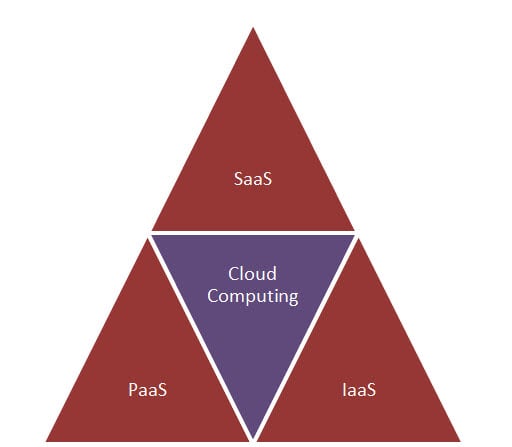
Cloud Service Models
Infrastructure-as-a-Service
Platform-as-a-Service
Software-as-a-Service
Identity-as-a-Service
Network-as-a-Service
Cloud Service Models
Infrastructure-as-a-Service
Platform-as-a-Service
Software-as-a-Service
Identity-as-a-Service
Network-as-a-Service
Cloud Computing Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure-as-a-Service provides access to fundamental resources such as physical machines, virtual machines, virtual storage, etc. Apart from these resources, the IaaS also offers:
- Virtual machine disk storage
- Virtual local area network (VLANs)
- Load balancers
- IP addresses
- Software bundles
All of the above resources are made available to end user via server virtualization. Moreover, these resources are accessed by the customers as if they own them.

Benefits
IaaS allows the cloud provider to freely locate the infrastructure over the Internet in a cost-effective manner. Some of the key benefits of IaaS are listed below:
- Full control of the computing resources through administrative access to VMs.
- Flexible and efficient renting of computer hardware.
- Portability, interoperability with legacy applications.
Full control over computing resources through administrative access to VMs
IaaS allows the customer to access computing resources through administrative access to virtual machines in the following manner:
- Customer issues administrative command to cloud provider to run the virtual machine or to save data on cloud server.
- Customer issues administrative command to virtual machines they owned to start web server or to install new applications.
Flexible and efficient renting of computer hardware
IaaS resources such as virtual machines, storage devices, bandwidth, IP addresses, monitoring services, firewalls, etc. are made available to the customers on rent. The payment is based upon the amount of time the customer retains a resource. Also with administrative access to virtual machines, the customer can run any software, even a custom operating system.
Portability, interoperability with legacy applications
It is possible to maintain legacy between applications and workloads between IaaS clouds. For example, network applications such as web server or e-mail server that normally runs on customer-owned server hardware can also run from VMs in IaaS cloud.
Issues
IaaS shares issues with PaaS and SaaS, such as Network dependence and browser based risks. It also has some specific issues, which are mentioned in the following diagram:

Compatibility with legacy security vulnerabilities
Because IaaS offers the customer to run legacy software in provider's infrastructure, it exposes customers to all of the security vulnerabilities of such legacy software.
Virtual Machine sprawl
The VM can become out-of-date with respect to security updates because IaaS allows the customer to operate the virtual machines in running, suspended and off state. However, the provider can automatically update such VMs, but this mechanism is hard and complex.
Robustness of VM-level isolation
IaaS offers an isolated environment to individual customers through hypervisor. Hypervisor is a software layer that includes hardware support for virtualization to split a physical computer into multiple virtual machines.
Data erase practices
The customer uses virtual machines that in turn use the common disk resources provided by the cloud provider. When the customer releases the resource, the cloud provider must ensure that next customer to rent the resource does not observe data residue from previous customer.
Characteristics
Here are the characteristics of IaaS service model:
- Virtual machines with pre-installed software.
- Virtual machines with pre-installed operating systems such as Windows, Linux, and Solaris.
- On-demand availability of resources.
- Allows to store copies of particular data at different locations.
- The computing resources can be easily scaled up and down.
Cloud Computing Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform-as-a-Service offers the runtime environment for applications. It also offers development and deployment tools required to develop applications. PaaS has a feature of point-and-click tools that enables non-developers to create web applications.
App Engine of Google and Force.com are examples of PaaS offering vendors. Developer may log on to these websites and use the built-in API to create web-based applications.
But the disadvantage of using PaaS is that, the developer locks-in with a particular vendor. For example, an application written in Python against API of Google, and using App Engine of Google is likely to work only in that environment.
The following diagram shows how PaaS offers an API and development tools to the developers and how it helps the end user to access business applications.

