking - These include VPC, Amazon CloudFront, Route53
2. What is the relation between the Availability Zone and Region?
AWS regions are separate geographical areas, like the US-West 1 (North California) and Asia South (Mumbai). On the other hand, availability zones are the areas that are present inside the regions. These are generally isolated zones that can replicate themselves whenever required.
AWS regions are separate geographical areas, like the US-West 1 (North California) and Asia South (Mumbai). On the other hand, availability zones are the areas that are present inside the regions. These are generally isolated zones that can replicate themselves whenever required.
3. What is auto-scaling?
Auto-scaling is a function that allows you to provision and launch new instances whenever there is a demand. It allows you to automatically increase or decrease resource capacity in relation to the demand.
Auto-scaling is a function that allows you to provision and launch new instances whenever there is a demand. It allows you to automatically increase or decrease resource capacity in relation to the demand.
4. What is geo-targeting in CloudFront?
Geo-Targeting is a concept where businesses can show personalized content to their audience based on their geographic location without changing the URL. This helps you create customized content for the audience of a specific geographical area, keeping their needs in the forefront.
Geo-Targeting is a concept where businesses can show personalized content to their audience based on their geographic location without changing the URL. This helps you create customized content for the audience of a specific geographical area, keeping their needs in the forefront.
5. What are the steps involved in a CloudFormation Solution?
Here are the steps involved in a CloudFormation solution:
- Create or use an existing CloudFormation template using JSON or YAML format.
- Save the code in an S3 bucket, which serves as a repository for the code.
- Use AWS CloudFormation to call the bucket and create a stack on your template.
- CloudFormation reads the file and understands the services that are called, their order, the relationship between the services, and provisions the services one after the other.
Here are the steps involved in a CloudFormation solution:
- Create or use an existing CloudFormation template using JSON or YAML format.
- Save the code in an S3 bucket, which serves as a repository for the code.
- Use AWS CloudFormation to call the bucket and create a stack on your template.
- CloudFormation reads the file and understands the services that are called, their order, the relationship between the services, and provisions the services one after the other.
6. How do you upgrade or downgrade a system with near-zero downtime?
You can upgrade or downgrade a system with near-zero downtime using the following steps of migration:
- Open EC2 console
- Choose Operating System AMI
- Launch an instance with the new instance type
- Install all the updates
- Install applications
- Test the instance to see if it’s working
- If working, deploy the new instance and replace the older instance
- Once it’s deployed, you can upgrade or downgrade the system with near-zero downtime.
Take home these interview Q&As and get much more. Download the complete AWS Interview Guide here:
You can upgrade or downgrade a system with near-zero downtime using the following steps of migration:
- Open EC2 console
- Choose Operating System AMI
- Launch an instance with the new instance type
- Install all the updates
- Install applications
- Test the instance to see if it’s working
- If working, deploy the new instance and replace the older instance
- Once it’s deployed, you can upgrade or downgrade the system with near-zero downtime.
Take home these interview Q&As and get much more. Download the complete AWS Interview Guide here:
7. What are the tools and techniques that you can use in AWS to identify if you are paying more than you should be, and how to correct it?
You can know that you are paying the correct amount for the resources that you are using by employing the following resources:
You can know that you are paying the correct amount for the resources that you are using by employing the following resources:
Check the Top Services Table
- It is a dashboard in the cost management console that shows you the top five most used services. This will let you know how much money you are spending on the resources in question.
- It is a dashboard in the cost management console that shows you the top five most used services. This will let you know how much money you are spending on the resources in question.
Cost Explorer
- There are cost explorer services available that will help you to view and analyze your usage costs for the last 13 months. You can also get a cost forecast for the upcoming three months.
- There are cost explorer services available that will help you to view and analyze your usage costs for the last 13 months. You can also get a cost forecast for the upcoming three months.
AWS Budgets
- This allows you to plan a budget for the services. Also, it will enable you to check if the current plan meets your budget and the details of how you use the services.
- This allows you to plan a budget for the services. Also, it will enable you to check if the current plan meets your budget and the details of how you use the services.
Cost Allocation Tags
- This helps in identifying the resource that has cost more in a particular month. It lets you organize your resources and cost allocation tags to keep track of your AWS costs.
- This helps in identifying the resource that has cost more in a particular month. It lets you organize your resources and cost allocation tags to keep track of your AWS costs.
Learn From The Best AWS Mentors!
8. Is there any other alternative tool to log into the cloud environment other than console?
The that can help you log into the AWS resources are:
- Putty
- AWS CLI for Linux
- AWS CLI for Windows
- AWS CLI for Windows CMD
- AWS SDK
- Eclipse
The that can help you log into the AWS resources are:
- Putty
- AWS CLI for Linux
- AWS CLI for Windows
- AWS CLI for Windows CMD
- AWS SDK
- Eclipse
9. What services can be used to create a centralized logging solution?
The essential services that you can use are Amazon CloudWatch Logs, store them in Amazon S3, and then use Amazon Elastic Search to visualize them. You can use Amazon Kinesis Firehose to move the data from Amazon S3 to Amazon ElasticSearch.
The essential services that you can use are Amazon CloudWatch Logs, store them in Amazon S3, and then use Amazon Elastic Search to visualize them. You can use Amazon Kinesis Firehose to move the data from Amazon S3 to Amazon ElasticSearch.
10. What are the native AWS Security logging capabilities?
Most of the AWS services have their logging options. Also, some of them have an account level logging, like in AWS CloudTrail, AWS Config, and others. Let’s take a look at two services in specific:
Most of the AWS services have their logging options. Also, some of them have an account level logging, like in AWS CloudTrail, AWS Config, and others. Let’s take a look at two services in specific:
AWS CloudTrail
This is a service that provides a history of the AWS API calls for every account. It lets you perform security analysis, resource change tracking, and compliance auditing of your AWS environment as well. The best part about this service is that it enables you to configure it to send notifications via AWS SNS when new logs are delivered.
This is a service that provides a history of the AWS API calls for every account. It lets you perform security analysis, resource change tracking, and compliance auditing of your AWS environment as well. The best part about this service is that it enables you to configure it to send notifications via AWS SNS when new logs are delivered.
AWS Config
This helps you understand the configuration changes that happen in your environment. This service provides an AWS inventory that includes configuration history, configuration change notification, and relationships between AWS resources. It can also be configured to send information via AWS SNS when new logs are delivered.
This helps you understand the configuration changes that happen in your environment. This service provides an AWS inventory that includes configuration history, configuration change notification, and relationships between AWS resources. It can also be configured to send information via AWS SNS when new logs are delivered.
11. What is a DDoS attack, and what services can minimize them?
DDoS is a cyber-attack in which the perpetrator accesses a website and creates multiple sessions so that the other legitimate users cannot access the service. The native tools that can help you deny the DDoS attacks on your AWS services are:
- AWS Shield
- AWS WAF
- Amazon Route53
- Amazon CloudFront
- ELB
- VPC
DDoS is a cyber-attack in which the perpetrator accesses a website and creates multiple sessions so that the other legitimate users cannot access the service. The native tools that can help you deny the DDoS attacks on your AWS services are:
- AWS Shield
- AWS WAF
- Amazon Route53
- Amazon CloudFront
- ELB
- VPC
12. You are trying to provide a service in a particular region, but you do not see the service in that region. Why is this happening, and how do you fix it?
