Different Amazon EC2 instance types are designed for certain activities. Consider the unique requirements of your workloads and applications when choosing an instance type. This might include needs for computing, memory, or storage.
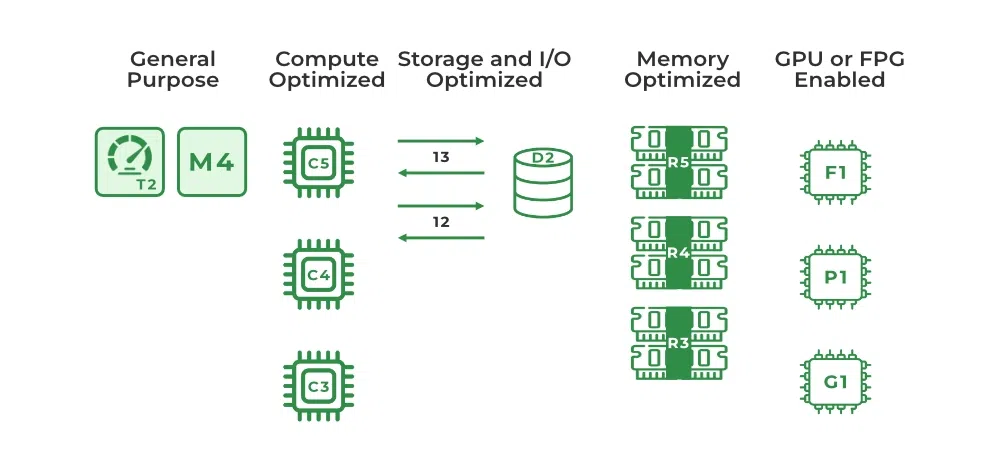
What are the AWS EC2 Instance Types?
The AWS EC2 Instance Types are as follows:
- General Purpose Instances
- Compute Optimized Instances
- Memory-Optimized Instances
- Storage Optimized Instances
- Accelerated Computing Instances
1. General-Purpose Instances
The computation, memory, and networking resources in general-purpose instances are balanced. Scenarios, where you can use General Purpose Instances, are gaming servers, small databases, personal projects, etc. Assume you have an application with a kind of equal computing, memory, and networking resource requirements. Because the program does not require optimization in any particular resource area, you can use a general-purpose instance to execute it.
Examples:
- The applications that require computing, storage, networking, server performance, or want something from everything, can utilize general-purpose instances.
- If high-performance CPUs are not required for your applications, you can go for general-purpose instances.
EC2 General-Purpose Instance Types
Here are several general-purpose examples from which we can pick:
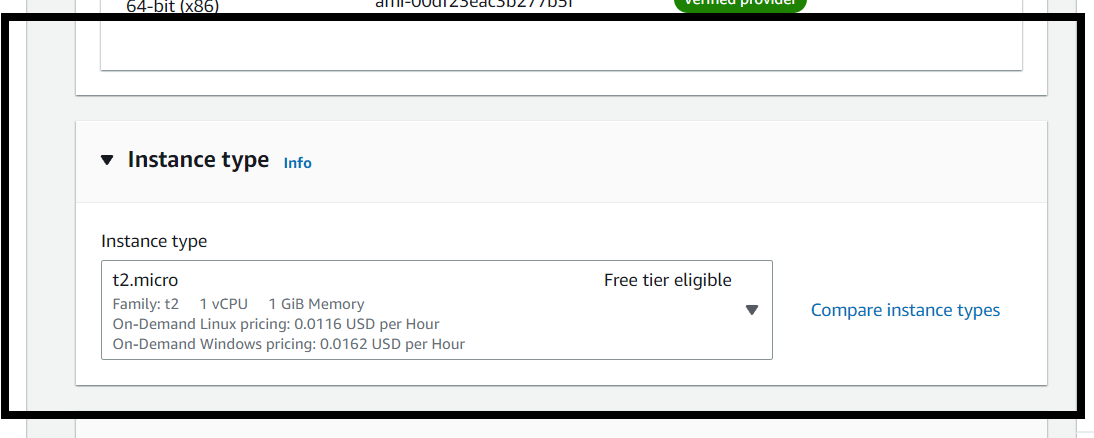
T2. micro: The most well-known instance in AWS is t2. micro, which gives 1 CPU and 1 GB of memory with low to moderate network performance. It is also free and highly helpful for individuals first starting AWS.