Benefits
Following are the benefits of PaaS model:

Lower administrative overhead
Customer need not bother about the administration because it is the responsibility of cloud provider.
Lower total cost of ownership
Customer need not purchase expensive hardware, servers, power, and data storage.
Scalable solutions
It is very easy to scale the resources up or down automatically, based on their demand.
More current system software
It is the responsibility of the cloud provider to maintain software versions and patch installations.
Issues
Like SaaS, PaaS also places significant burdens on customer's browsers to maintain reliable and secure connections to the provider’s systems. Therefore, PaaS shares many of the issues of SaaS. However, there are some specific issues associated with PaaS as shown in the following diagram:

Lack of portability between PaaS clouds
Although standard languages are used, yet the implementations of platform services may vary. For example, file, queue, or hash table interfaces of one platform may differ from another, making it difficult to transfer the workloads from one platform to another.
Event based processor scheduling
The PaaS applications are event-oriented which poses resource constraints on applications, i.e., they have to answer a request in a given interval of time.
Security engineering of PaaS applications
Since PaaS applications are dependent on network, they must explicitly use cryptography and manage security exposures.
Characteristics
Here are the characteristics of PaaS service model:
-
PaaS offers browser based development environment. It allows the developer to create database and edit the application code either via Application Programming Interface or point-and-click tools.
-
PaaS provides built-in security, scalability, and web service interfaces.
-
PaaS provides built-in tools for defining workflow, approval processes, and business rules.
-
It is easy to integrate PaaS with other applications on the same platform.
-
PaaS also provides web services interfaces that allow us to connect the applications outside the platform.
PaaS offers browser based development environment. It allows the developer to create database and edit the application code either via Application Programming Interface or point-and-click tools.
PaaS provides built-in security, scalability, and web service interfaces.
PaaS provides built-in tools for defining workflow, approval processes, and business rules.
It is easy to integrate PaaS with other applications on the same platform.
PaaS also provides web services interfaces that allow us to connect the applications outside the platform.
PaaS Types
Based on the functions, PaaS can be classified into four types as shown in the following diagram:

Stand-alone development environments
The stand-alone PaaS works as an independent entity for a specific function. It does not include licensing or technical dependencies on specific SaaS applications.
Application delivery-only environments
The application delivery PaaS includes on-demand scaling and application security.
Open platform as a service
Open PaaS offers an open source software that helps a PaaS provider to run applications.
Add-on development facilities
The add-on PaaS allows to customize the existing SaaS platform.
Cloud Computing Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software-as–a-Service (SaaS) model allows to provide software application as a service to the end users. It refers to a software that is deployed on a host service and is accessible via Internet. There are several SaaS applications listed below:
- Billing and invoicing system
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) applications
- Help desk applications
- Human Resource (HR) solutions
Some of the SaaS applications are not customizable such as Microsoft Office Suite. But SaaS provides us Application Programming Interface (API), which allows the developer to develop a customized application.
Characteristics
Here are the characteristics of SaaS service model:
-
SaaS makes the software available over the Internet.
-
The software applications are maintained by the vendor.
-
The license to the software may be subscription based or usage based. And it is billed on recurring basis.
-
SaaS applications are cost-effective since they do not require any maintenance at end user side.
-
They are available on demand.
-
They can be scaled up or down on demand.
-
They are automatically upgraded and updated.
-
SaaS offers shared data model. Therefore, multiple users can share single instance of infrastructure. It is not required to hard code the functionality for individual users.
-
All users run the same version of the software.
SaaS makes the software available over the Internet.
The software applications are maintained by the vendor.
The license to the software may be subscription based or usage based. And it is billed on recurring basis.
SaaS applications are cost-effective since they do not require any maintenance at end user side.
They are available on demand.
They can be scaled up or down on demand.
They are automatically upgraded and updated.
SaaS offers shared data model. Therefore, multiple users can share single instance of infrastructure. It is not required to hard code the functionality for individual users.
All users run the same version of the software.
Benefits
Using SaaS has proved to be beneficial in terms of scalability, efficiency and performance. Some of the benefits are listed below:
- Modest software tools
- Efficient use of software licenses
- Centralized management and data
- Platform responsibilities managed by provider
- Multitenant solutions
Modest software tools
The SaaS application deployment requires a little or no client side software installation, which results in the following benefits:
- No requirement for complex software packages at client side
- Little or no risk of configuration at client side
- Low distribution cost
Efficient use of software licenses
The customer can have single license for multiple computers running at different locations which reduces the licensing cost. Also, there is no requirement for license servers because the software runs in the provider's infrastructure.
Centralized management and data
The cloud provider stores data centrally. However, the cloud providers may store data in a decentralized manner for the sake of redundancy and reliability.
Platform responsibilities managed by providers
All platform responsibilities such as backups, system maintenance, security, hardware refresh, power management, etc. are performed by the cloud provider. The customer does not need to bother about them.
Multitenant solutions
Multitenant solutions allow multiple users to share single instance of different resources in virtual isolation. Customers can customize their application without affecting the core functionality.
Issues
There are several issues associated with SaaS, some of them are listed below:
- Browser based risks
- Network dependence
- Lack of portability between SaaS clouds
Browser based risks
If the customer visits malicious website and browser becomes infected, the subsequent access to SaaS application might compromise the customer's data.
To avoid such risks, the customer can use multiple browsers and dedicate a specific browser to access SaaS applications or can use virtual desktop while accessing the SaaS applications.
Network dependence
The SaaS application can be delivered only when network is continuously available. Also network should be reliable but the network reliability cannot be guaranteed either by cloud provider or by the customer.
Lack of portability between SaaS clouds
Transferring workloads from one SaaS cloud to another is not so easy because work flow, business logics, user interfaces, support scripts can be provider specific.
Open SaaS and SOA
Open SaaS uses those SaaS applications, which are developed using open source programming language. These SaaS applications can run on any open source operating system and database. Open SaaS has several benefits listed below:
- No License Required
- Low Deployment Cost
- Less Vendor Lock-in
- More portable applications
- More Robust Solution
The following diagram shows the SaaS implementation based on SOA:

