How to Add Linux Host to Nagios Monitoring Server Using NRPE Plugin
- Nagios 4.2.0 Installation Guide on RHEL/CentOS 7.x/6.x/5.x & Fedora 24-19
- How to Add Windows Host to Nagios Monitoring Server
Once you’ve installed, you can proceed further to install NRPE agent on your Remote Linux host. Before heading further, let us give you a short description about NRPE.
What is NRPE?
The NRPE (Nagios Remote Plugin Executor) plugin allows you to monitor any remote Linux/Unix services or network devices. This NRPE add-on allows Nagios to monitor any local resources like CPU load, Swap, Memory usage, Online users, etc. on remote Linux machines. After all, these local resources are not mostly exposed to external machines, an NRPE agent must be installed and configured on the remote machines.
Note: The NRPE addon requires that Nagios Plugins must be installed on the remote Linux machine. Without these, the NRPE daemon will not work and will not monitor anything.
Installation of NRPE Plugin
To use the NRPE, you will need to do some additional tasks on both the Nagios Monitoring Host and Remote Linux Host that the NRPE installed on. We will be covering both the installation parts separately.
We assume that you are installing the NRPE on a host that supports TCP wrappers and Xinted daemon installed on it. Today, most of the modern Linux distributions have these two installed by default. If not, we will install it later during the installation when required.
On Remote Linux Host
Please use the below instructions to install Nagios Plugins and NRPE daemon on the Remote Linux Host.
Step 1: Install Required Dependencies
We need to install required libraries like gcc, glibc, glibc-common and GD and its development libraries before installing.
Step 2: Create Nagios User
Create a new nagios user account and set a password.
Step 3: Install the Nagios Plugins
Create a directory for installation and all its future downloads.
Now download latest Nagios Plugins 2.1.2 package with wget command.
Step 4: Extract Nagios Plugins
Run the following tar command to extract the source code tarball.
After, extracting one new folder will appear in that directory.
Step 5: Compile and Install Nagios Plugins
Next, compile and install using following commands
Set the permissions on the plugin directory.
Step 6: Install Xinetd
Most of the systems, its by default installed. If not, install xinetd package using following yum command.
Step 7: Install NRPE Plugin
Download latest NRPE Plugin 3.0 packages with wget command.
Unpack the NRPE source code tarball.
Compile and install the NRPE addon.
Next, install the NRPE plugin daemon, and sample daemon config file.
Install the NRPE daemon under xinetd as a service.
Now open /etc/xinetd.d/nrpe file and add the localhost and IP address of the Nagios Monitoring Server.
Next, open /etc/services file add the following entry for the NRPE daemon at the bottom of the file.
Restart the xinetd service.
Step 8: Verify NRPE Daemon Locally
Run the following command to verify the NRPE daemon working correctly under xinetd.
If you get output similar to above, means it working correctly. If not, make sure to check the following things.
- Check you’ve added nrpe entry correctly in /etc/services file
- The only_from contains an entry for “nagios_ip_address” in the /etc/xinetd.d/nrpe file.
- The xinetd is installed and started.
- Check for the errors in the system log files for about xinetd or nrpe and fix those problems.
Next, verify the NRPE daemon is functioning properly. Run the “check_nrpe” command that was installed earlier for testing purposes.
You will get a following string on the screen, it shows you what version of NRPE is installed:
Step 9: Configure Firewall Rules
Make sure that the Firewall on the local machine will allow the NRPE daemon to be accessed from remote servers. To do this, run the following iptables command.
Run the following command to Save the new iptables rule so it will survive at system reboots.
Step 10: Customize NRPE commands
The default NRPE configuration file that got installed has several command definitions that will be used to monitor this machine. The sample configuration file located at.
The following are the default command definitions that are located at the bottom of the configuration file. For the time being, we assume you are using these commands. You can check them by using the following commands.
