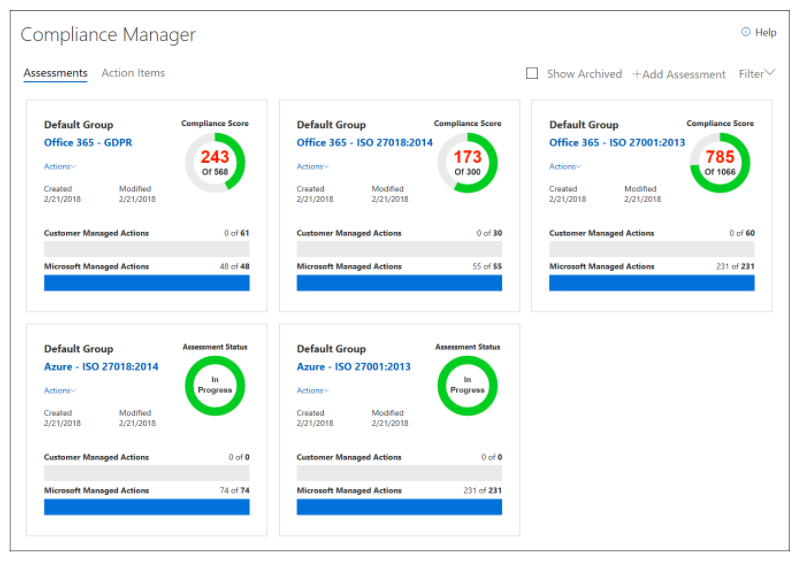
- A service that allows you to connect, monitor, and control one or more IoT devices that can communicate with back-end services hosted in the cloud.
- A PaaS solution that provides complete control over the collection and processing of IoT data.
- To create a complete end-to-end solution, you can integrate the IoT Hub with other Azure services.
- Azure Event Grid
- Azure Logic Apps
- Azure Machine Learning
- Azure Stream Analytics
- Message routing integration automatically helps you respond to a device-reported state change.
- You can use IoT Hub scaling if you are approaching the message limit on your IoT Hub.
- A SaaS solution that provides a collection of industry-specific application templates.
- You can create your own device template to define the characteristics and behavior of a device.
- Configure custom dashboards to monitor your device’s health and telemetry.
- Build custom rules when device telemetry crosses a specified threshold.
- You can apply single or bulk updates by creating jobs.
- An IoT security solution that helps you protect your data, privacy, and infrastructure.
- Components:
- Azure Sphere chip – a microcontroller unit that provides real-time processing capabilities.
- Azure Sphere OS – an operating system based on Linux that runs on an Azure Sphere chip.
- Azure Sphere Security Service – it supports certificate-based authentication, automatic software updates, and failure reporting. By default, the data is encrypted at rest.
- The Azure Sphere devices can run on two types of applications:
- High-level applications for containers.
- Real-time capable applications (RTApps) for bare metals.
- Azure IoT solution accelerators allow you to customize solution templates for common IoT scenarios.
- Azure IoT Edge enables you to deploy cloud analytics and custom business logic locally on IoT edge devices.
- Create knowledge graphs based on digital models of entire environments using Azure Digital Twins.
- If you need to monitor, analyze, and visualize your IoT data in real-time, you can use Azure Time Series Insights.
- Azure Sphere is an IoT security solution that helps you protect your data, privacy, and infrastructure.
- A real-time operating system for IoT devices, powered by MCUs is called Azure RTOS.
- Azure SQL Edge is an optimized SQL database engine for IoT and IoT Edge deployments.