Not all Amazon AWS services are available in all regions. When Amazon initially launches a new service, it doesn’t get immediately published in all the regions. They start small and then slowly expand to other regions. So, if you don’t see a specific service in your region, chances are the service hasn’t been published in your region yet. However, if you want to get the service that is not available, you can switch to the nearest region that provides the services.
Not all Amazon AWS services are available in all regions. When Amazon initially launches a new service, it doesn’t get immediately published in all the regions. They start small and then slowly expand to other regions. So, if you don’t see a specific service in your region, chances are the service hasn’t been published in your region yet. However, if you want to get the service that is not available, you can switch to the nearest region that provides the services.
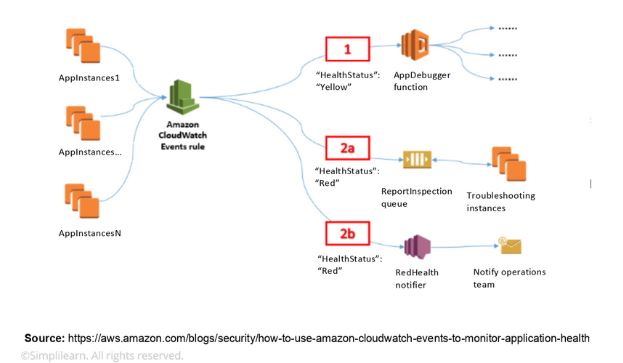
13. How do you set up a system to monitor website metrics in real-time in AWS?
Amazon CloudWatch helps you to monitor the application status of various AWS services and custom events. It helps you to monitor:
- State changes in Amazon EC2
- Auto-scaling lifecycle events
- Scheduled events
- AWS API calls
- Console sign-in events
Amazon CloudWatch helps you to monitor the application status of various AWS services and custom events. It helps you to monitor:
- State changes in Amazon EC2
- Auto-scaling lifecycle events
- Scheduled events
- AWS API calls
- Console sign-in events
14. What are the different types of virtualization in AWS, and what are the differences between them?
The three major types of virtualization in AWS are:
The three major types of virtualization in AWS are:
Hardware Virtual Machine (HVM)
- It is a fully virtualized hardware, where all the virtual machines act separate from each other. These virtual machines boot by executing a master boot record in the root block device of your image.
- It is a fully virtualized hardware, where all the virtual machines act separate from each other. These virtual machines boot by executing a master boot record in the root block device of your image.
Paravirtualization (PV)
- Paravirtualization-GRUB is the bootloader that boots the PV AMIs. The PV-GRUB chain loads the kernel specified in the menu.
- Paravirtualization-GRUB is the bootloader that boots the PV AMIs. The PV-GRUB chain loads the kernel specified in the menu.
Paravirtualization on HVM
- PV on HVM helps operating systems take advantage of storage and network I/O available through the host.
- PV on HVM helps operating systems take advantage of storage and network I/O available through the host.
15. Name some of the AWS services that are not region-specific
AWS services that are not region-specific are:
- IAM
- Route 53
- Web Application Firewall
- CloudFront
AWS services that are not region-specific are:
- IAM
- Route 53
- Web Application Firewall
- CloudFront
Want a Job at AWS? Find Out What It Takes
16. What are the differences between NAT Gateways and NAT Instances?
While both NAT Gateways and NAT Instances serve the same function, they still have some key differences.
While both NAT Gateways and NAT Instances serve the same function, they still have some key differences.
17. What is CloudWatch?
The Amazon CloudWatch has the following features:
- Depending on multiple metrics, it participates in triggering alarms.
- Helps in monitoring the AWS environments like CPU utilization, EC2, Amazon RDS instances, Amazon SQS, S3, Load Balancer, SNS, etc.
The Amazon CloudWatch has the following features:
- Depending on multiple metrics, it participates in triggering alarms.
- Helps in monitoring the AWS environments like CPU utilization, EC2, Amazon RDS instances, Amazon SQS, S3, Load Balancer, SNS, etc.
18. What is an Elastic Transcoder?
To support multiple devices with various resolutions like laptops, tablets, and smartphones, we need to change the resolution and format of the video. This can be done easily by an AWS Service tool called the Elastic Transcoder, which is a media transcoding in the cloud that exactly lets us do the needful. It is easy to use, cost-effective, and highly scalable for businesses and developers.
To support multiple devices with various resolutions like laptops, tablets, and smartphones, we need to change the resolution and format of the video. This can be done easily by an AWS Service tool called the Elastic Transcoder, which is a media transcoding in the cloud that exactly lets us do the needful. It is easy to use, cost-effective, and highly scalable for businesses and developers.
AWS Interview Questions for Intermediate and Experienced
19. With specified private IP addresses, can an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instance be launched? If so, which Amazon service makes it possible?
Yes. Utilizing VPC makes it possible (Virtual Private Cloud).
Yes. Utilizing VPC makes it possible (Virtual Private Cloud).
20. Define Amazon EC2 regions and availability zones?
Availability zones are geographically separate locations. As a result, failure in one zone has no effect on EC2 instances in other zones. When it comes to regions, they may have one or more availability zones. This configuration also helps to reduce latency and costs.
Availability zones are geographically separate locations. As a result, failure in one zone has no effect on EC2 instances in other zones. When it comes to regions, they may have one or more availability zones. This configuration also helps to reduce latency and costs.
21. Explain Amazon EC2 root device volume?
The image that will be used to boot an EC2 instance is stored on the root device drive. This occurs when an Amazon AMI runs a new EC2 instance. And this root device volume is supported by EBS or an instance store. In general, the root device data on Amazon EBS is not affected by the lifespan of an EC2 instance.
The image that will be used to boot an EC2 instance is stored on the root device drive. This occurs when an Amazon AMI runs a new EC2 instance. And this root device volume is supported by EBS or an instance store. In general, the root device data on Amazon EBS is not affected by the lifespan of an EC2 instance.
22. Mention the different types of instances in Amazon EC2 and explain its features.
- General Purpose Instances: They are used to compute a range of workloads and aid in the allocation of processing, memory, and networking resources.
- Compute Optimized Instances: These are ideal for compute-intensive applications. They can handle batch processing workloads, high-performance web servers, machine learning inference, and various other tasks.
- Memory Optimized: They process workloads that handle massive datasets in memory and deliver them quickly.
- Accelerated Computing: It aids in the execution of floating-point number calculations, data pattern matching, and graphics processing. These functions are carried out using hardware accelerators.
- Storage Optimised: They handle tasks that require sequential read and write access to big data sets on local storage.