M6a Instance: The third-generation AMD EPYC processors used in the M6 instance are perfect for general-purpose tasks. In m6a there are different sizes like m6a.large, m6a.2xlarge, m6a.4xlarge, and so on. m6a large offers 2 CPUs, 8GiB memory, and network performance up to 12.5 Gigabit.
M5 instance: The newest generation of general-purpose instances, known as M5, are powered by Intel’s Xeon Platinum 8175 processors. Its M5 divisions include m5. large, m5.12xlarge, and m5.24 large, and the sort of M5 service we select will depend on memory, CPUs, storage, and network speed.
Features
- Powered by specifically designed AWS Graviton3 processors.
- Default optimized with EBS.
- It consists of dedicated hardware and a lightweight hypervisor.
- The bandwidth is higher when compared to other types.
Applications
- Web Servers: The web servers can be hosted in General-purpose instances.EC2 instances provide a flexible and scalable platform for web applications.
- Development and Test Environment: The developers can use these General-purpose instances to build, test and deploy the applications. It is a cost-effective solution for running this environment.
- Content delivery: The hosting of content delivery networks (CDNs) that distribute content to users all over the world is possible using general-purpose instances. EC2 instances can be set up to provide content with low latency and great performance.
A popular option for many businesses, AWS EC2 general-purpose instances offer a versatile and scalable platform for a variety of applications.
2. Compute-Optimized Instances
Compute-optimized instances are appropriate for applications that require a lot of computation and help from high-performance CPUs. You may employ compute-optimized instances for workloads including web, application, and gaming servers just like general-purpose instances. This instance type is best suited for high-performance applications like web servers, Gaming servers.
Examples
- Applications that require high server performance or that employ a machine-learning model will benefit from compute-optimized instances.
- If you have some batch processing workloads or high-performance computing.
Compute-Optimized Some Instance Types
- c5d.24large: The c5d instance, which has 96 CPUs, 192 GiB of RAM, 3600 GB of SSD storage, and 12 Gigabit of network performance, was selected primarily for its excellent web server performance. There are other instance types, including giant and extra-large. Depending on our needs, we will choose between the c5a big and extra-large instance types.
Features
- Powered by specifically designed AWS Graviton3 processors.
- It will use DDR5 memory, by which it will get 50% more bandwidth than DDR4.
- By default EBS optimisation.
Applications
- Machine learning: Machine learning operations can be performed on Compute-optimized instances because it will manage heavy workloads. The processing capacity required to swiftly and effectively train massive machine learning models can be provided by compute-optimized instances.
- Gaming: Compute-optimised is well suited for heavy workloads so it can easily manage the Gaming operations easily. Compute-optimized will decrease the latency and it can deliver a high-quality gaming experience.
3. Memory-Optimized Instances
Memory-optimized instances are geared for workloads that need huge datasets to be processed in memory. Memory here defines RAM which allows us to do multiple tasks at a time. Data stored is used to perform the central processing unit (CPU) tasks it loads from storage to memory to run. This process of preloading gives the CPU direct access to the computer program. Assume you have a workload that necessitates the preloading of significant volumes of data prior to executing an application. A high-performance database or a task that requires real-time processing of a significant volume of unstructured data might be involved in this scenario. In this case, consider using a memory-optimized instance. It is used to run applications that require a lot of memory with high performance.
Examples:
- Helpful for databases that need to handle quickly.
- Processes that do not need a large quantity of data yet require speedy and real-time processing.