You can edit and add new command definitions by editing the NRPE config file. Finally, you’ve successfully installed and configured NRPE agent on the Remote Linux Host. Now it’s time to install a NRPE component and add some services on your Nagios Monitoring Server…
On Nagios Monitoring Server
Now login into your Nagios Monitoring Server. Here you will need to do following things:
- Install the check_nrpe plugin.
- Create a Nagios command definition using the check_nrpe plugin.
- Create Nagios host and add service definitions for monitoring the remote Linux host.
Step 1: Install NRPE Plugin
Go to the nagios download directory and download latest NRPE Plugin with wget command.
Unpack the NRPE source code tarball.
Compile and install the NRPE addon.
Step 2: Verify NRPE Daemon Remotely
Make sure that the check_nrpe plugin can communicate with the NRPE daemon on the remote Linux host. Add the IP address in the command below with the IP address of your Remote Linux host.
You will get a string back that shows you what version of NRPE is installed on the remote host, like this:
If your receive a plugin time-out error, then check the following things.
- Make sure your firewall isn’t blocking the communication between the remote host and the monitoring host.
- Make sure that the NRPE daemon is installed correctly under xinetd.
- Make sure that the remote Linux host firewall rules blocking the monitoring server from communicating to the NRPE daemon.
Adding Remote Linux Host to Nagios Monitoring Server
To add a remote host you need to create a two new files “hosts.cfg” and “services.cfg” under “/usr/local/nagios/etc/” location.
Now add these two files to main Nagios configuration file. Open nagios.cfg file with any editor.
Now add the two newly created files as shown below.
Now open hosts.cfg file and add the default host template name and define remote hosts as shown below. Make sure to replace host_name, alias and address with your remote host server details.
Next open services.cfg file add the following services to be monitored.
Now NRPE command definition needs to be created in commands.cfg file.
Add the following NRPE command definition at the bottom of the file.
Finally, verify Nagios Configuration files for any errors.
Restart Nagios:
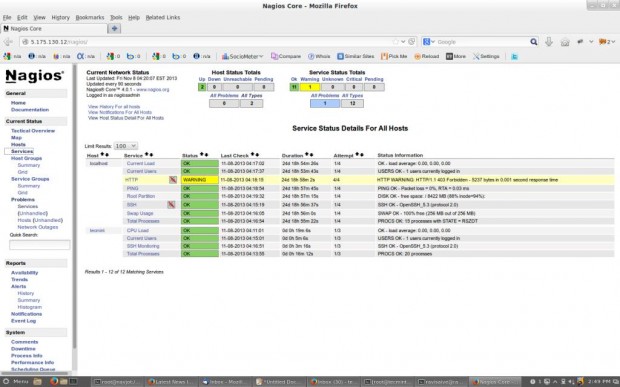
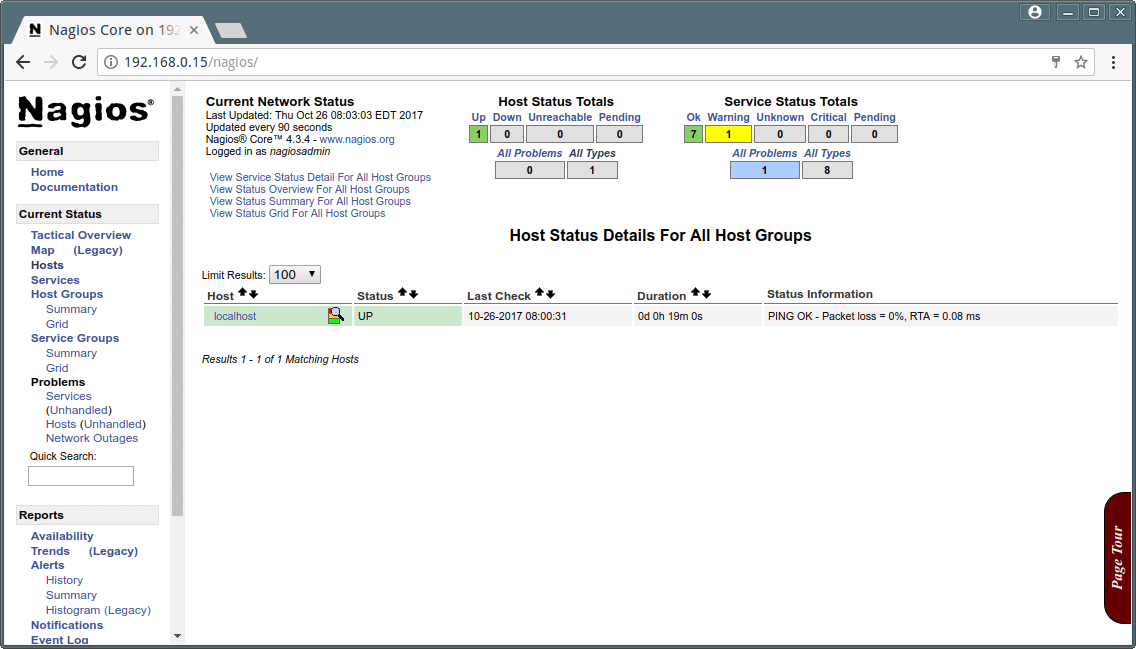
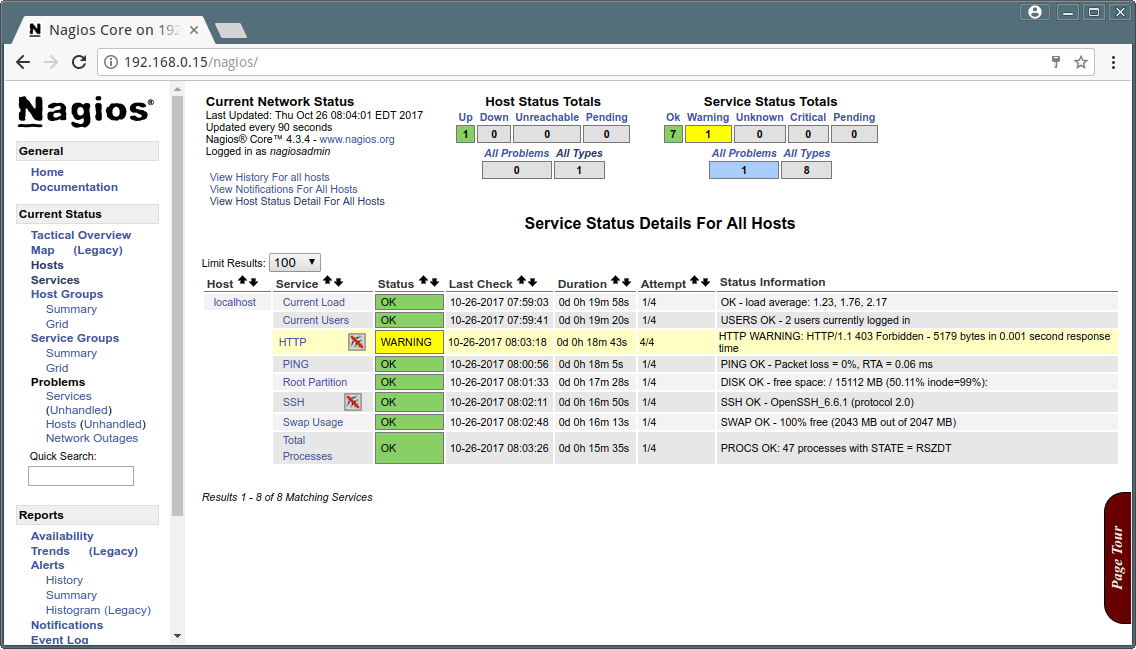
That’s it. Now go to Nagios Monitoring Web interface at “http://Your-server-IP-address/nagios” or “http://FQDN/nagios” and Provide the username “nagiosadmin” and password. Check that the Remote Linux Host was added and is being monitored.