- General Purpose Instances: They are used to compute a range of workloads and aid in the allocation of processing, memory, and networking resources.
- Compute Optimized Instances: These are ideal for compute-intensive applications. They can handle batch processing workloads, high-performance web servers, machine learning inference, and various other tasks.
- Memory Optimized: They process workloads that handle massive datasets in memory and deliver them quickly.
- Accelerated Computing: It aids in the execution of floating-point number calculations, data pattern matching, and graphics processing. These functions are carried out using hardware accelerators.
- Storage Optimised: They handle tasks that require sequential read and write access to big data sets on local storage.
23. Will your standby RDS be launched in the same availability zone as your primary?
No, standby instances are launched in different availability zones than the primary, resulting in physically separate infrastructures. This is because the entire purpose of standby instances is to prevent infrastructure failure. As a result, if the primary instance fails, the backup instance will assist in recovering all of the data.
No, standby instances are launched in different availability zones than the primary, resulting in physically separate infrastructures. This is because the entire purpose of standby instances is to prevent infrastructure failure. As a result, if the primary instance fails, the backup instance will assist in recovering all of the data.
Want a Job at AWS? Find Out What It Takes
Advanced AWS Interview Questions and Answers
24. What is the difference between a Spot Instance, an On-demand Instance, and a Reserved Instance?
Spot instances are unused EC2 instances that users can use at a reduced cost.
When you use on-demand instances, you must pay for computing resources without making long-term obligations.
Reserved instances, on the other hand, allow you to specify attributes such as instance type, platform, tenancy, region, and availability zone. Reserved instances offer significant reductions and capacity reservations when instances in certain availability zones are used.
Spot instances are unused EC2 instances that users can use at a reduced cost.
When you use on-demand instances, you must pay for computing resources without making long-term obligations.
Reserved instances, on the other hand, allow you to specify attributes such as instance type, platform, tenancy, region, and availability zone. Reserved instances offer significant reductions and capacity reservations when instances in certain availability zones are used.
25. How would you address a situation in which the relational database engine frequently collapses when traffic to your RDS instances increases, given that the RDS instance replica is not promoted as the master instance?
A larger RDS instance type is required for handling significant quantities of traffic, as well as producing manual or automated snapshots to recover data if the RDS instance fails.
A larger RDS instance type is required for handling significant quantities of traffic, as well as producing manual or automated snapshots to recover data if the RDS instance fails.
26. What do you understand by 'changing' in Amazon EC2?
To make limit administration easier for customers, Amazon EC2 now offers the option to switch from the current 'instance count-based limitations' to the new 'vCPU Based restrictions.' As a result, when launching a combination of instance types based on demand, utilization is measured in terms of the number of vCPUs.
To make limit administration easier for customers, Amazon EC2 now offers the option to switch from the current 'instance count-based limitations' to the new 'vCPU Based restrictions.' As a result, when launching a combination of instance types based on demand, utilization is measured in terms of the number of vCPUs.
27. Define Snapshots in Amazon Lightsail?
The point-in-time backups of EC2 instances, block storage drives, and databases are known as snapshots. They can be produced manually or automatically at any moment. Your resources can always be restored using snapshots, even after they have been created. These resources will also perform the same tasks as the original ones from which the snapshots were made.
The point-in-time backups of EC2 instances, block storage drives, and databases are known as snapshots. They can be produced manually or automatically at any moment. Your resources can always be restored using snapshots, even after they have been created. These resources will also perform the same tasks as the original ones from which the snapshots were made.
AWS Scenario-based Questions
28. On an EC2 instance, an application of yours is active. Once the CPU usage on your instance hits 80%, you must reduce the load on it. What strategy do you use to complete the task?
It can be accomplished by setting up an autoscaling group to deploy additional instances, when an EC2 instance's CPU use surpasses 80% and by allocating traffic across instances via the creation of an application load balancer and the designation of EC2 instances as target instances.
It can be accomplished by setting up an autoscaling group to deploy additional instances, when an EC2 instance's CPU use surpasses 80% and by allocating traffic across instances via the creation of an application load balancer and the designation of EC2 instances as target instances.
29. Multiple Linux Amazon EC2 instances running a web application for a firm are being used, and data is being stored on Amazon EBS volumes. The business is searching for a way to provide storage that complies with atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability while also increasing the application's resilience in the event of a breakdown (ACID). What steps should a solutions architect take to fulfill these demands?
AWS Auto Scaling groups can create an application load balancer that spans many availability zones. Mount a target on each instance and save data on Amazon EFS.
AWS Auto Scaling groups can create an application load balancer that spans many availability zones. Mount a target on each instance and save data on Amazon EFS.
30. Your business prefers to use its email address and domain to send and receive compliance emails. What service do you recommend to implement it easily and budget-friendly?
This can be accomplished by using Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES), a cloud-based email-sending service.
This can be accomplished by using Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES), a cloud-based email-sending service.
Technical and Non-Technical AWS Interview Questions
31. Describe SES.
Amazon offers the Simple Email Service (SES) service, which allows you to send bulk emails to customers swiftly at a minimal cost.
Amazon offers the Simple Email Service (SES) service, which allows you to send bulk emails to customers swiftly at a minimal cost.
32. Describe PaaS.
PaaS supports the operation of multiple cloud platforms, primarily for the development, testing, and oversight of the operation of the program.
PaaS supports the operation of multiple cloud platforms, primarily for the development, testing, and oversight of the operation of the program.
33. How many S3 buckets can be created?
Up to 100 buckets can be created by default.
Up to 100 buckets can be created by default.
34. What is the maximum limit of elastic IPs anyone can produce?
A maximum of five elastic IP addresses can be generated per location and AWS account.
A maximum of five elastic IP addresses can be generated per location and AWS account.
AWS Questions for Amazon EC2
35. What is Amazon EC2?
EC2 is short for Elastic Compute Cloud, and it provides scalable computing capacity. Using Amazon EC2 eliminates the need to invest in hardware, leading to faster development and deployment of applications. You can use Amazon EC2 to launch as many or as few virtual servers as needed, configure security and networking, and manage storage. It can scale up or down to handle changes in requirements, reducing the need to forecast traffic. EC2 provides virtual computing environments called “instances.”
EC2 is short for Elastic Compute Cloud, and it provides scalable computing capacity. Using Amazon EC2 eliminates the need to invest in hardware, leading to faster development and deployment of applications. You can use Amazon EC2 to launch as many or as few virtual servers as needed, configure security and networking, and manage storage. It can scale up or down to handle changes in requirements, reducing the need to forecast traffic. EC2 provides virtual computing environments called “instances.”
36. What Are Some of the Security Best Practices for Amazon EC2?
Security best practices for Amazon EC2 include using Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access to AWS resources; restricting access by only allowing trusted hosts or networks to access ports on an instance; only opening up those permissions you require, and disabling password-based logins for instances launched from your AMI.
Security best practices for Amazon EC2 include using Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access to AWS resources; restricting access by only allowing trusted hosts or networks to access ports on an instance; only opening up those permissions you require, and disabling password-based logins for instances launched from your AMI.