Memory-Optimized Some Instance Types
The R and X categories belong to memory-optimized. let’s discuss any one-off them.
R7g.medium: It is run on AWS Gravitation processors with ARM architecture. with 1 CPU, 8 (GiB) of memory, an EBS storage type, and a maximum of 12.5% network bandwidth.
x1: X1 is mainly suited for enterprise edition databases with memory applications and comes with 64 vCPU, 976 GiB of memory, 1 x 1,920 GB of SSD storage, 7,000 Mbps of dedicated EBS bandwidth, and 10 Gbps of network performance.
Features
- Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA) is supported on the r7g.16xlarge and r7g.metal instances.
- Includes the newest DDR5 memory, which provides 50% more bandwidth than DDR4.
- Compared to R6g instances, improved networking bandwidth is 20% more.
Applications
- In-Memory Databases: Memory-optimized instances are mostly suited for databases that contain high bandwidth and memory capacity is high.
- Big Data Processing: For big data processing workloads like Apache Spark and Apache Hadoop that demand high memory capacity and bandwidth, memory-optimized instances can be deployed. Instances that have been optimized for memory can offer the memory space and bandwidth required to process huge amounts of data fast and effectively.
4. Storage Optimized Instances
Storage-optimized instances are made for workloads that demand fast, sequential read and write access to huge datasets. Distributed file systems, data warehousing applications, and high-frequency online transaction processing (OLTP) systems are examples of workloads that are suited for storage-optimized instances. Storage-optimized instances are built to provide applications with the lowest latency while accessing the data.
Examples:
- The applications which high processing of databases can utilize storage-optimized instances.
- Data Warehousing applications or distributed file systems can use it.
Storage Optimized Instance Types
- Im4gn: Because Im4gn is powered by AWS Graviton processors, it offers the best pricing performance for workloads in Amazon EC2 that demand a lot of storage. Im4gn.large’s base configuration has 2 CPUs, 8 GiB of memory, and EBS storage with a network bandwidth of up to 25 Gbps. It offers some other instance types of ls4gn, l4i, D, and H.
Features
- Using AWS Graviton2 processors, which provide the best price/performance for workloads in Amazon EC2.
- Geared at tasks that correspond to 4 GB of RAM per vCPU.
- Improved Networking (ENA)-based Elastic Network Adapter (ENA)-based up to 100 Gbps of network bandwidth.
Applications
- Amazon EC2 C5d Instance: It is suitable for applications which are having very high intensive workloads. It can deliver high input and output performance with low latency.
- Amazon EC2 I3 instance: The storage-optimized instance is well-suited for applications with high storage needs. It also provides local NVMe storage.
5. Accelerated Computing Instances
Coprocessors are used in accelerated computing instances to execute specific operations more effectively than software running on CPUs. Floating-point numeric computations, graphics processing, and data pattern matching are examples of these functions. A Hardware-Accelerator/ Co-processor is a component in computing that may speed up data processing. Graphics applications, game streaming, and application streaming are all good candidates for accelerated computing instances.
Examples:
- If the application utilizes floating-point calculations or graphics processing, accelerated computing instances will be the best among all.
- Also, data pattern matching can be done more efficiently with this instance type.
Accelerated Computing Instance Types
- Accelerated computing consists of mainly P1, Inf2, G5, G5g, G4dn, G4ad, G3, F1 and VT1.
- P4: It offers 3.0 GHz 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Processors. of 8 GPUs, 96 CPUs, and memory of 1152(GiB) with network bandwidth of 400ENA and EFA.
Features
- 2nd Generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors, 3.0 GHz (Cascade Lake P-8275CL).
- 8 NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPUs maximum.
- 400 Gbps instance networking with support for NVIDIA GPUDirect RDMA and Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA) (remote direct memory access).
