In this article, we are going to discuss one of the important aspects of Amazon AWS, which is called Amazon SWS or SWF. it stands for Amazon simple workflow services. It’s a part of Amazon Web Services (AWS). AWS a cloud provider server. Which provides services in areas like computing, storage, administration, and networking, as well as on-demand services. This implies that customers can request a specific set of services. When it comes to hosting and building, one cloud service can help.
AWS has a free tier, which allows customers, who are just getting started with cloud computing to register an account and start utilizing the services for free.
Now let’s talk about the important part of amazon’s web service, Amazon SWF (Amazon Simple workflow services).
Amazon Simple Workflow Services:
Amazon Simple workflow services (Amazon SWF) are task-based Application interfaces, which are programmed to make it easy to coordinate different works across distributed application components. Here tasks represent a logical unit of work that is being performed by the application. It includes management of Inter-task dependencies, creating schedules, and concurrency according to the logical flow of the application.
With its help, you can have full control over task implementation. You can coordinate them without thinking about the underlying complexities. And the worries of tracking and maintaining their states are not a problem anymore. With its use, workers can be implemented to perform the tasks.
Tasks can be created for a long run or small period, or may time out after some time and may require restarts.
Amazon SWF stores the tasks and assigns them to workers when required. It also maintains their state and tracks their progress until their completion.
Amazon SWF supports a variety of application requirements and is suitable for a variety of different ranges of tasks including web application back-ends, analytics pipelines, etc.
How does it function?
The primary function of Amazon SWF is to control the workflow of your application. It serves as a coordination center for your application’s many components. When it comes to its functions, the most important ones are:
- It maintains the application’s state.
- It supervises the execution and progress of workflows
- It includes tasks such as holding and dispatching.
- It defines which of your application hosts’ responsibilities will be carried out.
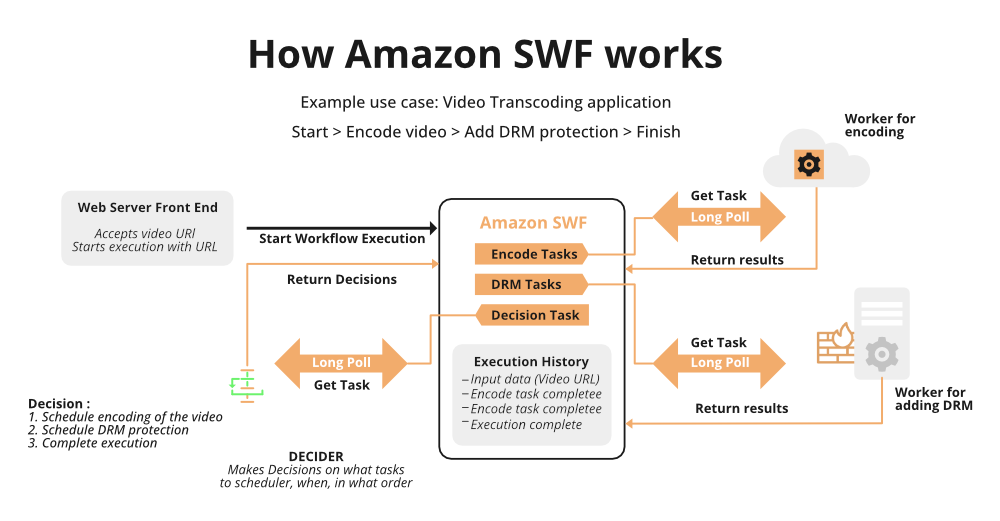
Concepts of Amazon SWF:
The primary concept comes first when it comes to concepts. In Amazon SWF, the phrase “workflow” is used. It’s a set of activities with specific goals and logic that are linked to certain tasks. We can better understand it if we use an example: a workflow can take an order and then conduct the steps required to complete it.
Each process is kept within an Amazon Web Services resource called a Domain. It is in charge of determining the scope of the workflow. Many domains can be used in an AWS account, and each one can contain many workflows, but workflows from different domains cannot communicate. You must briefly specify each of the required tasks and register each activity with Amazon when developing an Amazon SWF workflow Activity.
Some of the actions may need to be repeated several times during the process, depending on the requirements. You might, for example, create an activity that handles buy items in the client order sequence. If a consumer buys anything more than once, the activity will have to be repeated.
SWF Actors:
Actors can be workflow initiates, deciders, or activity workers, These actors use Amazon SWF’s API to connect with it. Any computer language may be used to create these characters. The Amazon SWF architecture, including Amazon SWF and its actors, is discussed below.
Workflow Starters:
Any program that may start process executions is referred to as a workflow starter. One workflow starter, for example, may be the website where the consumer puts an order. A mobile application or system used by a customer care agent to make an order on behalf of the client might be another workflow starter.
Deciders:
A decider is a program that performs the coordination logic of a workflow. The flow of activity tasks in a workflow execution is controlled by deciders. Any modification in the workflow, whether it’s the execution or completion of a task, is the responsibility of the deciders. When the decider receives the decision task from Amazon SWF, it examines the workflow execution history to identify the next actions to take. Using decisions, the decider transmits these actions back to Amazon SWF. A decision is an Amazon SWF data type that may be used to express a variety of next steps and decisions.