37. Can S3 Be Used with EC2 Instances, and If Yes, How?
Amazon S3 can be used for instances with root devices backed by local instance storage. That way, developers have access to the same highly scalable, reliable, fast, inexpensive data storage infrastructure that Amazon uses to run its own global network of websites. To execute systems in the Amazon EC2 environment, developers load Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) into Amazon S3 and then move them between Amazon S3 and Amazon EC2.
Amazon EC2 and Amazon S3 are two of the best-known web services that make up AWS.
Amazon S3 can be used for instances with root devices backed by local instance storage. That way, developers have access to the same highly scalable, reliable, fast, inexpensive data storage infrastructure that Amazon uses to run its own global network of websites. To execute systems in the Amazon EC2 environment, developers load Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) into Amazon S3 and then move them between Amazon S3 and Amazon EC2.
Amazon EC2 and Amazon S3 are two of the best-known web services that make up AWS.
38. What is the difference between stopping and terminating an EC2 instance?
While you may think that both stopping and terminating are the same, there is a difference. When you stop an EC2 instance, it performs a normal shutdown on the instance and moves to a stopped state. However, when you terminate the instance, it is transferred to a stopped state, and the EBS volumes attached to it are deleted and can never be recovered.
While you may think that both stopping and terminating are the same, there is a difference. When you stop an EC2 instance, it performs a normal shutdown on the instance and moves to a stopped state. However, when you terminate the instance, it is transferred to a stopped state, and the EBS volumes attached to it are deleted and can never be recovered.
39. What are the different types of EC2 instances based on their costs?
The three types of EC2 instances are:
The three types of EC2 instances are:
On-demand Instance
- It is cheap for a short time but not when taken for the long term
- It is cheap for a short time but not when taken for the long term
Spot Instance
- It is less expensive than the on-demand instance and can be bought through bidding.
- It is less expensive than the on-demand instance and can be bought through bidding.
Reserved Instance
- If you are planning to use an instance for a year or more, then this is the right one for you.
- If you are planning to use an instance for a year or more, then this is the right one for you.
Want a Job at AWS? Find Out What It Takes
40. How do you set up SSH agent forwarding so that you do not have to copy the key every time you log in?
Here’s how you accomplish this:
- Go to your PuTTY Configuration
- Go to the category SSH -> Auth
- Enable SSH agent forwarding to your instance
Here’s how you accomplish this:
- Go to your PuTTY Configuration
- Go to the category SSH -> Auth
- Enable SSH agent forwarding to your instance
41. What are Solaris and AIX operating systems? Are they available with AWS?
Solaris is an operating system that uses SPARC processor architecture, which is not supported by the public cloud currently.
AIX is an operating system that runs only on Power CPU and not on Intel, which means that you cannot create AIX instances in EC2.
Since both the operating systems have their limitations, they are not currently available with AWS.
Solaris is an operating system that uses SPARC processor architecture, which is not supported by the public cloud currently.
AIX is an operating system that runs only on Power CPU and not on Intel, which means that you cannot create AIX instances in EC2.
Since both the operating systems have their limitations, they are not currently available with AWS.
42. How do you configure CloudWatch to recover an EC2 instance?
Here’s how you can configure them:
- Create an Alarm using Amazon CloudWatch
- In the Alarm, go to Define Alarm -> Actions tab
- Choose Recover this instance option
Here’s how you can configure them:
- Create an Alarm using Amazon CloudWatch
- In the Alarm, go to Define Alarm -> Actions tab
- Choose Recover this instance option
43. What are the common types of AMI designs?
There are many types of AMIs, but some of the common AMIs are:
- Fully Baked AMI
- Just Enough Baked AMI (JeOS AMI)
- Hybrid AMI
There are many types of AMIs, but some of the common AMIs are:
- Fully Baked AMI
- Just Enough Baked AMI (JeOS AMI)
- Hybrid AMI
44. What are Key-Pairs in AWS?
The Key-Pairs are password-protected login credentials for the Virtual Machines that are used to prove our identity while connecting the Amazon EC2 instances. The Key-Pairs are made up of a Private Key and a Public Key which lets us connect to the instances.
The Key-Pairs are password-protected login credentials for the Virtual Machines that are used to prove our identity while connecting the Amazon EC2 instances. The Key-Pairs are made up of a Private Key and a Public Key which lets us connect to the instances.
AWS Interview Questions for S3
45. What is Amazon S3?
S3 is short for Simple Storage Service, and Amazon S3 is the most supported storage platform available. S3 is object storage that can store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere. Despite that versatility, it is practically unlimited as well as cost-effective because it is storage available on demand. In addition to these benefits, it offers unprecedented levels of durability and availability. Amazon S3 helps to manage data for cost optimization, access control, and compliance.
S3 is short for Simple Storage Service, and Amazon S3 is the most supported storage platform available. S3 is object storage that can store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere. Despite that versatility, it is practically unlimited as well as cost-effective because it is storage available on demand. In addition to these benefits, it offers unprecedented levels of durability and availability. Amazon S3 helps to manage data for cost optimization, access control, and compliance.
MBA With IU, Germany
46. How can you recover/login to an EC2 instance for which you have lost the key?
Follow the steps provided below to recover an EC2 instance if you have lost the key:
- Verify that the EC2Config service is running
- Detach the root volume for the instance
- Attach the volume to a temporary instance
- Modify the configuration file
- Restart the original instance
Follow the steps provided below to recover an EC2 instance if you have lost the key:
- Verify that the EC2Config service is running
- Detach the root volume for the instance
- Attach the volume to a temporary instance
- Modify the configuration file
- Restart the original instance
47. What are some critical differences between AWS S3 and EBS?
Here are some differences between AWS S3 and EBS
Here are some differences between AWS S3 and EBS
48. How do you allow a user to gain access to a specific bucket?
You need to follow the four steps provided below to allow access. They are:
- Categorize your instances
- Define how authorized users can manage specific servers.
- Lockdown your tags
- Attach your policies to IAM users
You need to follow the four steps provided below to allow access. They are:
- Categorize your instances
- Define how authorized users can manage specific servers.
- Lockdown your tags
- Attach your policies to IAM users
49. How can you monitor S3 cross-region replication to ensure consistency without actually checking the bucket?
Follow the flow diagram provided below to monitor S3 cross-region replication:
Follow the flow diagram provided below to monitor S3 cross-region replication:
50. What is SnowBall?
To transfer terabytes of data outside and inside of the AWS environment, a small application called SnowBall is used.
Data transferring using SnowBall is done in the following ways:
- A job is created.
- The SnowBall application is connected.
- The data is copied into the SnowBall application.
- Data is then moved to the AWS S3.
To transfer terabytes of data outside and inside of the AWS environment, a small application called SnowBall is used.
Data transferring using SnowBall is done in the following ways:
- A job is created.
- The SnowBall application is connected.
- The data is copied into the SnowBall application.
- Data is then moved to the AWS S3.