Applications
- Amazon EC2 P3 Instances: High-performance computing, rendering, and machine learning workloads are all well-suited to these instances. Its NVIDIA V100 GPUs enable them to deliver up to 1 petaflop of mixed-precision performance per instance, which makes them perfect for simulations of computational fluid dynamics, molecular dynamics, and complicated deep learning models.
- Amazon EC2 G4 Instances: These instances are designed for graphically demanding tasks like video transcoding, virtual desktops, and gaming. They provide up to 65 teraflops of single-precision performance per instance and are driven by NVIDIA T4 GPUs.
AWS Instance Types Pricing
AWS Free tier offers EC2 instances for free. t2.micro instance was for up to a certain limit like 750 hours. If you want to go for a premium plan then it offers three types of plans. They are
On-Demand
On-Demand it charges based on the no.of hours or seconds you use. With the help of on-demand instances, you can avoid maintaining infrastructure costs.
On-Demand Instances are recommended for:
- Low cost without any upfront payment or long-term commitment.
- For testing applications that are being developed.
Saving Plan
When compared to on-demand you can reduce the bill by up to 72%. In order to do that you need to give a commitment to AWS of using for such an amount of time like up to 1 to 3-year term.
Types of saving plans:
- Compute Savings Plans.
- EC2 Instance Savings Plans.
- SageMaker Savings Plans.
Savings Plans are recommended for:
- For faster and newest families.
- Steady and consistent usage.
Amazon EC2 Spot Instances
When compared to other instance plans you can cheaper upto 90% discount. These are unused instances.
Spot Instances are recommended for:
- Applications which doesn’t want to save their state.
- Application flexible start and end time.
AWS Instance Type Cost Calculator
Aws cost calculator is used for calculating the cost of AWS instances based on the types. This AWS instance-type calculator is a service provided by Amazon itself.
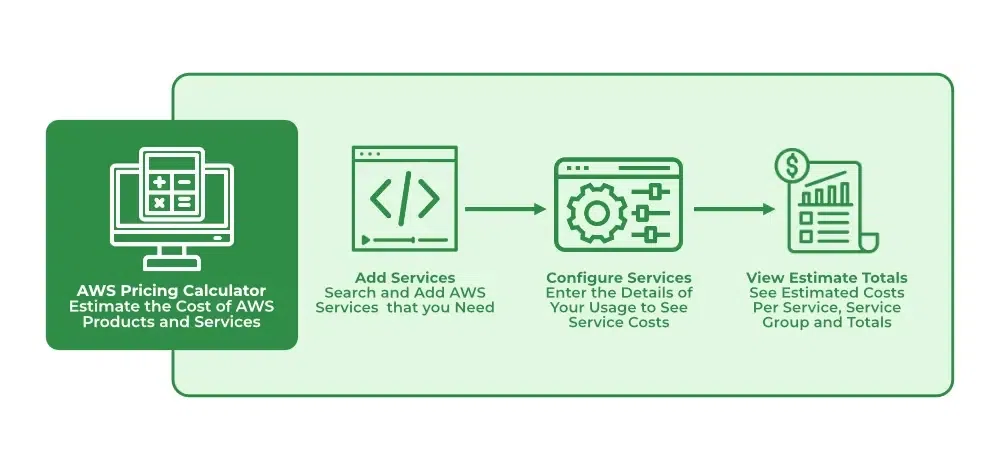
By using the AWS Pricing Calculator you can estimate the cost of services offered by AWS of its pricing. It is very simple to use first you need to open the AWS console and search for AWS Pricing Calculator after that add the service to the calculator that you want to know the cost. After all the configuration is done you will get the estimated cost as a graph or documented format.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate Amazon instance type is crucial when installing apps. If the Amazon instance type you selected is inappropriate for the application you intend to install, we may experience a variety of issues, including latency and insufficient storage. When choosing the type of instance, be selective.





-(1).webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
-(3).webp)
-(1).webp)
.webp)
.webp)
-(1).webp)
-(1).webp)
-(1).webp)
.webp)
-(1).webp)