Activity Workers:
An activity worker is a procedure that completes the activity tasks required by the workflow. One of the tasks that you identified in your application is the activity task. You must first register an activity task in your workflow using the Amazon SWF console or the Registration activity. Each activity worker polls in the Amazon SWF for new tasks that are suited for them to do; some activities are only available to specific activity workers. The activity worker receives a task, processes and completes it, and then communicates the task’s completion to Amazon SWF, along with the results. After that, the activity worker polls for a new assignment.
In such a way, the Amazon SWF service serves as a dependable central hub via which data may be shared between the decider, activity workers, and other important organizations such as the person in charge of the workflow. The condition of each workflow execution is also maintained by Amazon SWF, saving your app from having to maintain the state in a long-term manner.
Execution history:
The events that are saved in the program history are referred to as execution history. The workflow history is a comprehensive, consistent, and accurate record of its activities.
Workflow Execution:
Here we are going to discuss some simple and easy steps to execute a workflow in Amazon SWF.
- Create activity workers to carry out the workflow’s processing phases.
- Create a decider to execute your workflow’s coordination logic.
- Use Amazon SWF to register your actions and process. This step can be completed programmatically or using the AWS Management Console.
- Get your activity workers and deciders up and running. these actors can be executed on any. To host a decider or activity worker, you may employ cloud computing instances like Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2), servers in your data center, or even a mobile device. Once the decider and activity workers are up and running, they should begin polling Amazon SWF for assignments.
Here comes the simple Workflow Example that will help you understand the working and execution of Amazon SWF workflow:
Let’s take an example of an E-Commerce Application, here the following figure is showing a simple e-commerce order-processing in a workflow. Here the people and automated processes both are involved in the following example.
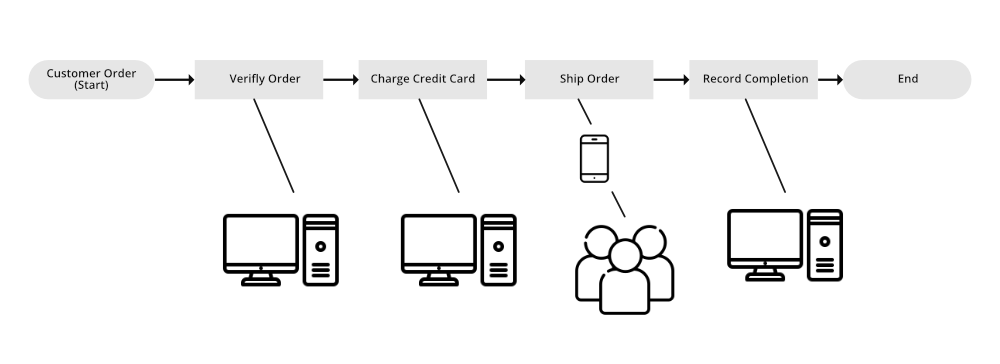
Registration and Execution of Workflows starts, When a consumer placed an order, the workflow begins. It consists of four tasks:
- Double-check the order.
- Charge the customer if the order is legitimate.
- Once payment has been received, dispatch the order.
- Save the order information if the purchase has been sent.
Order must be validated before a credit card can be charged a credit card must be successfully charged before an order can be dispatched, and order must be shipped before it can be recorded. Nonetheless, These tasks can be carried out in multiple places since Amazon SWF enables distributed operations. If the tasks are programmatic, they can be written in a variety of programming languages or using a variety of tools.
Benefits:
- Logical Separation: AWS SWF separates the control flow of your backdrop activities from the actual units of workers that hold the specific business logic, and modifies it progressively and rationally. This enables you to manage, maintain, expand, and state your application one by one, starting with the underlying business logic that makes it unique. As your business needs change, you may easily change the application logic without worrying about the underlying state machinery, task dispatch, or flow control.
- Simple: Amazon SWF is a totally managed new cloud workflow internet service that replaces the quality of traditional workflow solutions and method automation software systems. Amazon Simple Workflow relieves developers with the burden of managing the infrastructural plumbing of method automation, allowing them to concentrate on the unique functionality of their application.
- Reliable: Traditional workflow services and process control software systems are being replaced by Amazon SWF, as a fully managed new cloud workflow internet service, it is a completely reliable server that relieves developers with the effort of maintaining method automation’s infrastructure plumbing, enabling them to focus on their application’s unique features.
- Scalable: Amazon SWF extends with your application’s use in real-time. As you add more cloud processes to your application or improve the quality of your workflows, you won’t need to manage the workflow service manually.
- Flexible: The user can change the application components with Amazon Simple Workflow. It also alters coordinating logic written in any programming language and runs it in the cloud or on-premises.
So far, we’ve covered some of the basic and key concepts and features of the Amazon SWF. Finally, we may state that it is really powerful. It’s a simple and adaptable tool that’s beneficial and straightforward to use. It might be extremely beneficial to your business It’s a practical, user-friendly, and adaptable tool.