51. What are the Storage Classes available in Amazon S3?
The Storage Classes that are available in the Amazon S3 are the following:
- Amazon S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval storage class
- Amazon S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval (Formerly S3 Glacier) storage class
- Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive (S3 Glacier Deep Archive)
- S3 Outposts storage class
- Amazon S3 Standard-Infrequent Access (S3 Standard-IA)
- Amazon S3 One Zone-Infrequent Access (S3 One Zone-IA)
- Amazon S3 Standard (S3 Standard)
- Amazon S3 Reduced Redundancy Storage
- Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering (S3 Intelligent-Tiering)
The Storage Classes that are available in the Amazon S3 are the following:
- Amazon S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval storage class
- Amazon S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval (Formerly S3 Glacier) storage class
- Amazon S3 Glacier Deep Archive (S3 Glacier Deep Archive)
- S3 Outposts storage class
- Amazon S3 Standard-Infrequent Access (S3 Standard-IA)
- Amazon S3 One Zone-Infrequent Access (S3 One Zone-IA)
- Amazon S3 Standard (S3 Standard)
- Amazon S3 Reduced Redundancy Storage
- Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering (S3 Intelligent-Tiering)
Want a Job at AWS? Find Out What It Takes
AWS Interview Questions for VPC
52. What Is Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and Why Is It Used?
A VPC is the best way of connecting to your cloud resources from your own data center. Once you connect your datacenter to the VPC in which your instances are present, each instance is assigned a private IP address that can be accessed from your data center. That way, you can access your public cloud resources as if they were on your own private network.
A VPC is the best way of connecting to your cloud resources from your own data center. Once you connect your datacenter to the VPC in which your instances are present, each instance is assigned a private IP address that can be accessed from your data center. That way, you can access your public cloud resources as if they were on your own private network.
53. VPC is not resolving the server through DNS. What might be the issue, and how can you fix it?
To fix this problem, you need to enable the DNS hostname resolution, so that the problem resolves itself.
To fix this problem, you need to enable the DNS hostname resolution, so that the problem resolves itself.
54. How do you connect multiple sites to a VPC?
If you have multiple VPN connections, you can provide secure communication between sites using the AWS VPN CloudHub. Here’s a diagram that will show you how to connect various sites to a VPC:
If you have multiple VPN connections, you can provide secure communication between sites using the AWS VPN CloudHub. Here’s a diagram that will show you how to connect various sites to a VPC:
55. Name and explain some security products and features available in VPC?
Here is a selection of security products and features:
- Security groups - This acts as a firewall for the EC2 instances, controlling inbound and outbound traffic at the instance level.
- Network access control lists - It acts as a firewall for the subnets, controlling inbound and outbound traffic at the subnet level.
- Flow logs - These capture the inbound and outbound traffic from the network interfaces in your VPC.
Here is a selection of security products and features:
- Security groups - This acts as a firewall for the EC2 instances, controlling inbound and outbound traffic at the instance level.
- Network access control lists - It acts as a firewall for the subnets, controlling inbound and outbound traffic at the subnet level.
- Flow logs - These capture the inbound and outbound traffic from the network interfaces in your VPC.
56. How do you monitor Amazon VPC?
You can monitor VPC by using:
- CloudWatch and CloudWatch logs
- VPC Flow Logs
You can monitor VPC by using:
- CloudWatch and CloudWatch logs
- VPC Flow Logs
57. How many Subnets can you have per VPC?
We can have up to 200 Subnets per Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
We can have up to 200 Subnets per Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
General AWS Interview Questions
58. When Would You Prefer Provisioned IOPS over Standard Rds Storage?
You would use Provisioned IOPS when you have batch-oriented workloads. Provisioned IOPS delivers high IO rates, but it is also expensive. However, batch processing workloads do not require manual intervention.
You would use Provisioned IOPS when you have batch-oriented workloads. Provisioned IOPS delivers high IO rates, but it is also expensive. However, batch processing workloads do not require manual intervention.
59. How Do Amazon Rds, Dynamodb, and Redshift Differ from Each Other?
Amazon RDS is a database management service for relational databases. It manages patching, upgrading, and data backups automatically. It’s a database management service for structured data only. On the other hand, DynamoDB is a NoSQL database service for dealing with unstructured data. Redshift is a data warehouse product used in data analysis.
Amazon RDS is a database management service for relational databases. It manages patching, upgrading, and data backups automatically. It’s a database management service for structured data only. On the other hand, DynamoDB is a NoSQL database service for dealing with unstructured data. Redshift is a data warehouse product used in data analysis.
60. What Are the Benefits of AWS’s Disaster Recovery?
Businesses use cloud computing in part to enable faster disaster recovery of critical IT systems without the cost of a second physical site. The AWS cloud supports many popular disaster recovery architectures ranging from small customer workload data center failures to environments that enable rapid failover at scale. With data centers all over the world, AWS provides a set of cloud-based disaster recovery services that enable rapid recovery of your IT infrastructure and data.
Businesses use cloud computing in part to enable faster disaster recovery of critical IT systems without the cost of a second physical site. The AWS cloud supports many popular disaster recovery architectures ranging from small customer workload data center failures to environments that enable rapid failover at scale. With data centers all over the world, AWS provides a set of cloud-based disaster recovery services that enable rapid recovery of your IT infrastructure and data.
61. How can you add an existing instance to a new Auto Scaling group?
Here’s how you can add an existing instance to a new Auto Scaling group:
- Open EC2 console
- Select your instance under Instances
- Choose Actions -> Instance Settings -> Attach to Auto Scaling Group
- Select a new Auto Scaling group
- Attach this group to the Instance
- Edit the Instance if needed
- Once done, you can successfully add the instance to a new Auto Scaling group
Here’s how you can add an existing instance to a new Auto Scaling group:
- Open EC2 console
- Select your instance under Instances
- Choose Actions -> Instance Settings -> Attach to Auto Scaling Group
- Select a new Auto Scaling group
- Attach this group to the Instance
- Edit the Instance if needed
- Once done, you can successfully add the instance to a new Auto Scaling group
Want a Job at AWS? Find Out What It Takes
62. What are the factors to consider while migrating to Amazon Web Services?
Here are the factors to consider during AWS migration:
- Operational Costs - These include the cost of infrastructure, ability to match demand and supply, transparency, and others.
- Workforce Productivity
- Cost avoidance
- Operational resilience
- Business agility
Here are the factors to consider during AWS migration:
- Operational Costs - These include the cost of infrastructure, ability to match demand and supply, transparency, and others.
- Workforce Productivity
- Cost avoidance
- Operational resilience
- Business agility
63. What is RTO and RPO in AWS?
RTO or Recovery Time Objective is the maximum time your business or organization is willing to wait for a recovery to complete in the wake of an outage. On the other hand, RPO or Recovery Point Objective is the maximum amount of data loss your company is willing to accept as measured in time.