Cloud Computing Identity as a Service (IDaaS)
Employees in a company require to login to system to perform various tasks. These systems may be based on local server or cloud based. Following are the problems that an employee might face:
- Remembering different username and password combinations for accessing multiple servers.
- If an employee leaves the company, it is required to ensure that each account of that user is disabled. This increases workload on IT staff.
To solve above problems, a new technique emerged which is known as Identity-as–a-Service (IDaaS).
IDaaS offers management of identity information as a digital entity. This identity can be used during electronic transactions.
Identity
Identity refers to set of attributes associated with something to make it recognizable. All objects may have same attributes, but their identities cannot be the same. A unique identity is assigned through unique identification attribute.
There are several identity services that are deployed to validate services such as validating web sites, transactions, transaction participants, client, etc. Identity-as-a-Service may include the following:
- Directory services
- Federated services
- Registration
- Authentication services
- Risk and event monitoring
- Single sign-on services
- Identity and profile management
Single Sign-On (SSO)
To solve the problem of using different username and password combinations for different servers, companies now employ Single Sign-On software, which allows the user to login only one time and manage the access to other systems.
SSO has single authentication server, managing multiple accesses to other systems, as shown in the following diagram:

SSO Working
There are several implementations of SSO. Here, we discuss the common ones:

Following steps explain the working of Single Sign-On software:
- User logs into the authentication server using a username and password.
- The authentication server returns the user's ticket.
- User sends the ticket to intranet server.
- Intranet server sends the ticket to the authentication server.
- Authentication server sends the user's security credentials for that server back to the intranet server.
If an employee leaves the company, then disabling the user account at the authentication server prohibits the user's access to all the systems.
Federated Identity Management (FIDM)
FIDM describes the technologies and protocols that enable a user to package security credentials across security domains. It uses Security Markup Language (SAML) to package a user's security credentials as shown in the following diagram:

OpenID
It offers users to login into multiple websites with single account. Google, Yahoo!, Flickr, MySpace, WordPress.com are some of the companies that support OpenID.
Benefits
- Increased site conversation rates
- Access to greater user profile content
- Fewer problems with lost passwords
- Ease of content integration into social networking sites
Cloud Computing Network as a Service (NaaS)
Network-as-a-Service allows us to access to network infrastructure directly and securely. NaaS makes it possible to deploy custom routing protocols.
NaaS uses virtualized network infrastructure to provide network services to the customer. It is the responsibility of NaaS provider to maintain and manage the network resources. Having a provider working for a customer decreases the workload of the customer. Moreover, NaaS offers network as a utility. NaaS is also based on pay-per-use model.
How NaaS is delivered?
To use NaaS model, the customer is required to logon to the web portal, where he can get online API. Here, the customer can customize the route.
In turn, customer has to pay for the capacity used. It is also possible to turn off the capacity at any time.
Mobile NaaS
Mobile NaaS offers more efficient and flexible control over mobile devices. It uses virtualization to simplify the architecture thereby creating more efficient processes.
Following diagram shows the Mobile NaaS service elements:

NaaS Benefits
NaaS offers a number of benefits as discussed below:

Independence
Each customer is independent and can segregate the network.
Bursting
The customer pays for high-capacity network only on requirement.
Resilience
The reliability treatments are available, which can be applied for critical applications.
Analytics
The data protection solutions are available, which can be applied for highly sensitive applications.
Ease of Adding New Service Elements
It is very easy to integrate new service elements to the network.
Support Models
A number of support models are available to reduce operation cost.
Isolation of Customer Traffic
The customer traffic is logically isolated.