RTO or Recovery Time Objective is the maximum time your business or organization is willing to wait for a recovery to complete in the wake of an outage. On the other hand, RPO or Recovery Point Objective is the maximum amount of data loss your company is willing to accept as measured in time.
64. If you would like to transfer vast amounts of data, which is the best option among Snowball, Snowball Edge, and Snowmobile?
AWS Snowball is basically a data transport solution for moving high volumes of data into and out of a specified AWS region. On the other hand, AWS Snowball Edge adds additional computing functions apart from providing a data transport solution. The snowmobile is an exabyte-scale migration service that allows you to transfer data up to 100 PB.
AWS Snowball is basically a data transport solution for moving high volumes of data into and out of a specified AWS region. On the other hand, AWS Snowball Edge adds additional computing functions apart from providing a data transport solution. The snowmobile is an exabyte-scale migration service that allows you to transfer data up to 100 PB.
65. Explain what T2 instances are?
The T2 Instances are intended to give the ability to burst to a higher performance whenever the workload demands it and also provide a moderate baseline performance to the CPU.
The T2 instances are General Purpose instance types and are low in cost as well. They are usually used wherever workloads do not consistently or often use the CPU.
The T2 Instances are intended to give the ability to burst to a higher performance whenever the workload demands it and also provide a moderate baseline performance to the CPU.
The T2 instances are General Purpose instance types and are low in cost as well. They are usually used wherever workloads do not consistently or often use the CPU.
66. What are the advantages of AWS IAM?
AWS IAM allows an administrator to provide multiple users and groups with granular access. Various user groups and users may require varying levels of access to the various resources that have been developed. We may assign roles to users and create roles with defined access levels using IAM.
It further gives us Federated Access, which allows us to grant applications and users access to resources without having to create IAM Roles.
AWS IAM allows an administrator to provide multiple users and groups with granular access. Various user groups and users may require varying levels of access to the various resources that have been developed. We may assign roles to users and create roles with defined access levels using IAM.
It further gives us Federated Access, which allows us to grant applications and users access to resources without having to create IAM Roles.
67. Explain Connection Draining
Connection Draining is an AWS service that allows us to serve current requests on the servers that are either being decommissioned or updated.
By enabling this Connection Draining, we let the Load Balancer make an outgoing instance finish its existing requests for a set length of time before sending it any new requests. A departing instance will immediately go off if Connection Draining is not enabled, and all pending requests will fail.
Connection Draining is an AWS service that allows us to serve current requests on the servers that are either being decommissioned or updated.
By enabling this Connection Draining, we let the Load Balancer make an outgoing instance finish its existing requests for a set length of time before sending it any new requests. A departing instance will immediately go off if Connection Draining is not enabled, and all pending requests will fail.
68. What is Power User Access in AWS?
The AWS Resources owner is identical to an Administrator User. The Administrator User can build, change, delete, and inspect resources, as well as grant permissions to other AWS users.
Administrator Access without the ability to control users and permissions is provided to a Power User. A Power User Access user cannot provide permissions to other users but has the ability to modify, remove, view, and create resources.
The AWS Resources owner is identical to an Administrator User. The Administrator User can build, change, delete, and inspect resources, as well as grant permissions to other AWS users.
Administrator Access without the ability to control users and permissions is provided to a Power User. A Power User Access user cannot provide permissions to other users but has the ability to modify, remove, view, and create resources.AWS Questions for CloudFormation
69. How is AWS CloudFormation different from AWS Elastic Beanstalk?
Here are some differences between AWS CloudFormation and AWS Elastic Beanstalk:
- AWS CloudFormation helps you provision and describe all of the infrastructure resources that are present in your cloud environment. On the other hand, AWS Elastic Beanstalk provides an environment that makes it easy to deploy and run applications in the cloud.
- AWS CloudFormation supports the infrastructure needs of various types of applications, like legacy applications and existing enterprise applications. On the other hand, AWS Elastic Beanstalk is combined with the developer tools to help you manage the lifecycle of your applications.
Here are some differences between AWS CloudFormation and AWS Elastic Beanstalk:
- AWS CloudFormation helps you provision and describe all of the infrastructure resources that are present in your cloud environment. On the other hand, AWS Elastic Beanstalk provides an environment that makes it easy to deploy and run applications in the cloud.
- AWS CloudFormation supports the infrastructure needs of various types of applications, like legacy applications and existing enterprise applications. On the other hand, AWS Elastic Beanstalk is combined with the developer tools to help you manage the lifecycle of your applications.
70. What are the elements of an AWS CloudFormation template?
AWS CloudFormation templates are YAML or JSON formatted text files that are comprised of five essential elements, they are:
- Template parameters
- Output values
- Data tables
- Resources
- File format version
AWS CloudFormation templates are YAML or JSON formatted text files that are comprised of five essential elements, they are:
- Template parameters
- Output values
- Data tables
- Resources
- File format version
71. What happens when one of the resources in a stack cannot be created successfully?
If the resource in the stack cannot be created, then the CloudFormation automatically rolls back and terminates all the resources that were created in the CloudFormation template. This is a handy feature when you accidentally exceed your limit of Elastic IP addresses or don’t have access to an EC2 AMI.
If the resource in the stack cannot be created, then the CloudFormation automatically rolls back and terminates all the resources that were created in the CloudFormation template. This is a handy feature when you accidentally exceed your limit of Elastic IP addresses or don’t have access to an EC2 AMI.
AWS Questions for Elastic Block Storage
72. How can you automate EC2 backup using EBS?
Use the following steps in order to automate EC2 backup using EBS:
- Get the list of instances and connect to AWS through API to list the Amazon EBS volumes that are attached locally to the instance.
- List the snapshots of each volume, and assign a retention period of the snapshot. Later on, create a snapshot of each volume.
- Make sure to remove the snapshot if it is older than the retention period.
Use the following steps in order to automate EC2 backup using EBS:
- Get the list of instances and connect to AWS through API to list the Amazon EBS volumes that are attached locally to the instance.
- List the snapshots of each volume, and assign a retention period of the snapshot. Later on, create a snapshot of each volume.
- Make sure to remove the snapshot if it is older than the retention period.
73. What is the difference between EBS and Instance Store?
EBS is a kind of permanent storage in which the data can be restored at a later point. When you save data in the EBS, it stays even after the lifetime of the EC2 instance. On the other hand, Instance Store is temporary storage that is physically attached to a host machine. With an Instance Store, you cannot detach one instance and attach it to another. Unlike in EBS, data in an Instance Store is lost if any instance is stopped or terminated.
EBS is a kind of permanent storage in which the data can be restored at a later point. When you save data in the EBS, it stays even after the lifetime of the EC2 instance. On the other hand, Instance Store is temporary storage that is physically attached to a host machine. With an Instance Store, you cannot detach one instance and attach it to another. Unlike in EBS, data in an Instance Store is lost if any instance is stopped or terminated.
74. Can you take a backup of EFS like EBS, and if yes, how?
Yes, you can use the EFS-to-EFS backup solution to recover from unintended changes or deletion in Amazon EFS. Follow these steps:
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console
- Click the launch EFS-to-EFS-restore button
- Use the region selector in the console navigation bar to select region
- Verify if you have chosen the right template on the Select Template page
- Assign a name to your solution stack
- Review the parameters for the template and modify them if necessary
Yes, you can use the EFS-to-EFS backup solution to recover from unintended changes or deletion in Amazon EFS. Follow these steps:
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console
- Click the launch EFS-to-EFS-restore button
- Use the region selector in the console navigation bar to select region
- Verify if you have chosen the right template on the Select Template page
- Assign a name to your solution stack
- Review the parameters for the template and modify them if necessary
75. How do you auto-delete old snapshots?
Here’s the procedure for auto-deleting old snapshots:
- As per procedure and best practices, take snapshots of the EBS volumes on Amazon S3.
- Use AWS Ops Automator to handle all the snapshots automatically.
- This allows you to create, copy, and delete Amazon EBS snapshots.
Here’s the procedure for auto-deleting old snapshots:
- As per procedure and best practices, take snapshots of the EBS volumes on Amazon S3.
- Use AWS Ops Automator to handle all the snapshots automatically.
- This allows you to create, copy, and delete Amazon EBS snapshots.
AWS Interview Questions for Elastic Load Balancing
76. What are the different types of load balancers in AWS?
There are three types of load balancers that are supported by Elastic Load Balancing:
- Application Load Balancer
- Network Load Balancer
- Classic Load Balancer
There are three types of load balancers that are supported by Elastic Load Balancing:
- Application Load Balancer
- Network Load Balancer
- Classic Load Balancer
77. What are the different uses of the various load balancers in AWS Elastic Load Balancing?
Application Load Balancer
Used if you need flexible application management and TLS termination.
Used if you need flexible application management and TLS termination.
Network Load Balancer
Used if you require extreme performance and static IPs for your applications.
Used if you require extreme performance and static IPs for your applications.
Classic Load Balancer
Used if your application is built within the EC2 Classic network
Used if your application is built within the EC2 Classic network
AWS Interview Questions for Security
78. What Is Identity and Access Management (IAM) and How Is It Used?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a web service for securely controlling access to AWS services. IAM lets you manage users, security credentials such as access keys, and permissions that control which AWS resources users and applications can access.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a web service for securely controlling access to AWS services. IAM lets you manage users, security credentials such as access keys, and permissions that control which AWS resources users and applications can access.
79. How can you use AWS WAF in monitoring your AWS applications?
AWS WAF or AWS Web Application Firewall protects your web applications from web exploitations. It helps you control the traffic flow to your applications. With WAF, you can also create custom rules that block common attack patterns. It can be used for three cases: allow all requests, prevent all requests, and count all requests for a new policy.
AWS WAF or AWS Web Application Firewall protects your web applications from web exploitations. It helps you control the traffic flow to your applications. With WAF, you can also create custom rules that block common attack patterns. It can be used for three cases: allow all requests, prevent all requests, and count all requests for a new policy.
80. What are the different AWS IAM categories that you can control?
Using AWS IAM, you can do the following:
- Create and manage IAM users
- Create and manage IAM groups
- Manage the security credentials of the users
- Create and manage policies to grant access to AWS services and resources
Using AWS IAM, you can do the following:
- Create and manage IAM users
- Create and manage IAM groups
- Manage the security credentials of the users
- Create and manage policies to grant access to AWS services and resources
81. What are the policies that you can set for your users’ passwords?
Here are some of the policies that you can set:
- You can set a minimum length of the password, or you can ask the users to add at least one number or special characters in it.
- You can assign requirements of particular character types, including uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and non-alphanumeric characters.
- You can enforce automatic password expiration, prevent reuse of old passwords, and request for a password reset upon their next AWS sign in.
- You can have the AWS users contact an account administrator when the user has allowed the password to expire.
Here are some of the policies that you can set:
- You can set a minimum length of the password, or you can ask the users to add at least one number or special characters in it.
- You can assign requirements of particular character types, including uppercase letters, lowercase letters, numbers, and non-alphanumeric characters.
- You can enforce automatic password expiration, prevent reuse of old passwords, and request for a password reset upon their next AWS sign in.
- You can have the AWS users contact an account administrator when the user has allowed the password to expire.
82. What is the difference between an IAM role and an IAM user?
The two key differences between the IAM role and IAM user are:
- An IAM role is an IAM entity that defines a set of permissions for making AWS service requests, while an IAM user has permanent long-term credentials and is used to interact with the AWS services directly.
- In the IAM role, trusted entities, like IAM users, applications, or an AWS service, assume roles whereas the IAM user has full access to all the AWS IAM functionalities.
The two key differences between the IAM role and IAM user are:
- An IAM role is an IAM entity that defines a set of permissions for making AWS service requests, while an IAM user has permanent long-term credentials and is used to interact with the AWS services directly.
- In the IAM role, trusted entities, like IAM users, applications, or an AWS service, assume roles whereas the IAM user has full access to all the AWS IAM functionalities.
83. What are the managed policies in AWS IAM?
There are two types of managed policies; one that is managed by you and one that is managed by AWS. They are IAM resources that express permissions using IAM policy language. You can create, edit, and manage them separately from the IAM users, groups, and roles to which they are attached.
There are two types of managed policies; one that is managed by you and one that is managed by AWS. They are IAM resources that express permissions using IAM policy language. You can create, edit, and manage them separately from the IAM users, groups, and roles to which they are attached.
84. Can you give an example of an IAM policy and a policy summary?
Here’s an example of an IAM policy to grant access to add, update, and delete objects from a specific folder.
Here’s an example of a policy summary:
Here’s an example of an IAM policy to grant access to add, update, and delete objects from a specific folder.
Here’s an example of a policy summary:
85. How does AWS IAM help your business?
IAM enables to:
- Manage IAM users and their access - AWS IAM provides secure resource access to multiple users
- Manage access for federated users – AWS allows you to provide secure access to resources in your AWS account to your employees and applications without creating IAM roles
IAM enables to:
- Manage IAM users and their access - AWS IAM provides secure resource access to multiple users
- Manage access for federated users – AWS allows you to provide secure access to resources in your AWS account to your employees and applications without creating IAM roles
AWS Interview Questions for Route 53
86. What Is Amazon Route 53?
Amazon Route 53 is a scalable and highly available Domain Name System (DNS). The name refers to TCP or UDP port 53, where DNS server requests are addressed.
Amazon Route 53 is a scalable and highly available Domain Name System (DNS). The name refers to TCP or UDP port 53, where DNS server requests are addressed.
87. What Is Cloudtrail and How Do Cloudtrail and Route 53 Work Together?
CloudTrail is a service that captures information about every request sent to the Amazon Route 53 API by an AWS account, including requests that are sent by IAM users. CloudTrail saves log files of these requests to an Amazon S3 bucket. CloudTrail captures information about all requests. You can use information in the CloudTrail log files to determine which requests were sent to Amazon Route 53, the IP address that the request was sent from, who sent the request, when it was sent, and more.
CloudTrail is a service that captures information about every request sent to the Amazon Route 53 API by an AWS account, including requests that are sent by IAM users. CloudTrail saves log files of these requests to an Amazon S3 bucket. CloudTrail captures information about all requests. You can use information in the CloudTrail log files to determine which requests were sent to Amazon Route 53, the IP address that the request was sent from, who sent the request, when it was sent, and more.
88. What is the difference between Latency Based Routing and Geo DNS?
The Geo Based DNS routing takes decisions based on the geographic location of the request. Whereas, the Latency Based Routing utilizes latency measurements between networks and AWS data centers. Latency Based Routing is used when you want to give your customers the lowest latency possible. On the other hand, Geo Based routing is used when you want to direct the customer to different websites based on the country or region they are browsing from.
The Geo Based DNS routing takes decisions based on the geographic location of the request. Whereas, the Latency Based Routing utilizes latency measurements between networks and AWS data centers. Latency Based Routing is used when you want to give your customers the lowest latency possible. On the other hand, Geo Based routing is used when you want to direct the customer to different websites based on the country or region they are browsing from.
89. What is the difference between a Domain and a Hosted Zone?
Domain
A domain is a collection of data describing a self-contained administrative and technical unit. For example, www.simplilearn.com is a domain and a general DNS concept.
A domain is a collection of data describing a self-contained administrative and technical unit. For example, www.simplilearn.com is a domain and a general DNS concept.
Hosted zone
A hosted zone is a container that holds information about how you want to route traffic on the internet for a specific domain. For example, lms.simplilearn.com is a hosted zone.
A hosted zone is a container that holds information about how you want to route traffic on the internet for a specific domain. For example, lms.simplilearn.com is a hosted zone.
90. How does Amazon Route 53 provide high availability and low latency?
Here’s how Amazon Route 53 provides the resources in question:
Here’s how Amazon Route 53 provides the resources in question:
Globally Distributed Servers
Amazon is a global service and consequently has DNS services globally. Any customer creating a query from any part of the world gets to reach a DNS server local to them that provides low latency.
Amazon is a global service and consequently has DNS services globally. Any customer creating a query from any part of the world gets to reach a DNS server local to them that provides low latency.
Dependency
Route 53 provides a high level of dependability required by critical applications
Route 53 provides a high level of dependability required by critical applications
Optimal Locations
Route 53 uses a global anycast network to answer queries from the optimal position automatically.
Route 53 uses a global anycast network to answer queries from the optimal position automatically.
AWS Interview Questions for Config
91. How does AWS config work with AWS CloudTrail?
AWS CloudTrail records user API activity on your account and allows you to access information about the activity. Using CloudTrail, you can get full details about API actions such as the identity of the caller, time of the call, request parameters, and response elements. On the other hand, AWS Config records point-in-time configuration details for your AWS resources as Configuration Items (CIs).
You can use a CI to ascertain what your AWS resource looks like at any given point in time. Whereas, by using CloudTrail, you can quickly answer who made an API call to modify the resource. You can also use Cloud Trail to detect if a security group was incorrectly configured.
AWS CloudTrail records user API activity on your account and allows you to access information about the activity. Using CloudTrail, you can get full details about API actions such as the identity of the caller, time of the call, request parameters, and response elements. On the other hand, AWS Config records point-in-time configuration details for your AWS resources as Configuration Items (CIs).
You can use a CI to ascertain what your AWS resource looks like at any given point in time. Whereas, by using CloudTrail, you can quickly answer who made an API call to modify the resource. You can also use Cloud Trail to detect if a security group was incorrectly configured.
92. Can AWS Config aggregate data across different AWS accounts?
Yes, you can set up AWS Config to deliver configuration updates from different accounts to one S3 bucket, once the appropriate IAM policies are applied to the S3 bucket.
Yes, you can set up AWS Config to deliver configuration updates from different accounts to one S3 bucket, once the appropriate IAM policies are applied to the S3 bucket.
AWS Interview Questions for Database
93. How are reserved instances different from on-demand DB instances?
Reserved instances and on-demand instances are the same when it comes to function. They only differ in how they are billed.
Reserved instances are purchased as one-year or three-year reservations, and in return, you get very low hourly based pricing when compared to the on-demand cases that are billed on an hourly basis.
Reserved instances and on-demand instances are the same when it comes to function. They only differ in how they are billed.
Reserved instances are purchased as one-year or three-year reservations, and in return, you get very low hourly based pricing when compared to the on-demand cases that are billed on an hourly basis.
94. Which type of scaling would you recommend for RDS and why?
There are two types of scaling - vertical scaling and horizontal scaling. Vertical scaling lets you vertically scale up your master database with the press of a button. A database can only be scaled vertically, and there are 18 different instances in which you can resize the RDS. On the other hand, horizontal scaling is good for replicas. These are read-only replicas that can only be done through Amazon Aurora.
There are two types of scaling - vertical scaling and horizontal scaling. Vertical scaling lets you vertically scale up your master database with the press of a button. A database can only be scaled vertically, and there are 18 different instances in which you can resize the RDS. On the other hand, horizontal scaling is good for replicas. These are read-only replicas that can only be done through Amazon Aurora.
95. What is a maintenance window in Amazon RDS? Will your DB instance be available during maintenance events?
RDS maintenance window lets you decide when DB instance modifications, database engine version upgrades, and software patching have to occur. The automatic scheduling is done only for patches that are related to security and durability. By default, there is a 30-minute value assigned as the maintenance window and the DB instance will still be available during these events though you might observe a minimal effect on performance.
RDS maintenance window lets you decide when DB instance modifications, database engine version upgrades, and software patching have to occur. The automatic scheduling is done only for patches that are related to security and durability. By default, there is a 30-minute value assigned as the maintenance window and the DB instance will still be available during these events though you might observe a minimal effect on performance.
96. What are the consistency models in DynamoDB?
There are two consistency models In DynamoDB. First, there is the Eventual Consistency Model, which maximizes your read throughput. However, it might not reflect the results of a recently completed write. Fortunately, all the copies of data usually reach consistency within a second. The second model is called the Strong Consistency Model. This model has a delay in writing the data, but it guarantees that you will always see the updated data every time you read it.
There are two consistency models In DynamoDB. First, there is the Eventual Consistency Model, which maximizes your read throughput. However, it might not reflect the results of a recently completed write. Fortunately, all the copies of data usually reach consistency within a second. The second model is called the Strong Consistency Model. This model has a delay in writing the data, but it guarantees that you will always see the updated data every time you read it.
97. What type of query functionality does DynamoDB support?
DynamoDB supports GET/PUT operations by using a user-defined primary key. It provides flexible querying by letting you query on non-primary vital attributes using global secondary indexes and local secondary indexes.
DynamoDB supports GET/PUT operations by using a user-defined primary key. It provides flexible querying by letting you query on non-primary vital attributes using global secondary indexes and local secondary indexes.